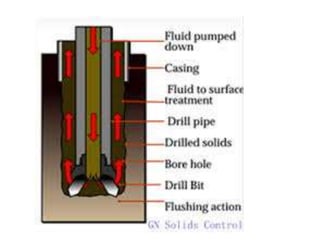
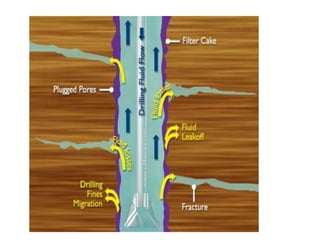
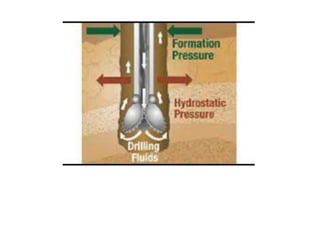
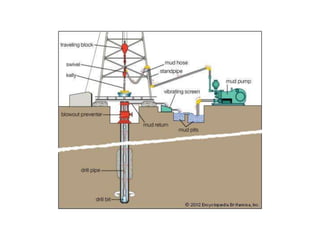
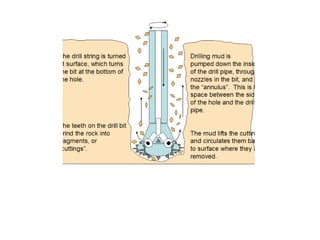
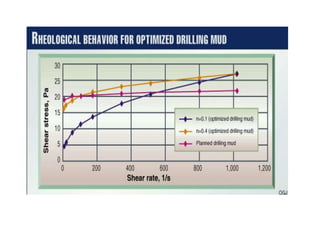
This document discusses sustainable drilling fluid solutions. It begins with basic terminology used in drilling fluids like mud types, additives, and functions of mud. Water-based mud and oil-based mud are compared, noting that WBM is less toxic and can meet environmental issues but is not stable above 400°F, while OBM is stable above 400°F but more toxic. New developments in bio-polymers are discussed that can viscosify drilling fluids with less toxicity and better stability. In conclusion, water-based muds with bio-polymers are the most sustainable option while also addressing environmental concerns related to drilling fluids.