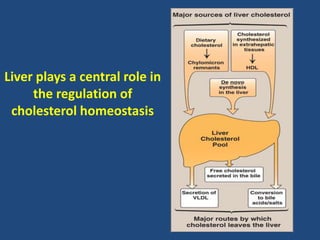
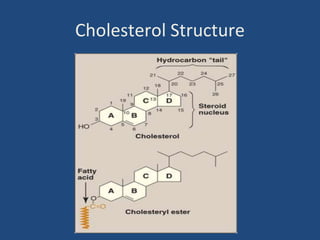
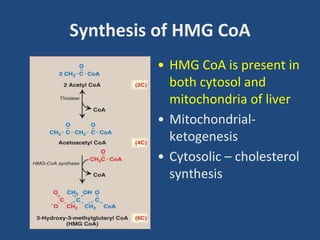
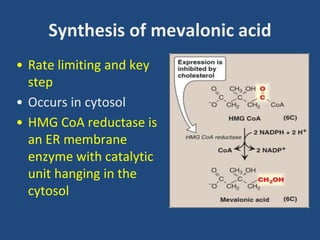
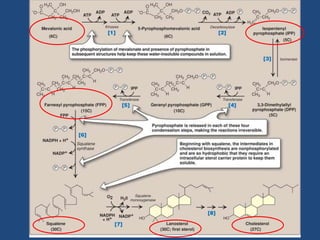
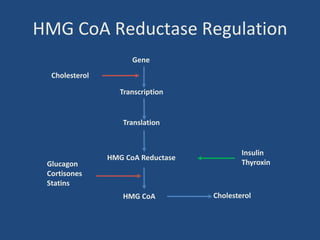
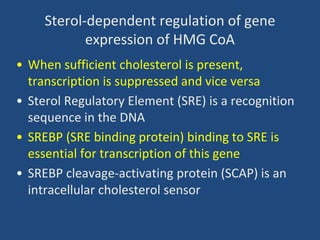
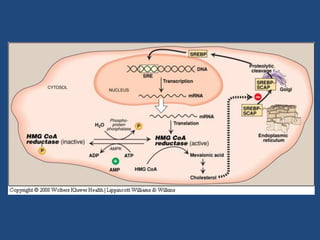
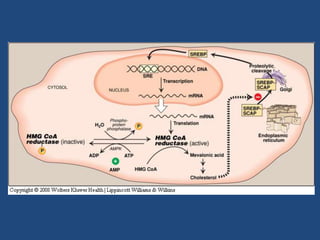
Cholesterol is an important animal steroid that maintains membrane fluidity and is the parent molecule for bile acids, steroid hormones, and vitamin D3. The liver plays a central role in regulating cholesterol homeostasis through synthesis and excretion. Cholesterol synthesis is regulated by the rate-limiting enzyme HMG CoA reductase, which is controlled by sterol-dependent and -independent mechanisms as well as hormones like insulin and glucagon. Excess cholesterol is excreted in bile and eliminated in feces, while hypercholesterolemia can be treated with statin drugs that inhibit HMG CoA reductase or plant sterols that block cholesterol absorption.