The document discusses various financial functions in Excel including NPV, FV, PMT, SLN, and IRR. It provides the formulas and examples for calculating net present value, future value, loan payments, straight-line depreciation, and internal rate of return. Each function is explained along with notes on its use and how to interpret results.



![Formula of NPV
• =NPV(rate, value 1, [value 2],….)
where,
• Rate= Rate of discount
• Value 1= Initial cost of investment
• Value 2, 3,….= Future Payments
6Prepared By:- Rutvik Poshiya](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/financialfunctionsinexcel-200229062951/75/Financial-functions-in-MS-Excel-6-2048.jpg)


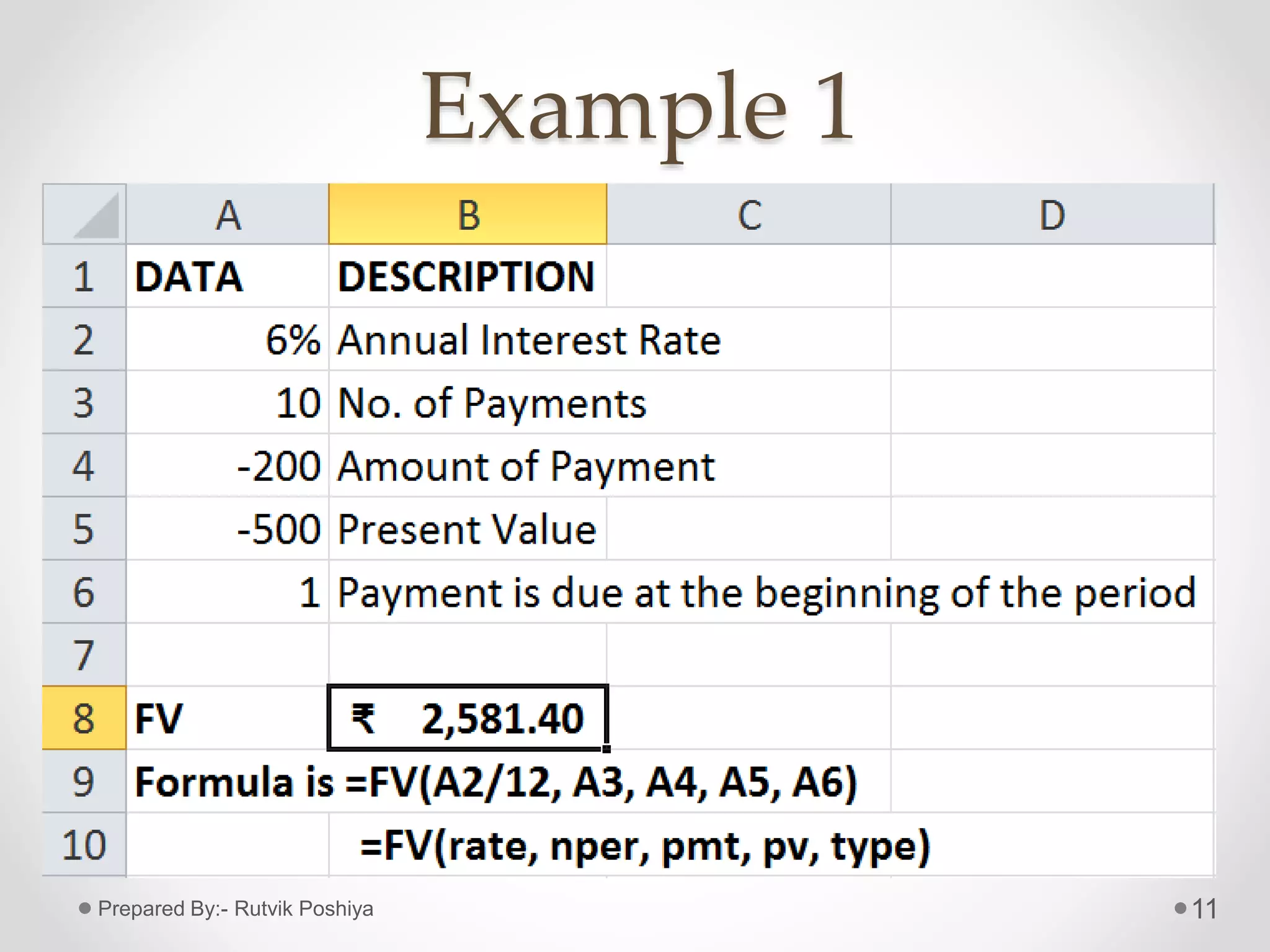
![Formula of FV Function
• Formula:- =FV(rate, nper, pmt, [pv], [type])
• Where,
• Rate= Interest rate per period
• Nper= Total no. of payment periods in an Annuity
• Pmt= Payment made in each period
• Pv= Present value of future payments
• Type= It indicates when payments are due. (it can
take values 0 or 1, if type is omitted, it is
assumed to be 0)
10Prepared By:- Rutvik Poshiya](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/financialfunctionsinexcel-200229062951/75/Financial-functions-in-MS-Excel-10-2048.jpg)



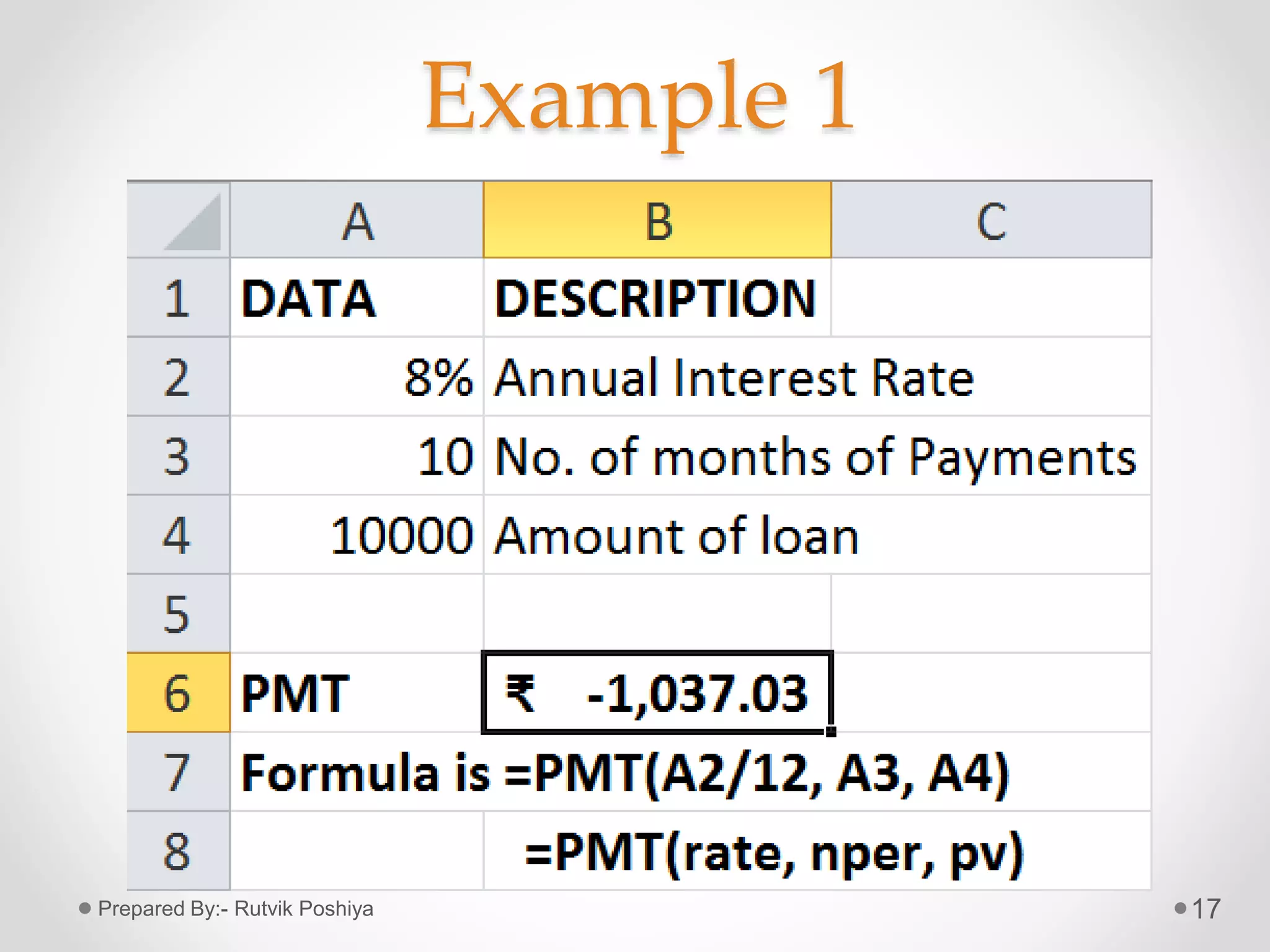
![Formula of PMT
• =PMT(rate, nper, pv, [fv], [type])
• Where,
• Rate= Interest rate per period for the loan.
• Nper= Total no. of payments for the loan.
• Pv= Present value of future payments; also
known as The Principal.
• Fv= Future value or cash balance to be attained
after the last payment is made.
• Type= It indicates when payments are due.
15Prepared By:- Rutvik Poshiya](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/financialfunctionsinexcel-200229062951/75/Financial-functions-in-MS-Excel-15-2048.jpg)
![NOTE:
• In the formula,
• =PMT(rate, nper, pv, [fv], [type])
• ,
16
Set type equal to If payments are due
0 At the end of the period
1 At the beginning of the period
Prepared By:- Rutvik Poshiya](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/financialfunctionsinexcel-200229062951/75/Financial-functions-in-MS-Excel-16-2048.jpg)




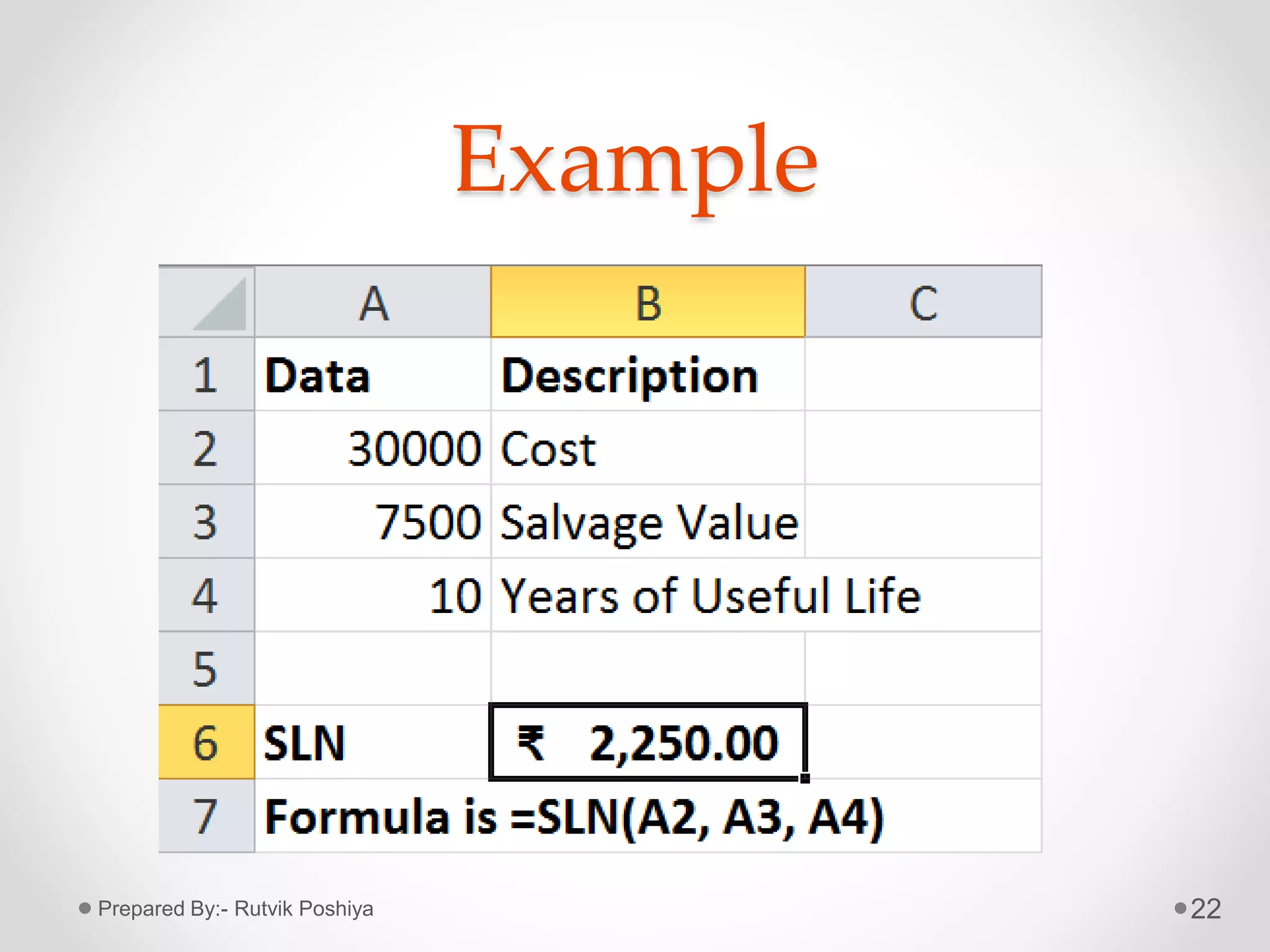



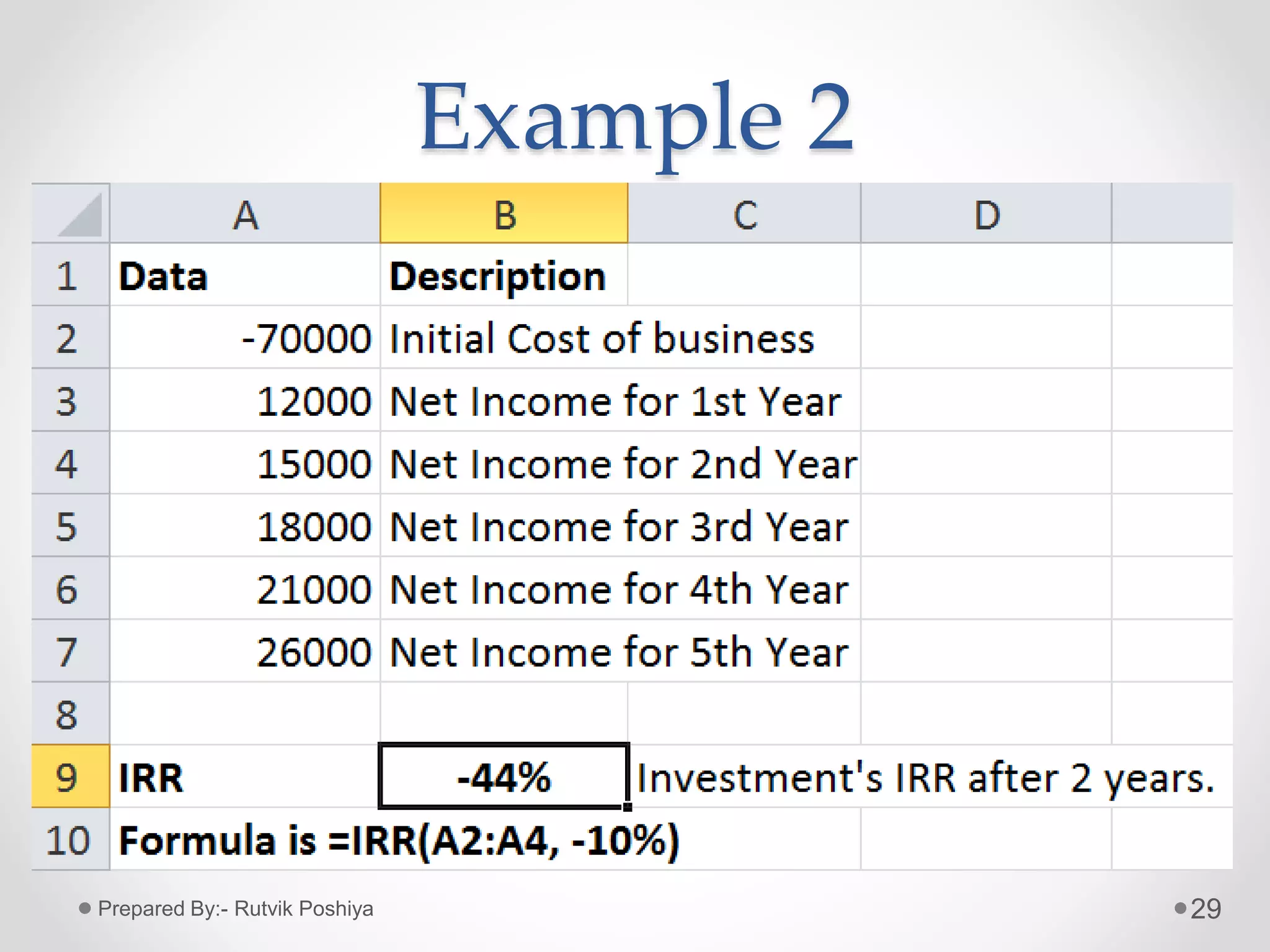
![Formula of IRR Function
• =IRR(values, [guess])
• Where,
• Value= a reference to cells that contains series of
cash flows (Investment and Net Income
values); and it must contain one positive and
one negative value.
• Guess= An initial guess at what the user think the
IRR might be. This is an optional argument, which,
if omitted, takes on the default value of 0.1 (10%)
26Prepared By:- Rutvik Poshiya](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/financialfunctionsinexcel-200229062951/75/Financial-functions-in-MS-Excel-26-2048.jpg)