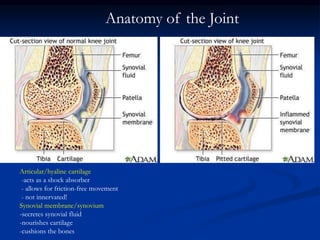
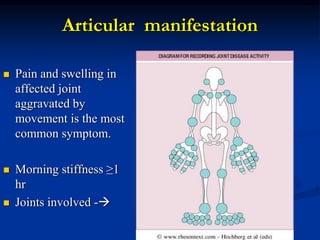
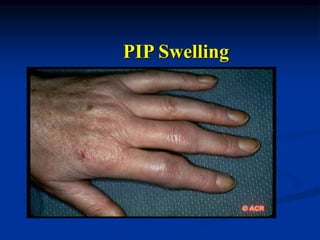
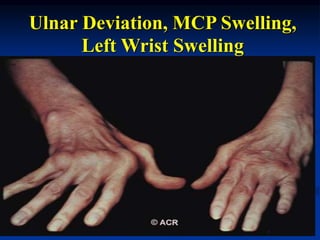
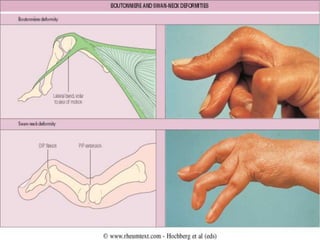
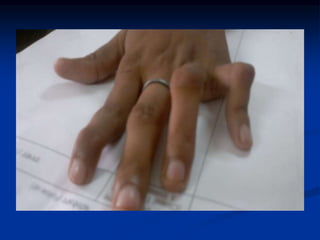
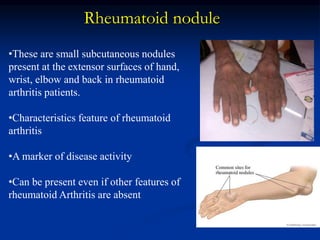
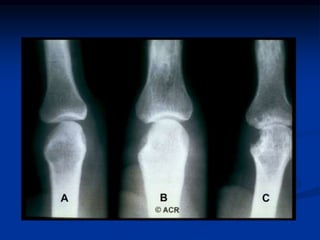
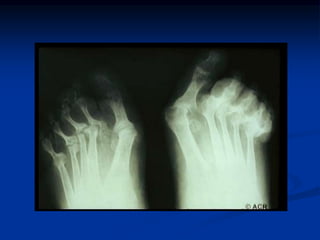
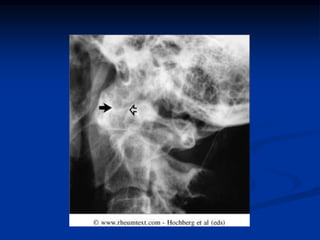
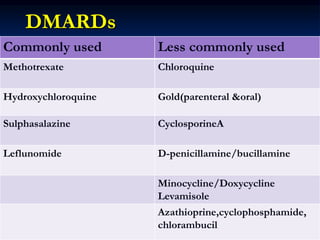
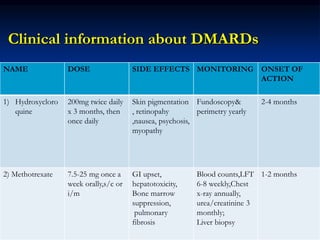
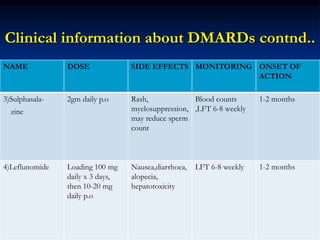
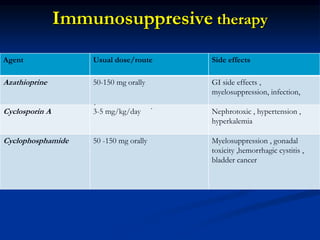
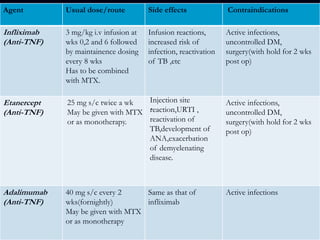
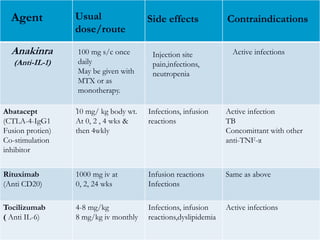
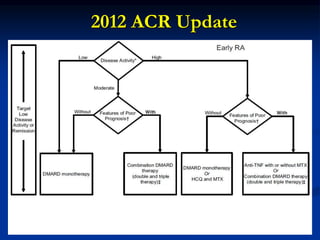
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease that causes inflammation of the joints, resulting in pain, swelling, stiffness and destruction of cartilage and bone. It most commonly affects small joints in the hands and feet. Conventional treatments include NSAIDs, disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs like methotrexate, and corticosteroids. However, these may have side effects or lose effectiveness over time. Biological therapies targeting cytokines like TNF-α have significantly improved treatment outcomes, with anti-TNF agents infliximab, etanercept and adalimumab being widely used options.