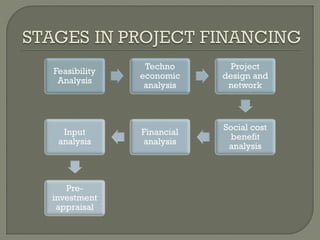
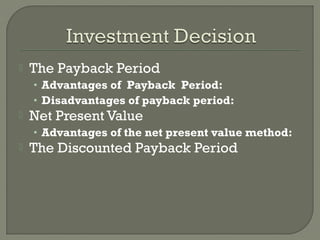
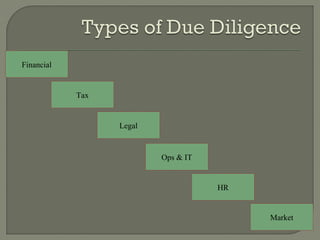
This document discusses project financing. It provides an overview of the stages of project financing, sources of financing, participants and criteria. It also discusses principal agreements, project risks, and risk identification through due diligence. Project financing refers to financing of long-term infrastructure, industrial projects, and public services based on a non-recourse or limited recourse financial structure where project debt and equity used to finance the project are paid back from the cashflow generated by the project.