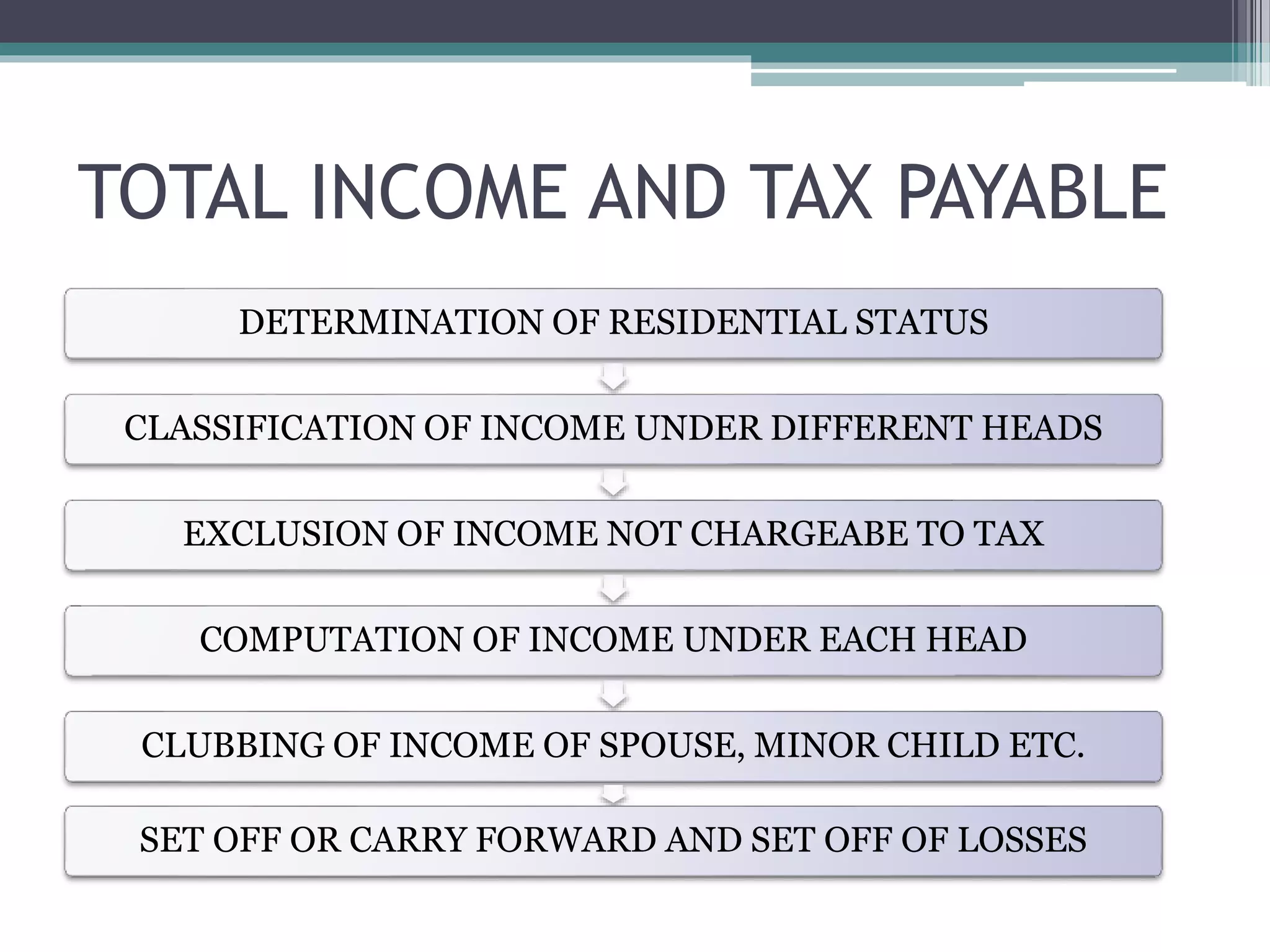
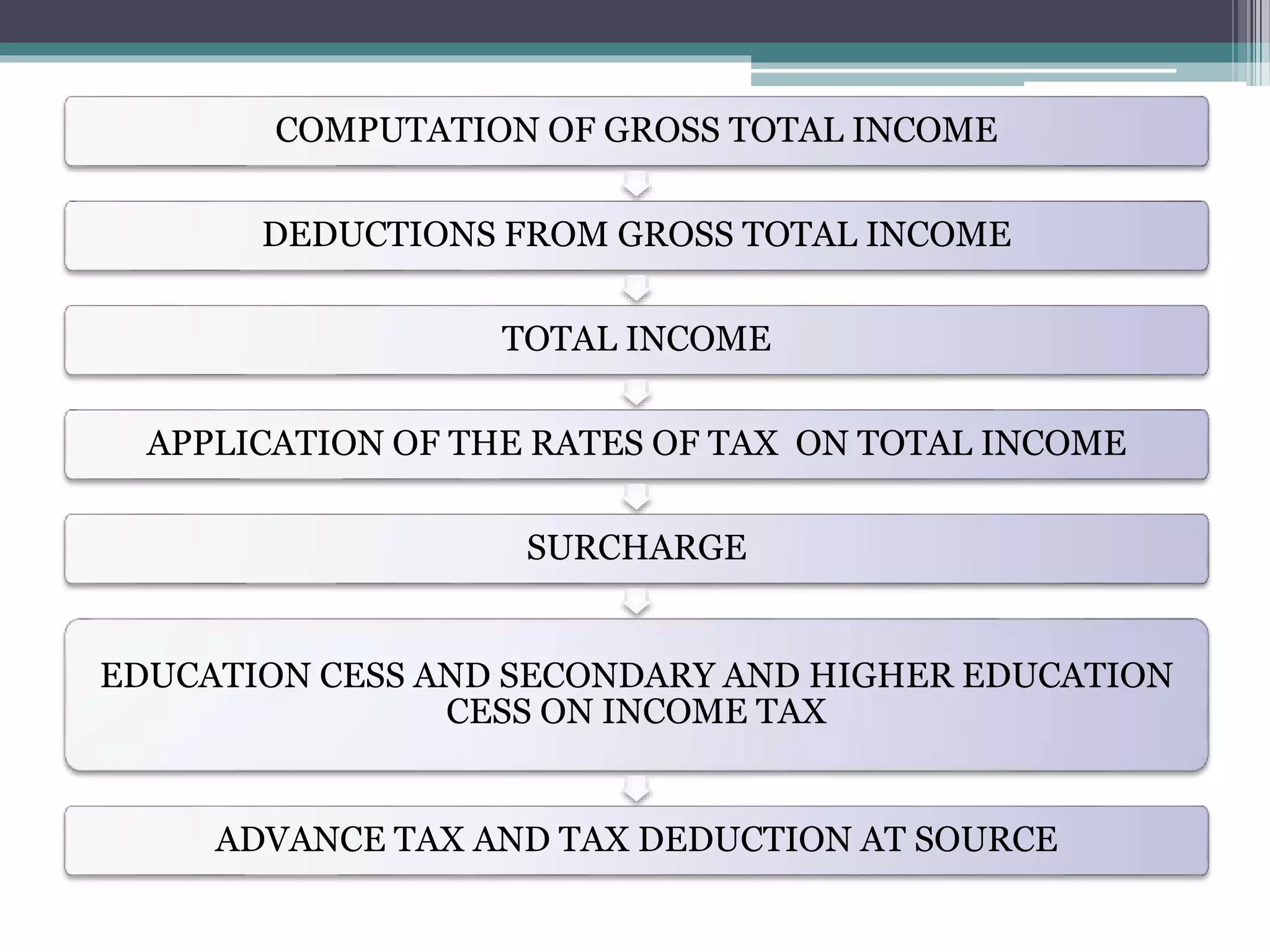
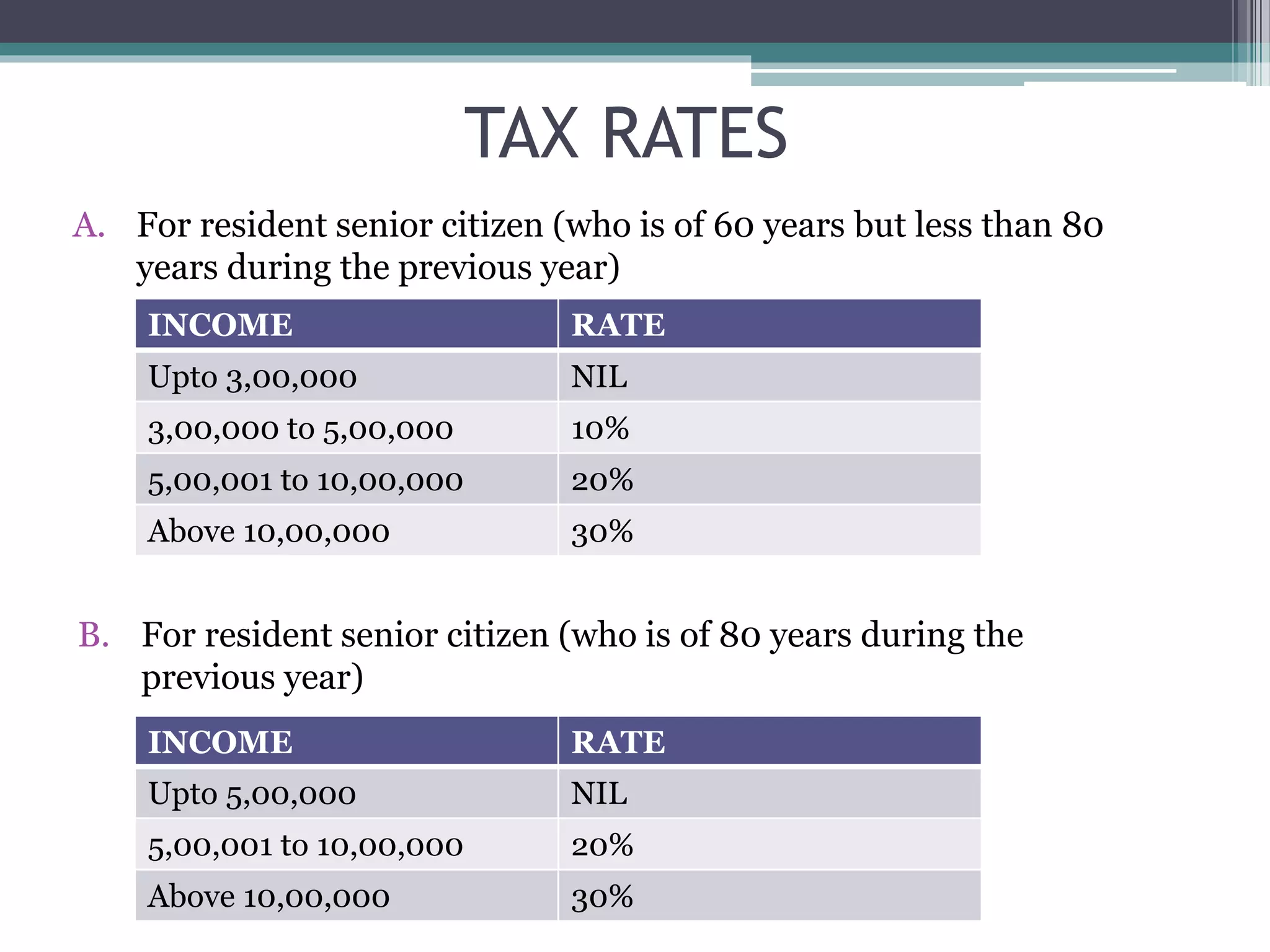
The document provides an overview of basic concepts related to income tax in India, including definitions of key terms like tax, direct tax, indirect tax, income, assessee, capital/revenue receipts and expenditures. It explains that the Income Tax Act of 1961 governs income tax and its provisions for determining taxable income and tax liability. Income includes various sources like profits, dividends, capital gains, interest etc. Computation of taxable income involves calculating income under different heads, applying deductions and exemptions, and determining the final tax liability.




![INCOME
As per [Section 2(24)], Income includes :
1. Profits or gains of business or profession.
2. Dividend.
3. Voluntary Contribution received by a Charitable / Religious Trust or University /
Education Institution or Hospital
4. Value of perquisite or profit in lieu of salary taxable u/s 17 and special allowance or
benefit specifically granted either to meet personal expenses or for performance of
duties of an office or an employment of profit.
5. Export incentives, like Duty Drawback, Cash Compensatory Support, Sale of licences
etc.
6. Interest, salary, bonus, commission or remuneration earned by a partner of a Firm from
such Firm.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/it-160219155655/75/Introduction-to-Income-Tax-5-2048.jpg)



![ ASSESSMENT YEAR [SECTION 2(9)]
“Assessment year” means the period of twelve months commencing on 1st
April every year and ending on 31st March of the next year. Income of
previous year of an assessee is taxed during the following assessment year
at the rates prescribed by the relevant Finance Act.
PREVIOUS YEAR (SECTION 3)
Income earned in a year is taxable in the next year. The year in which
income is earned is known as previous year. From the assessment year
1989-90 onwards, all assessees are required to follow financial year (i.e.
April 1 to March 31) as previous year. The uniform previous year has to be
followed for all sources of income.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/it-160219155655/75/Introduction-to-Income-Tax-9-2048.jpg)












![ROUNDING OFF TOTAL INCOME AND TAX
• Rounding Off Income [Sec. 288A]: The Total Income computed
under this Act, shall be rounded off to the nearest multiple of 10.
• Rounding Off Tax [Sec. 288B] : The amount of Tax including Tax
Deducted at Source (TDS) and advance tax, interest, penalty, fine or
any other sum payable, and the amount of refund due under the
Income Tax Act, shall be rounded off to the nearest ‘10.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/it-160219155655/75/Introduction-to-Income-Tax-23-2048.jpg)