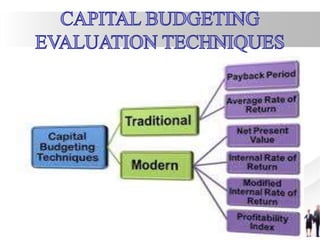
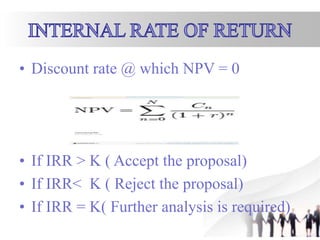
The document outlines key concepts of financial planning, emphasizing the importance of financial statement analysis, capital structure, and budgeting for maximizing a company's profitability and wealth. It covers various financing methods, including debt and equity, as well as the evaluation of investment proposals through metrics like payback period, net present value, and internal rate of return. Additionally, it discusses liquidity, dividend policy, and the need for careful risk management in financial decision-making.