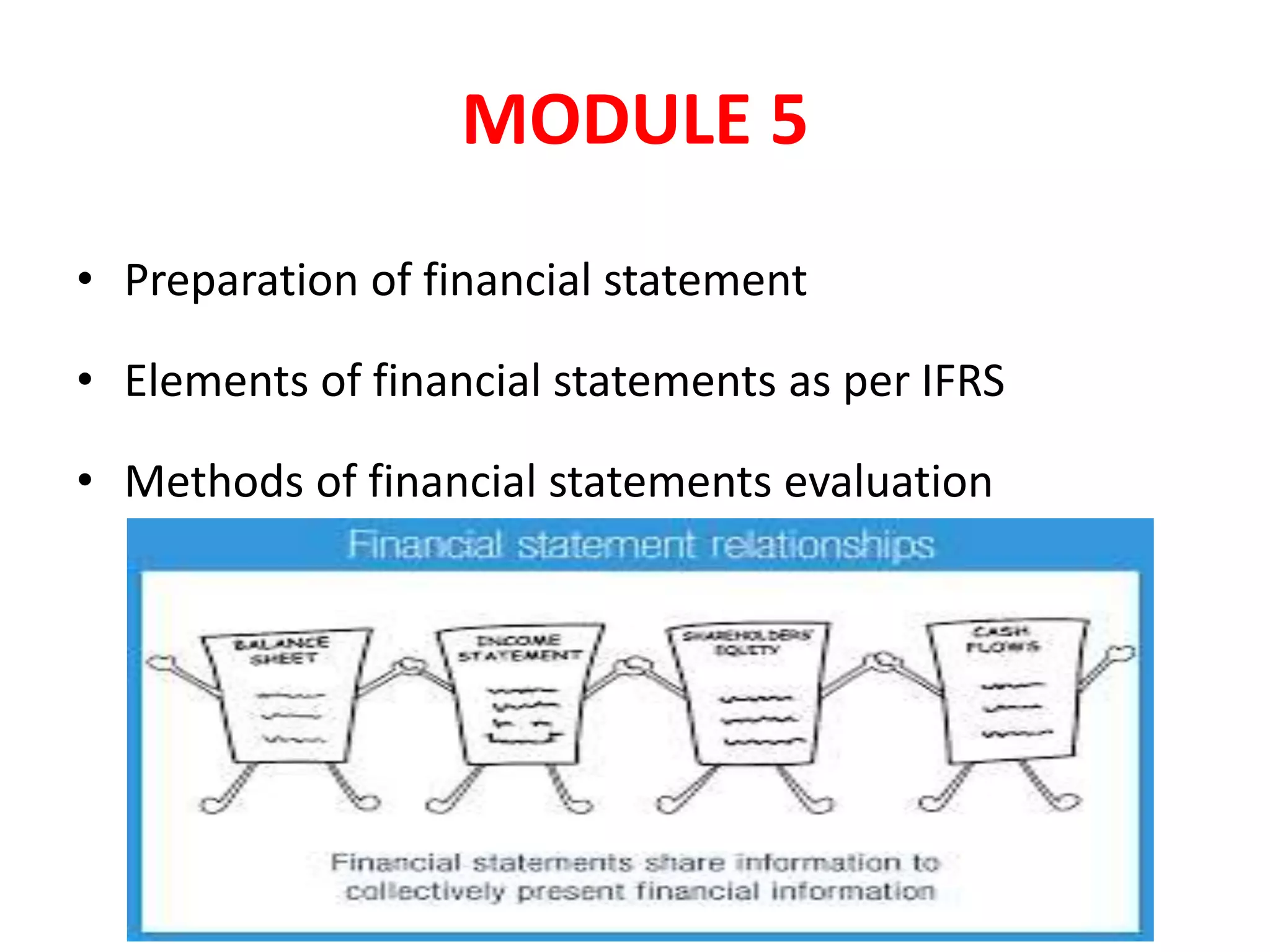
This document summarizes key elements of preparing and analyzing financial statements according to IFRS standards. It outlines the components and purpose of income statements, statements of retained earnings, balance sheets, and cash flow statements. It also discusses the bases of preparation for cash flow statements and analyzes operating, investing and financing cash flows. Finally, it reviews methods of financial statement analysis including horizontal analysis, vertical analysis and various ratio analyses, and lists some countries that use IFRS standards.