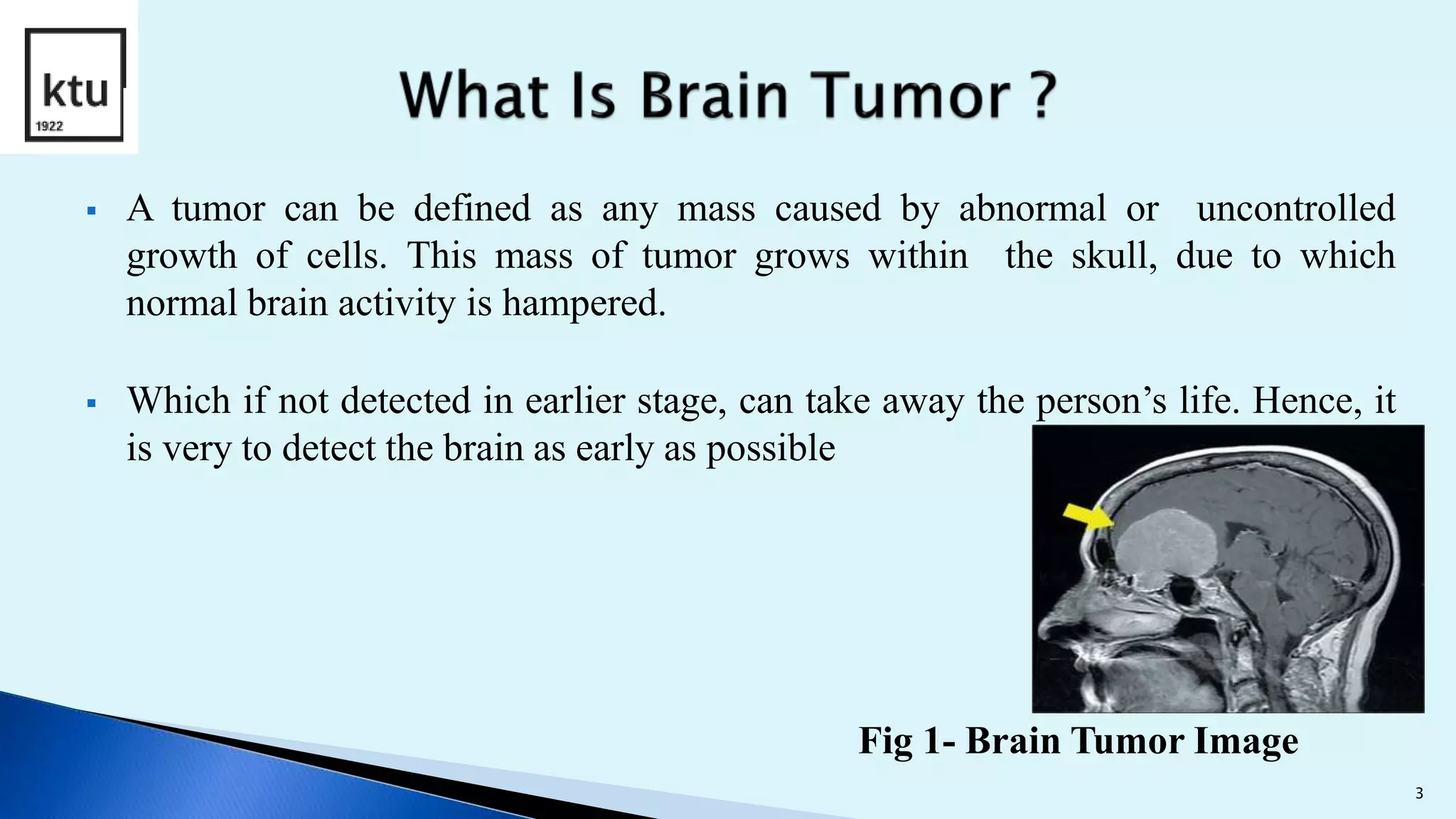
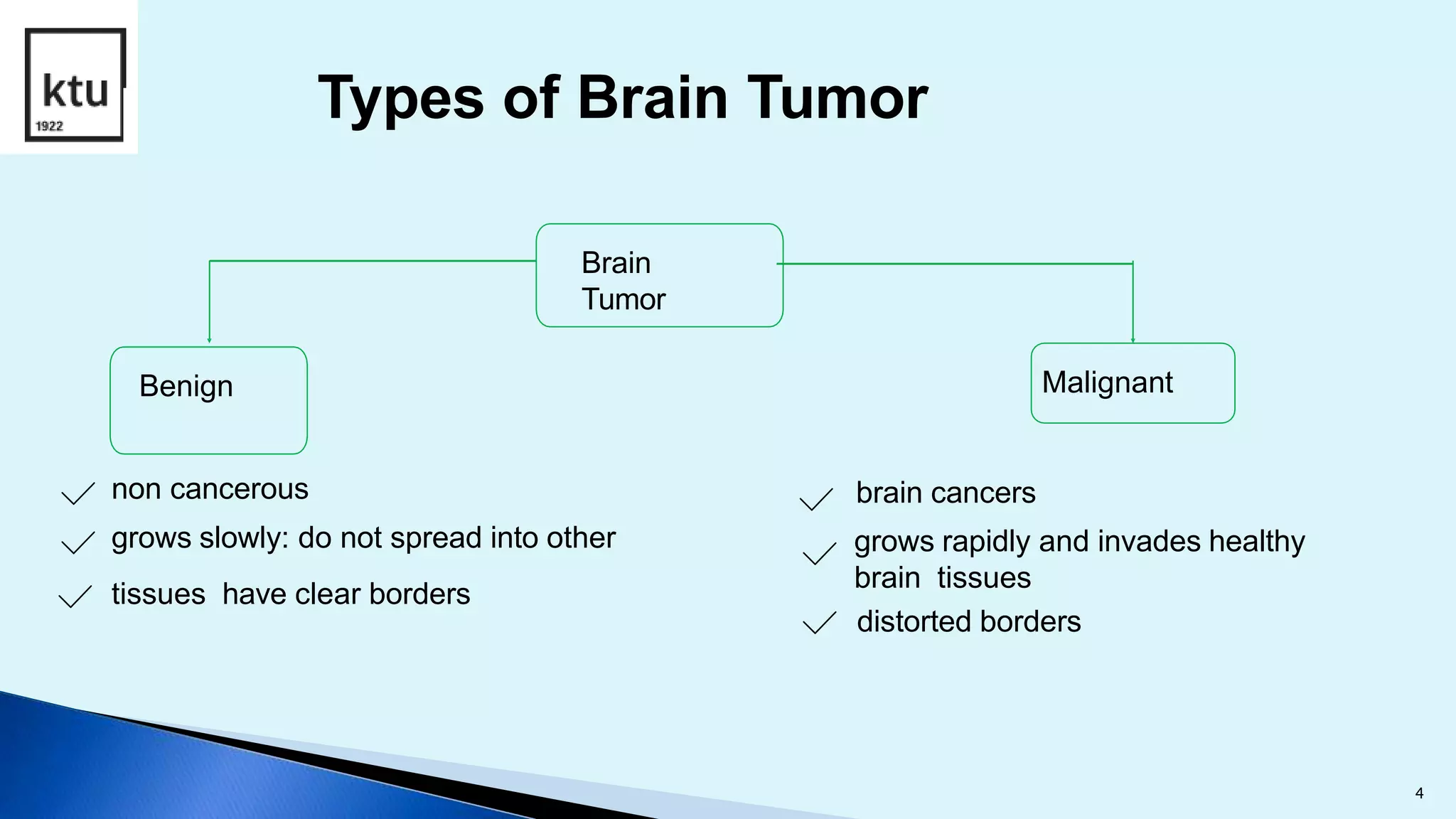
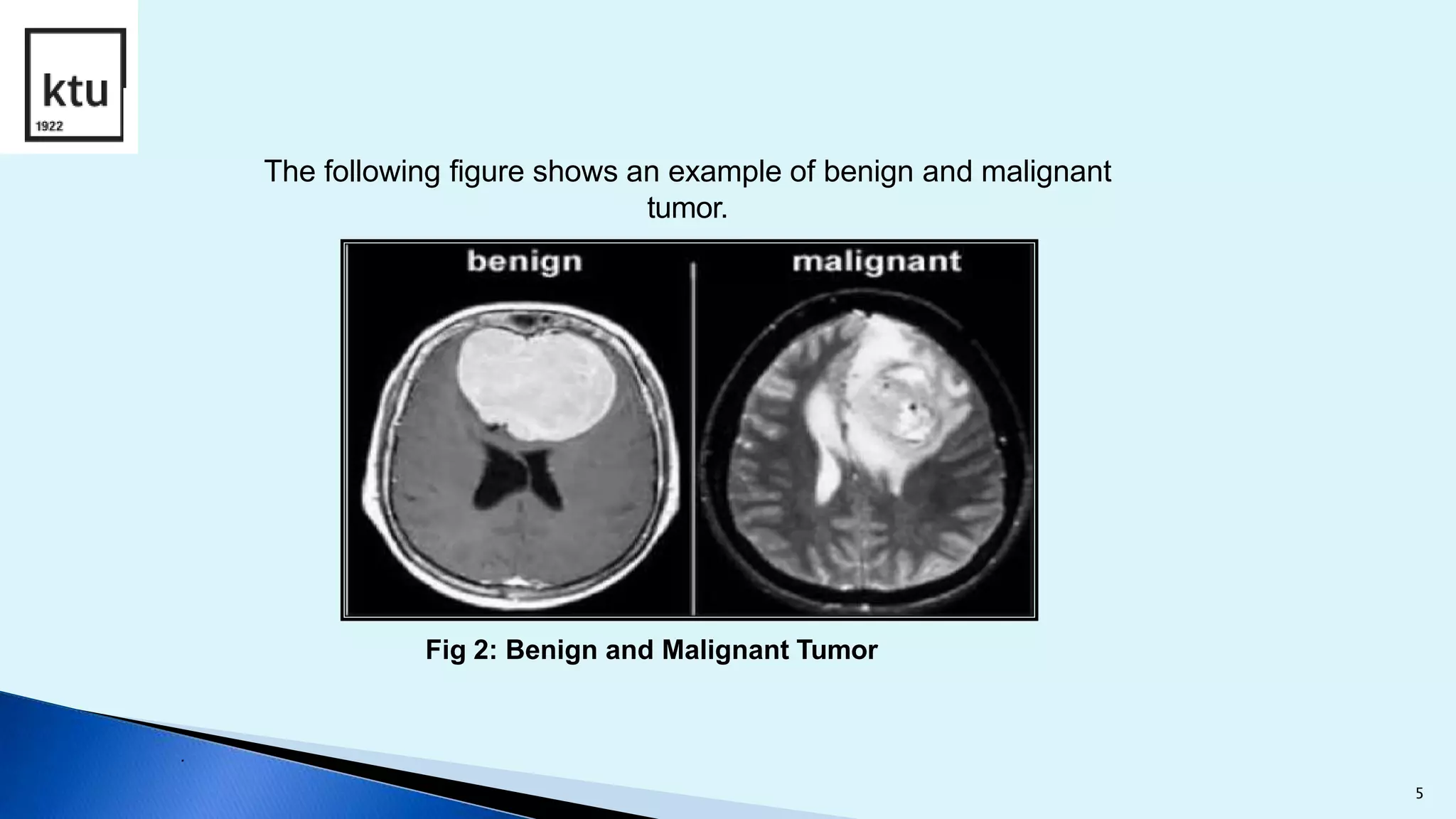
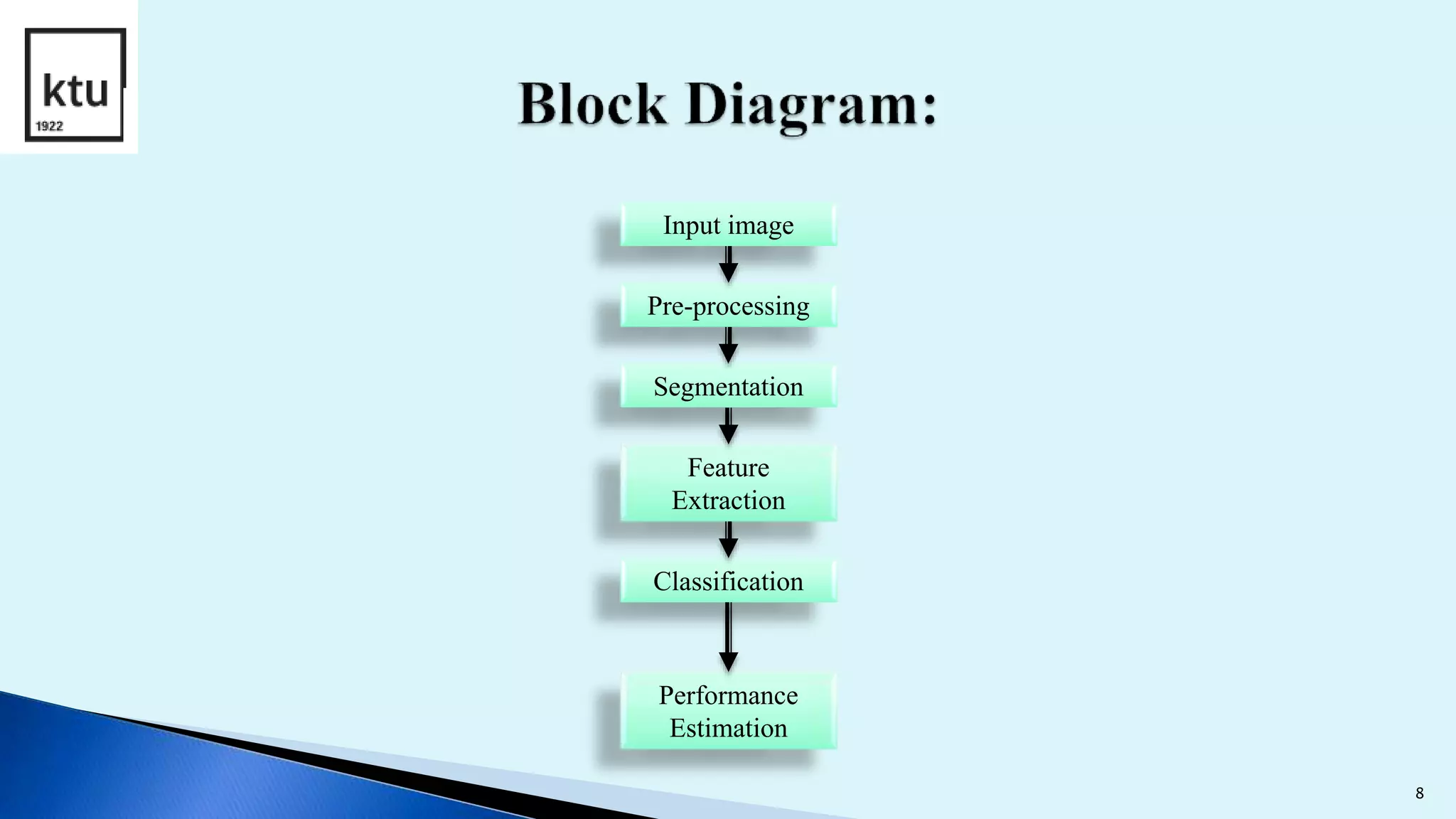
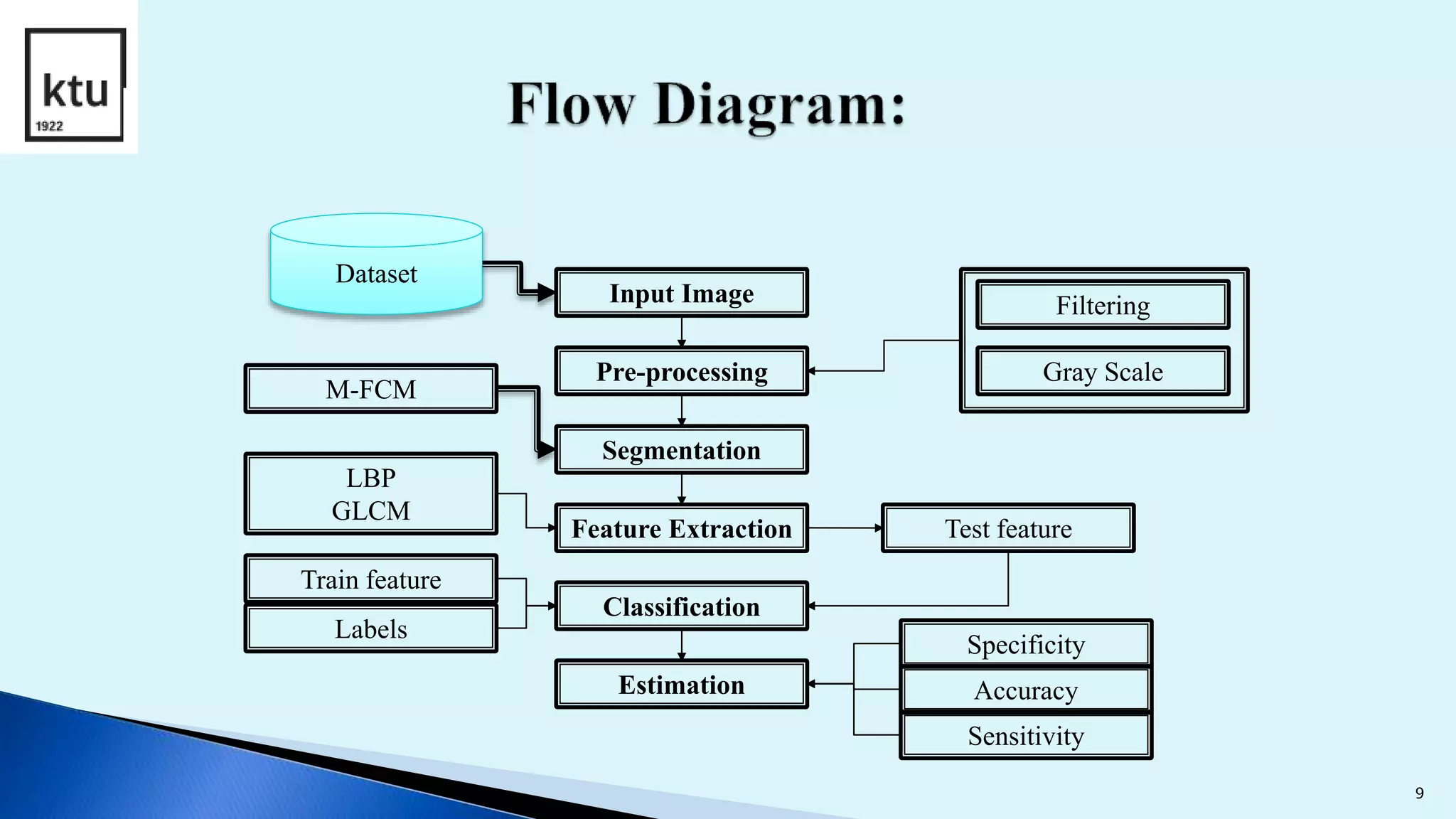
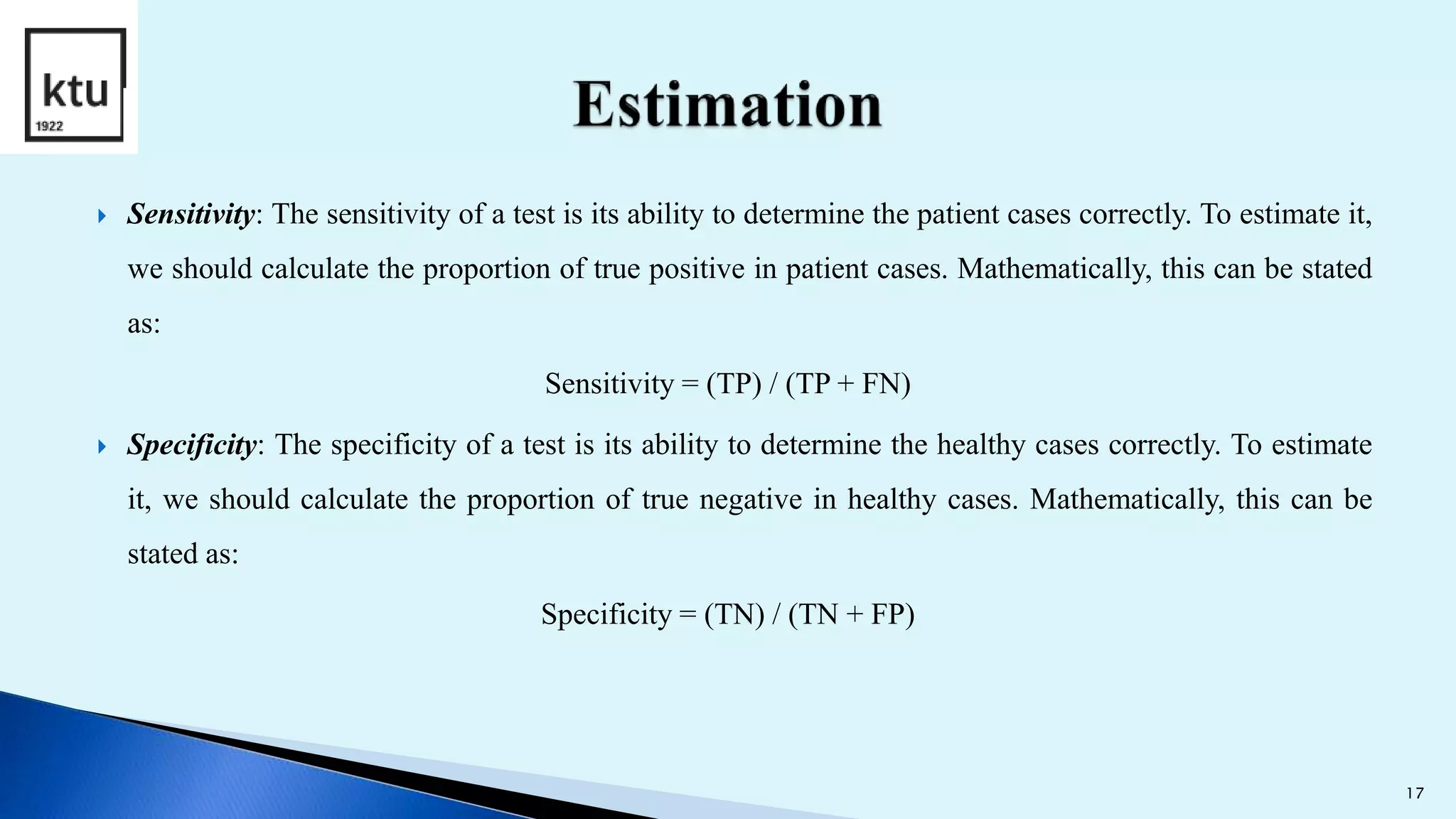
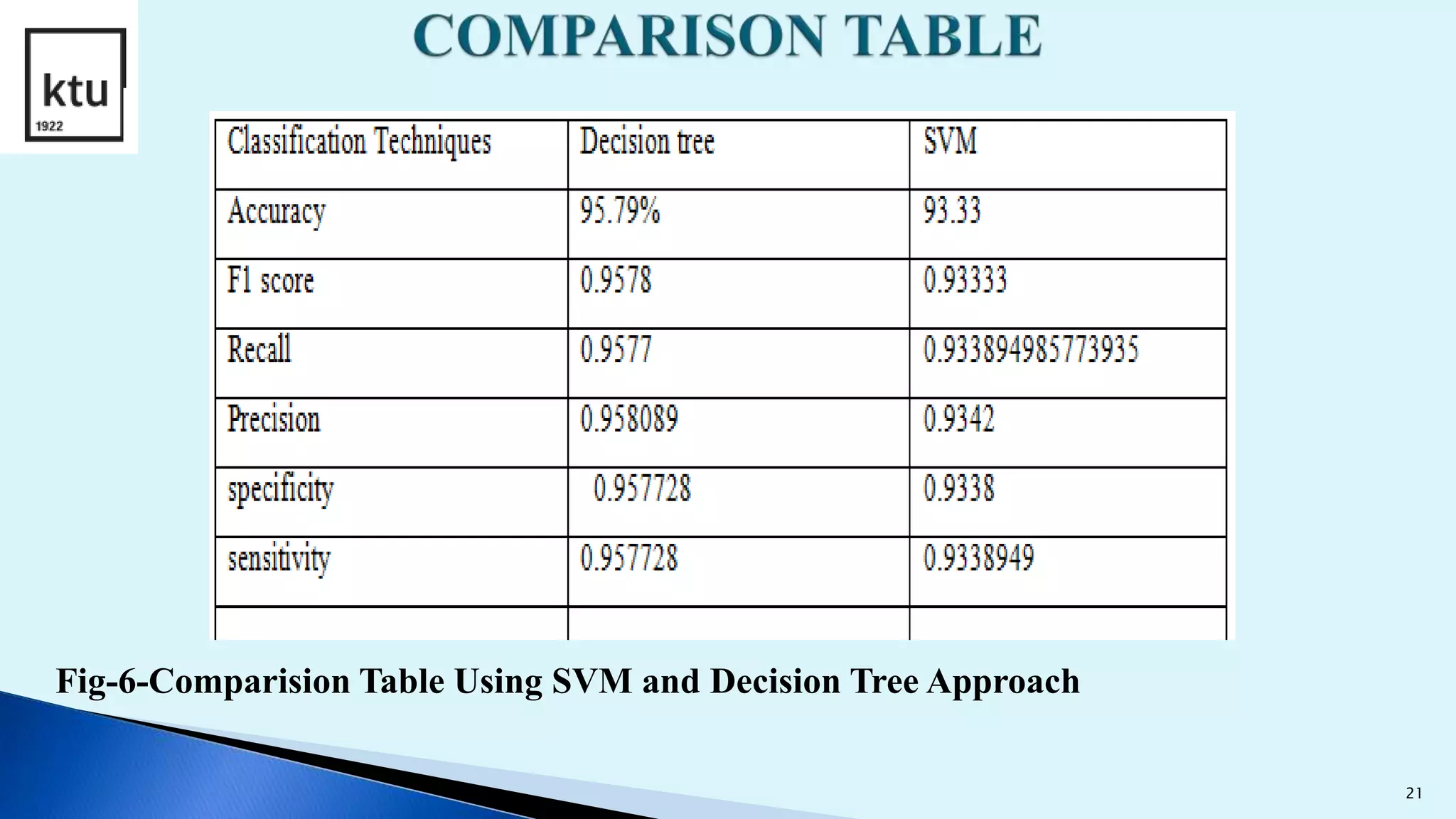
The document discusses brain tumor segmentation from MRI images. It describes how brain tumors are classified, outlines the segmentation process which includes preprocessing, segmentation, feature extraction and classification. Local binary patterns and support vector machines are used for feature extraction and classification. The accuracy, sensitivity and specificity are calculated to measure the performance of the segmentation system. Figures show examples of segmented images and comparisons of results from support vector machines and decision tree approaches.