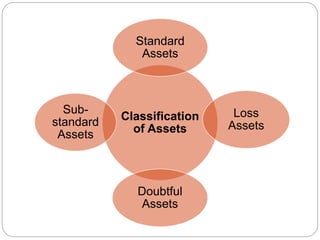
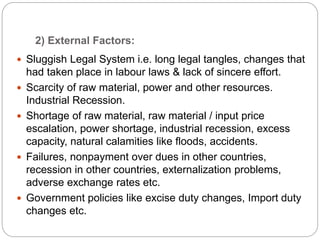
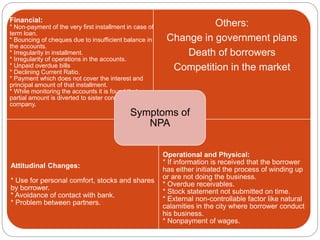
This document discusses non-performing assets (NPAs) in the banking sector. It defines NPAs as loans where interest or principal payments are overdue by more than 180 days. It describes the different categories of NPAs based on their risk level and explains how gross and net NPAs are calculated. The document then outlines various internal and external factors that can cause loans to become NPAs, the impact of high NPAs on banks' profitability and liquidity, and some methods that banks use to reduce their NPAs, such as the SARFAESI Act, Lok Adalats, and compromise settlements.