ATHRITIS Presentation, diqgnosis an.pptx
- 1. Presented by: Okii Daniel & Ayekundiire liz. Hope Missionary Hospital. 14th june 2023
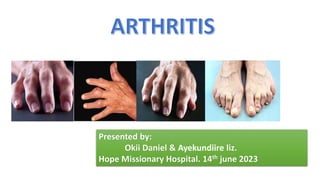
- 2. ARTHRITIS Swelling and tenderness of one or more joints causing pain and inflammation. It is majorly categorized into; • Rheumatoid Arthritis • Osteoarthritis
- 3. RHEUMATOID ATHRITIS Defns; A systemic autoimmune disease of unknown cause with its primary manifestation in synovial tissues. Alternatively: RA can be defined as Chronic and usually progressive inflammatory disorder of unknown etiology x-terised by polyarticular symmetric joint involvement and systemic manifestations. -*THE Synovial tissues proliferate in an uncontrolled fashion resulting in stretching of tendon and ligaments and erosions of bone. RA is theorized to develop when a genetically susceptible individual experiences an external trigger (e.g, cigarette smoking, infection, or trauma) that triggers an autoimmune reaction 5 Months of Disease 5 Years of Disease Rheumatoid Arthritis: 10 Years Later
- 4. Aetiology and pathophysiology The cause of rheumatoid arthritis remains unclear with hormonal, genetic and environmental factors playing a key role. Genetic factors contribute 53–65% of the risk of developing this disease. The HLA-DR4 allele is associated with both the development and severity of rheumatoid arthritis. Cigarette smoking is a strong risk factor for developing rheumatoid arthritis. Pathologically, rheumatoid arthritis is characterized by the infiltration of a variety of inflammatory cells into the joint. The synovial membrane, which is normally acellular, becomes highly vascularised and hypertrophied, creating a so-called pannus formation. There is proliferation of synovial fibroblasts and an increase in the number of inflammatory cells present within the joint.
- 5. Con’t The inflammatory cells involved in rheumatoid arthritis include T-cells (predominantly CD4 helper cells), B-cells, macrophages and plasma cells. Cytokines are released by these cells which cause the synovium to release proteolytic enzymes, resulting in the destruction of bone and cartilage. Key cytokines involved in rheumatoid arthritis include tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-a, interleukin-1, interleukin-6 and granulocyte macrophage colony- stimulating factor (GM-CSF). These play a crucial role in the pro inflammatory reaction.
- 6. CLINICAL PRESENTATION The disease may present as a polyarticular arthritis with gradual onset, extra-articular manifestations may be present. The disease is usually insidious with predominant Signs and symptoms of: pain, Tenderness, warmth at the joints, swollen joints, Joint stiffness that is usually worse in the mornings and after inactivity. Fatigue, fever and loss of appetite. etc
- 7. Investigations Inflammatory markers, including C-reactive protein (CRP) and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), are usually but not always elevated in active disease and are useful for monitoring response to treatment. Rheumatoid factor (RF), CBC, Cyclic citrullinated peptide (CCP), antinuclear antibody (ANA) are among the other investigations. NB: -Those patients who do not have a detectable RF are said to be ‘seronegative’. RF is not specific to rheumatoid arthritis, its is also present in patients with chronic lung and liver disease, other connective tissue diseases, neoplasia, infections Radiographies such ultrasound, x-rays for aparticular suspected joint can be also done.
- 8. American College of Rheumatology (formerly American Rheumatism Association) revised classification criteria for rheumatoid arthritis Criterion Description 1. Morning stiffness Morning stiffness in and around the joints, lasting at least one hour before maximal improvement 2. Arthritis of three or more joint areas At least three joint areas (out of 14 possible areas; right or left PIP, MCP, wrist, elbow, knee, ankle, MTP joints) simultaneously have had soft tissue swelling or fluid (not bony overgrowth alone) 3. Arthritis of hand joints At least one area swollen (as defined above) in a wrist, MCP, or PIP joint Diagnosis is based on the ACR criterion as shown in the table below:
- 9. 4. Symmetric arthritis Simultaneous involvement of the same joint areas (as defined above) on both sides of the body (bilateral involvement of PIPs, MCPs, or MTPs, without absolute symmetry is acceptable). 5. Rheumatoid nodules Subcutaneous nodules over bony prominences or extensor surfaces, or in juxta-articular regions as observed by a physician 6. Serum rheumatoid factor Demonstration of abnormal amounts of serum rheumatoid factor by any method for which the result has been positive in less than 5 percent of normal control subjects. 7. Radiographic changes Radiographic changes typical of rheumatoid arthritis on posteroanterior hand or wrist radiographs, which must include erosions or unequivocal bony decalcification localised in, or most marked adjacent to, the involved joints (osteoarthritis changes alone do not qualify).
- 10. Con’t… • NB: • For classification purposes, a patient is said to have rheumatoid arthritis if he or she has satisfied at least four of the above seven criteria. Criteria 1 through 4 must be present for at least 6 weeks. Patients with two clinical diagnoses are not excluded. Designation as classic, definite, or probable rheumatoid arthritis is not to be made.
- 11. GOAL OF THERAPY The ultimate goal of RA treatment is to:- Induce a complete remission, although this may be difficult to achieve. Reduce joint swelling, stiffness, and pain; Preserve range of motion and joint function; Improve quality of life; Prevent systemic complications; and slow destructive joint changes.
- 12. Management strategies for RA Non-pharmacological approach Pharmacological approach -Education Heat and cold therapies -Psychological support and employment counselling -Occupational therapy -Physiotherapy -Surgical interventions, such as synovectomy and arthroplasty, may be useful to relieve pain and restore function. -NSAIDs, cox-2 selective ihibitors -Corticosteroids -DMARDS:- Conventional e.g, Methotrexate, Hydrochloroquine, Sulfasalazine, Leflunomide, Gold, Azathioprine, Minocycline, leflunomide. Biologicals e.g, >TNFα antagonists like Etanercept (Enbrel), Infliximab (Remicade), Adalimumab (Humira), >Interleukin-1 antagonist like Anakinra (Kineret), >Suppress T-Cell activation like Abatacept (Orencia) >Anti B-Cell monoclonal antibody like Rituximab (Rituxan)
- 13. OSTEOARTHRITIS • Osteoarthritis (OA) is a degenerative disorder with inflammatory components arising from the biochemical breakdown of articular (hyaline) cartilage in the synovial joints. • OA primarily affects the weight-bearing diarthrodial joints of the peripheral and axial skeleton, and it’s characterized by progressive deterioration and loss of articular cartilage, resulting in osteophyte formation, pain, limitation of motion, deformity, and progressive disability. The current view holds that osteoarthritis involves not only the articular cartilage but the entire joint organ, including the subchondral bone and synovium. • It is the most common type of joint disease and the leading cause of chronic disability in older adults • NB;Inflammation may or may not be present in the affected joints.
- 14. OSTEOATHRITIS • It is a chronic degenerative disorder of the synovial joints in which there is progressive softening and erosion/disintegration of the articular cartilage.
- 15. OSTEOARTHRITIS • It occurs when the protective cartilage that cushions the ends of the bones wears down over time. • Although osteoarthritis can damage any joint, the disorder most commonly affects joints in your hands, knees, hips and spine.
- 17. RISK FACTORS •Joint injury or overuse—Injury or overuse, such as knee bending and repetitive stress on a joint, can damage a joint and increase the risk of OA in that joint. •Age—The risk of developing OA increases with age. •Gender—Women are more likely to develop OA than men, especially after age 50. •Obesity—Extra weight puts more stress on joints, particularly weight-bearing joints like the hips and knees. This stress increases the risk of OA in that joint. Obesity may also have metabolic effects that increase the risk of OA. •Genetics—People who have family members with OA are more likely to develop OA. People who have hand OA are more likely to develop knee OA. •Race— Some Asian populations have lower risk for OA. •Life style-the more active people are likely to develop OA.
- 18. SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS Signs and symptoms • Deep, achy joint pain exacerbated by extensive use - The disease’s primary symptom • Reduced range of motion and crepitus - Frequently present • Stiffness during rest (gelling) - May develop, with morning joint stiffness usually lasting for less than 30 minutes • Swelling
- 19. CONT Osteoarthritis of the hand • Distal interphalangeal (DIP) joints are most often affected • Proximal interphalangeal (PIP) joints and the carpometacarpal (cmc) joints at the base of the thumb are also typically involved • Heberden nodes, which represent palpable osteophytes in the DIP joints, are more characteristic in women than in men • Inflammatory changes are typically absent, less pronounced, or go unnoticed
- 20. OSTEOARTHRITIS MANAGEMENT Investigations • Imaging: US, XRAY,CT, MRI • Arthrocentesis
- 21. NONPHARMACOLOGIC INTERVENTIONS • The cornerstones of osteoarthritis therapy, nonpharmacologic interventions include the following: • Patient education, Heat and cold, Weight loss • Exercise, Physical therapy • Muscle training (eg, quadriceps strengthening for knee OA) • Occupational therapy (use of assistive devices for independence in ADL) • Unloading in certain joints (eg, knee and hip)
- 22. PHARMACOLOGIC THERAPY Topical capsaicin Topical nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) Oral NSAIDs, Tramadol, Glucosamine and chondroitins Acetaminophen Intra-articular corticosteroid injections. (methylprednisolone acetate or triamcinolone Hexacetonide) Surgery Arthroscopy Osteotomy Arthroplasty - Particularly with knee or hip osteoarthritis Fusion
- 23. CON’T…. NB. Glucosamine and chondroitin are dietary supplements that were shown to stimulate proteoglycan synthesis from articular cartilage in vitro. SOME of the examples of drugs in this classes include: Jointace capsules, osteomin tabs, osteocare, osteoflex tabs etc Hyaluronate Injections. High-molecular-weight hyaluronic acid is a constituent of normal cartilage that provides lubrication with motion and shock absorbency during rapid movements.
- 28. References:- https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/331715-overview https://www.healthline.com/health/rheumatoid-arthritis/rheumatoid- arthritis-test Pharmacotherapy handbook 7th edition by Barbara g. Wells Joseph T. Dipiro Terry L.
Editor's Notes
- Osteoarthritis: Practice Essentials, Background, Anatomy (medscape.com)
- Osteoarthritis: Practice Essentials, Background, Anatomy (medscape.com)
- Osteoarthritis: Practice Essentials, Background, Anatomy (medscape.com)