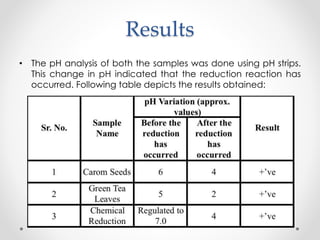
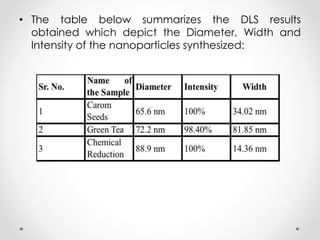
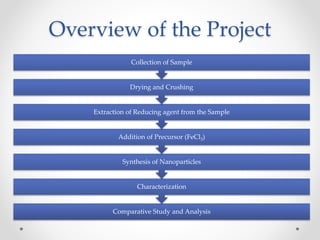
Iron nanoparticles were synthesized using green technology from carrom seeds and green tea, and through chemical synthesis. The nanoparticles were characterized through pH analysis, UV-Vis spectroscopy, and dynamic light scattering. pH analysis indicated reduction reactions occurred. UV-Vis spectroscopy showed absorbance peaks around 500 nm for all samples, consistent with iron nanoparticles. Dynamic light scattering showed particle sizes of 65.6 nm, 72.7 nm, and 88.9 nm for carrom seed, green tea, and chemically synthesized nanoparticles, respectively, confirming synthesis of nanoparticles in the desired size range.



![Review of Literature
Application of Iron Nanoparticles:
• Huber Dr. D. L. et. al. described in their paper titled “Synthesis,
Properties, and Applications of Iron Nanoparticles”: Iron as a
nanoparticle has been somewhat neglected in favor of its own
oxides, as well as other metals such as cobalt, nickel, gold, and
platinum. Iron's reactivity is important in macroscopic applications
(particularly rusting), but is a dominant concern at the nanoscale.
Recent work has begun to take advantage of irons potential,
and work in this field appears to be blossoming. [Huber Dr., D. L.
et. al., (2005)]
• Takada Prof. J. et. al. described in their paper titled “Research
and application of iron oxide nanoparticles explored”: Iron oxide
NP of about 100 nm produced yellowish red, and larger particles
sizes led to red and eventually dark purple colors. This study
revealed the application of BIOX as an ecofriendly anode in Li-
ion batteries. [Takada Prof, J. et. al., (2014)] [Laurent, S. et. al.,
(2008)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/47ff1eb5-2fdd-4970-aa6d-b1f94786aa9d-150623103526-lva1-app6892/85/Final-Presentation-on-Iron-Nanoparticles_Prajwal-1-5-320.jpg)
![Synthesis of Iron Nanoparticles using Green Technology:
• Pattanayak et. al. described in their paper titled “Ecofriendly
synthesis of Iron Nanoparticles from various Plants and Spices
extract”: Biosynthesis from different parts (mostly leaf) of the plant
is found to be the most effective process of synthesis at a very
affordable cost. Appropriate precursors such as Ferric Chloride
can be used for the reduction of plant extracts. Scientists report
the synthesis of nanoparticles, reducing Ferric ions present in the
aqueous solution of Ferric chloride by the help of different plant
extracts. Through elaborate screening process involving about 45
plants, we selected 10 most suitable plants as the potential
candidates for the synthesis of iron nanoparticles. [Pattanayak,
M. et. al., (2013)] [Li, L. et. al., (2006)]
• Iravani, S. et. al. described in their paper titled “Green synthesis of
metal nanoparticles using plants”: This study reveals that in recent
years, the development of efficient green chemistry methods for
synthesis of metal nanoparticles has become a major focus of
researchers. Investigations in order to find out an eco-friendly
technique for production of well-characterized nanoparticles
have been carried out. One of the most considered methods is
production of metal nanoparticles using organisms. Among these
organisms plants seem to be the best candidates and they are
suitable for large-scale biosynthesis of nanoparticles.
Nanoparticles produced by plants are more stable and the rate
of synthesis is faster than in the case of microorganisms. [Iravani,
S., (2011)] [Raveendran, P. et. al., (2013)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/47ff1eb5-2fdd-4970-aa6d-b1f94786aa9d-150623103526-lva1-app6892/85/Final-Presentation-on-Iron-Nanoparticles_Prajwal-1-6-320.jpg)
![Biomedical Applications of Iron Nanoparticles:
• Gupta, A. K. et. al. described in their paper titled “Synthesis and
surface engineering of iron oxide nanoparticles for biomedical
applications” : Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles
(SPION) with appropriate surface chemistry have been widely
used experimentally for numerous in vivo applications such as
magnetic resonance imaging contrast enhancement, tissue
repair, immunoassay, detoxification of biological fluids,
hyperthermia, drug delivery and in cell separation, etc. All
these biomedical and bioengineering applications require
that these nanoparticles have high magnetization values and
size smaller than 100 nm with overall narrow particle size
distribution, so that the particles have uniform physical and
chemical properties. To this end, most work in this field has
been done in improving the biocompatibility of the materials,
but only a few scientific investigations and developments
have been carried out in improving the quality of magnetic
particles, their size distribution, their shape and surface in
addition to characterizing them to get a protocol for the
quality control of these particles. [Gupta, A., K. et. al., (2005)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/47ff1eb5-2fdd-4970-aa6d-b1f94786aa9d-150623103526-lva1-app6892/85/Final-Presentation-on-Iron-Nanoparticles_Prajwal-1-7-320.jpg)
![Characterization:
• Nurmi, J. E. et. al. described in their paper titled “Characterization
and Properties of Metallic Iron Nanoparticles: Spectroscopy,
Electrochemistry, and Kinetics” : Superparamagnetic iron oxide
nanoparticles (SPION) with appropriate surface chemistry
have been widely used experimentally for numerous in vivo.
All these biomedical and bioengineering applications require
that these nanoparticles have high magnetization values and
size smaller than 100 nm with overall narrow particle size
distribution, so that the particles have uniform physical and
chemical properties. [Nurmi, J., E. et. al., (2004)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/47ff1eb5-2fdd-4970-aa6d-b1f94786aa9d-150623103526-lva1-app6892/85/Final-Presentation-on-Iron-Nanoparticles_Prajwal-1-8-320.jpg)
![Introduction
• What are Nanoparticles? – Particles with sizes in the
range of 10 – 100 nm are called nanoparticles. [Khan, F.
A., et. al., (2012)]
• This range (10 – 100 nm) is known as the Nanoscale.
• Why do they interest us? – Nanoparticle research is
currently an area of intense scientific research due to a
wide variety of potential applications in biomedical,
optical and electronic fields.
• Iron nanoparticles have been found to be an effective
measure to treat several types of ground contamination
and are easily transportable through ground water for in
situ treatment. These factors combined makes this
method cheaper than most methods currently being
used. [Kulkarni, L. et. al., (2009)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/47ff1eb5-2fdd-4970-aa6d-b1f94786aa9d-150623103526-lva1-app6892/85/Final-Presentation-on-Iron-Nanoparticles_Prajwal-1-9-320.jpg)
![• Iron oxide nanoparticles can easily be reduced to
magnetite and maghemite which preferred in
biomedical in vivo applications because they are
biocompatible and potentially non – toxic to
humans.
• They also show magnetic and paramagnetic
properties which make them a potentially useful
drug delivery system.
• Recent advancements in the field of
nanotechnology have led to the development of
various techniques for the biosynthesis of metal
nanoparticles. [Murphy, C. J. et. al., (2002)]
• Green Technology - Designing chemical products
and processes in a way that reduces or eliminates
hazardous substances from the beginning to end of
a chemical product’s life cycle.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/47ff1eb5-2fdd-4970-aa6d-b1f94786aa9d-150623103526-lva1-app6892/85/Final-Presentation-on-Iron-Nanoparticles_Prajwal-1-10-320.jpg)