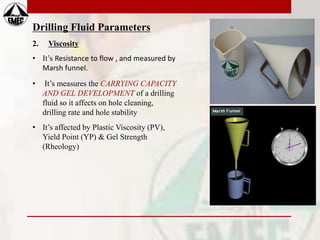
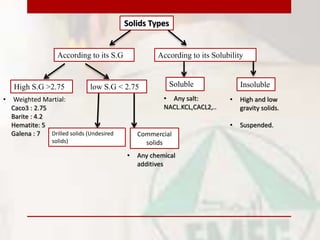
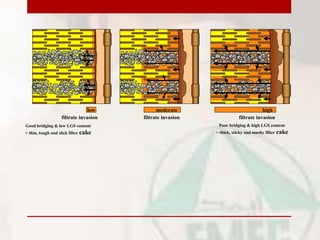
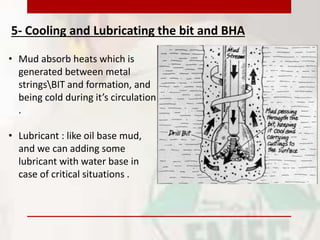
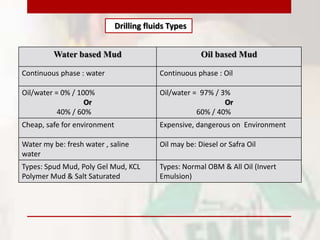
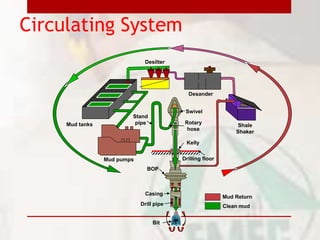
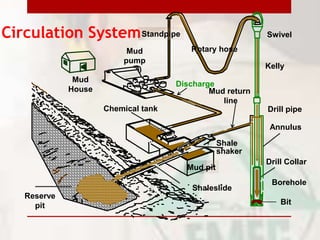
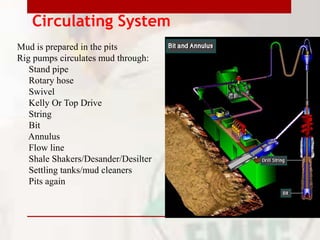
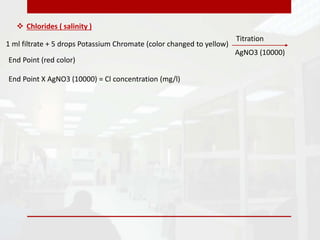
This document provides information on drilling fluids engineering including definitions, parameters, functions, and types of drilling fluids as well as practical mud tests. It defines drilling fluid as a preparation of water and chemicals circulated in well drilling for cooling and flushing cuttings. Key parameters discussed include mud weight (pounds per gallon), viscosity and rheology (plastic viscosity, yield point, gel strength). The functions of drilling fluids include controlling formation pressures, suspending and releasing cuttings, sealing permeable formations, and lubricating and cooling the drill bit. Common mud types are oil-based and water-based muds. Practical mud tests described are measuring mud weight, viscosity and rheology, API filter press test, pH