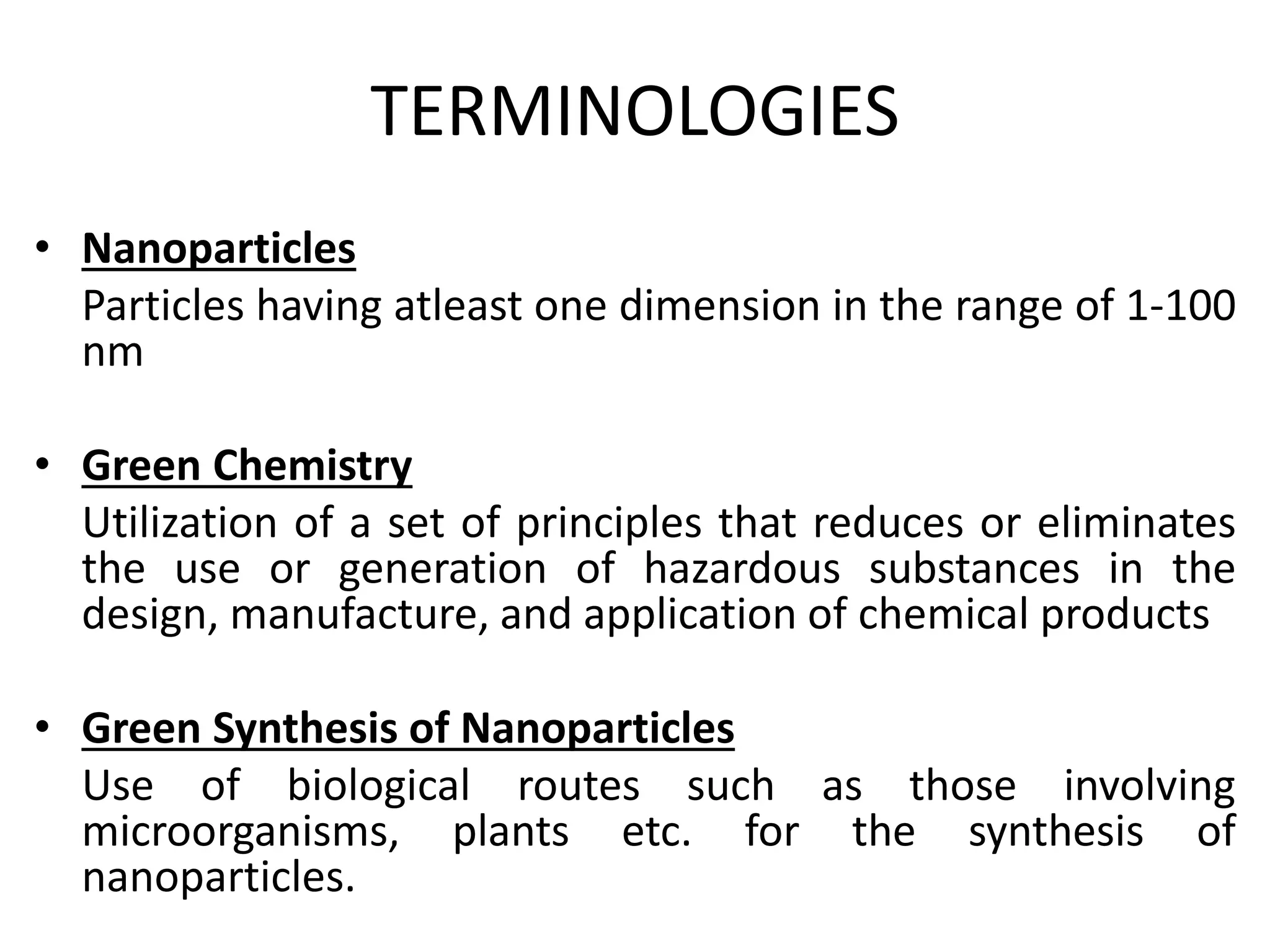
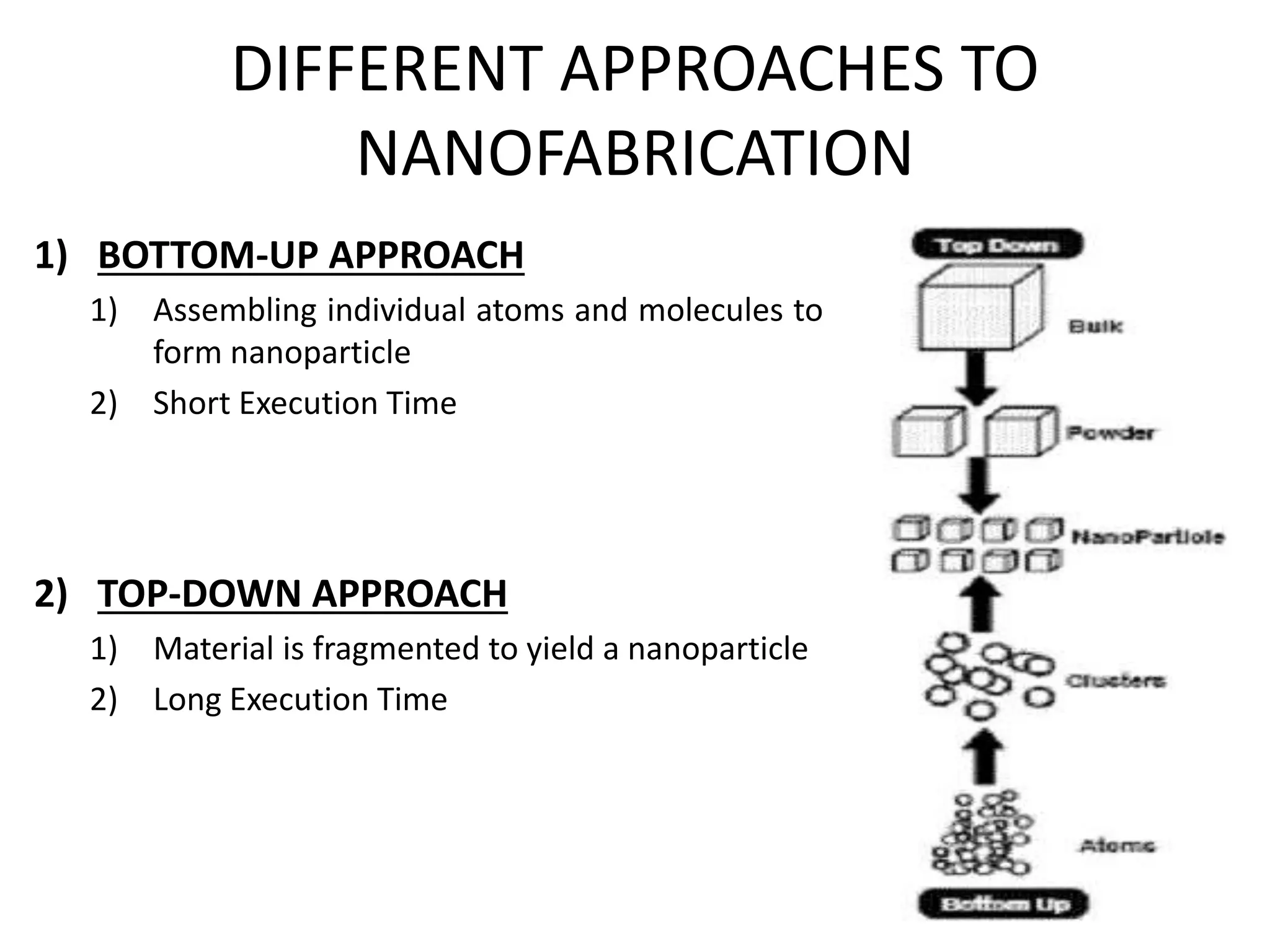
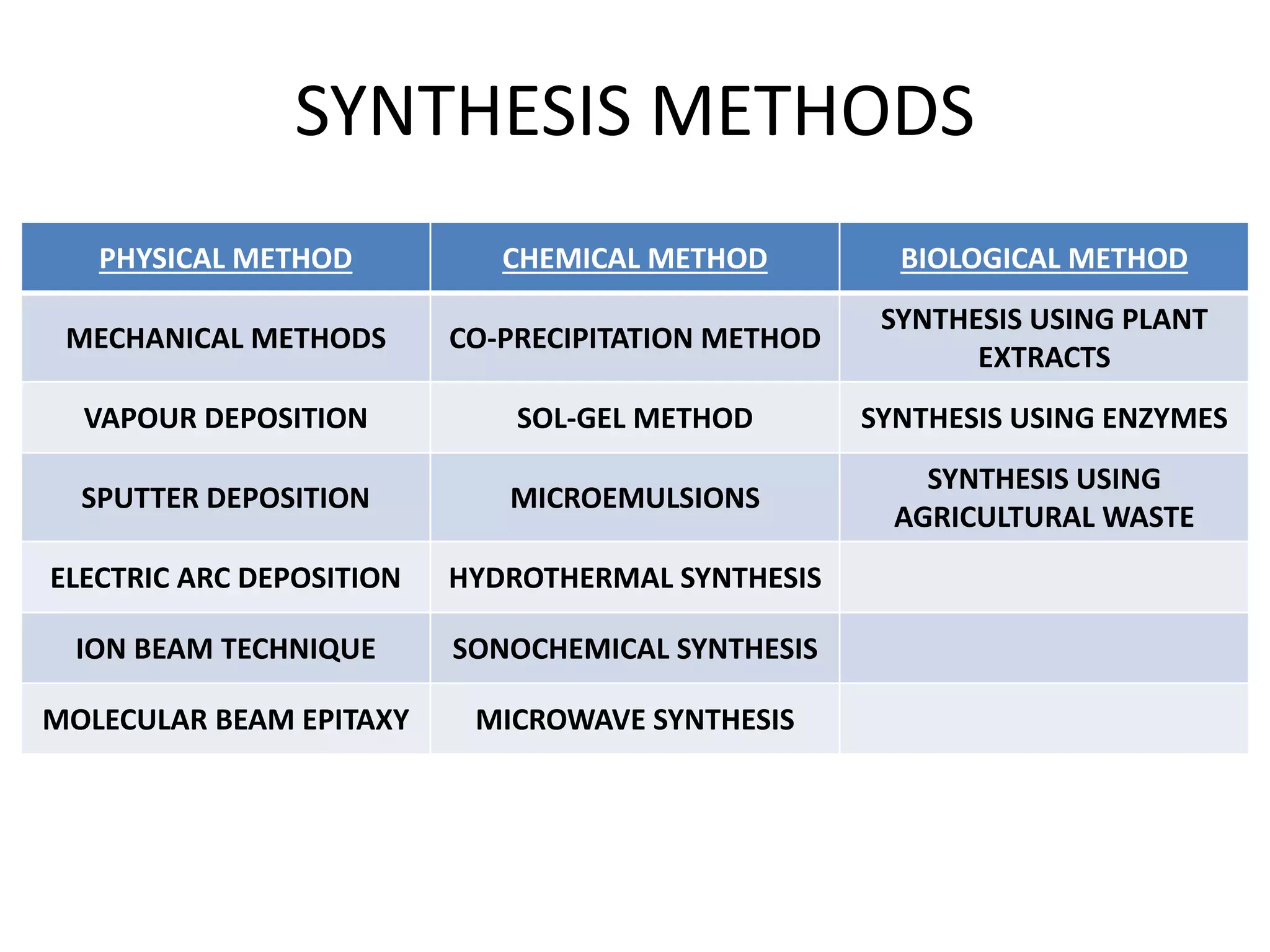
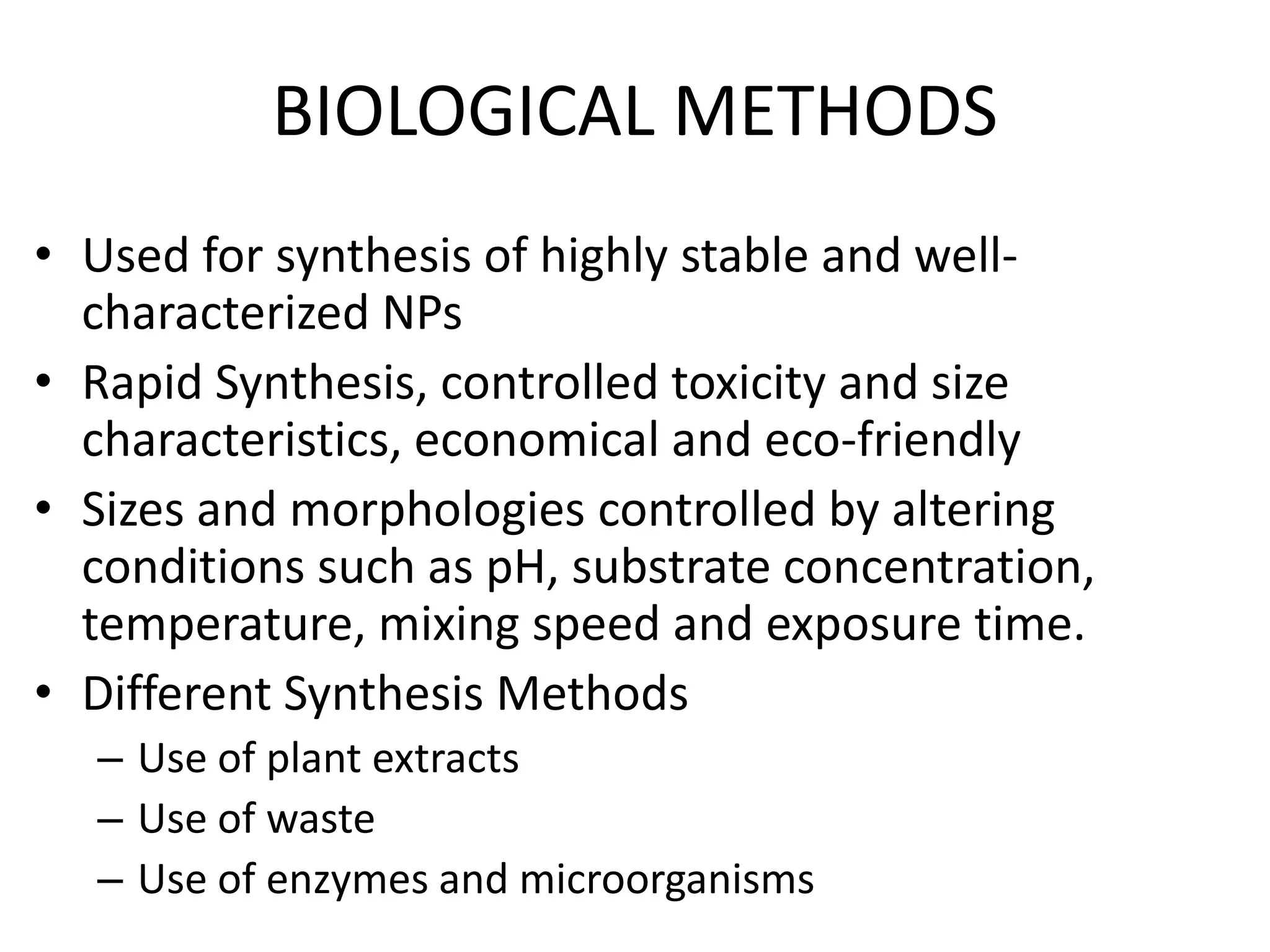
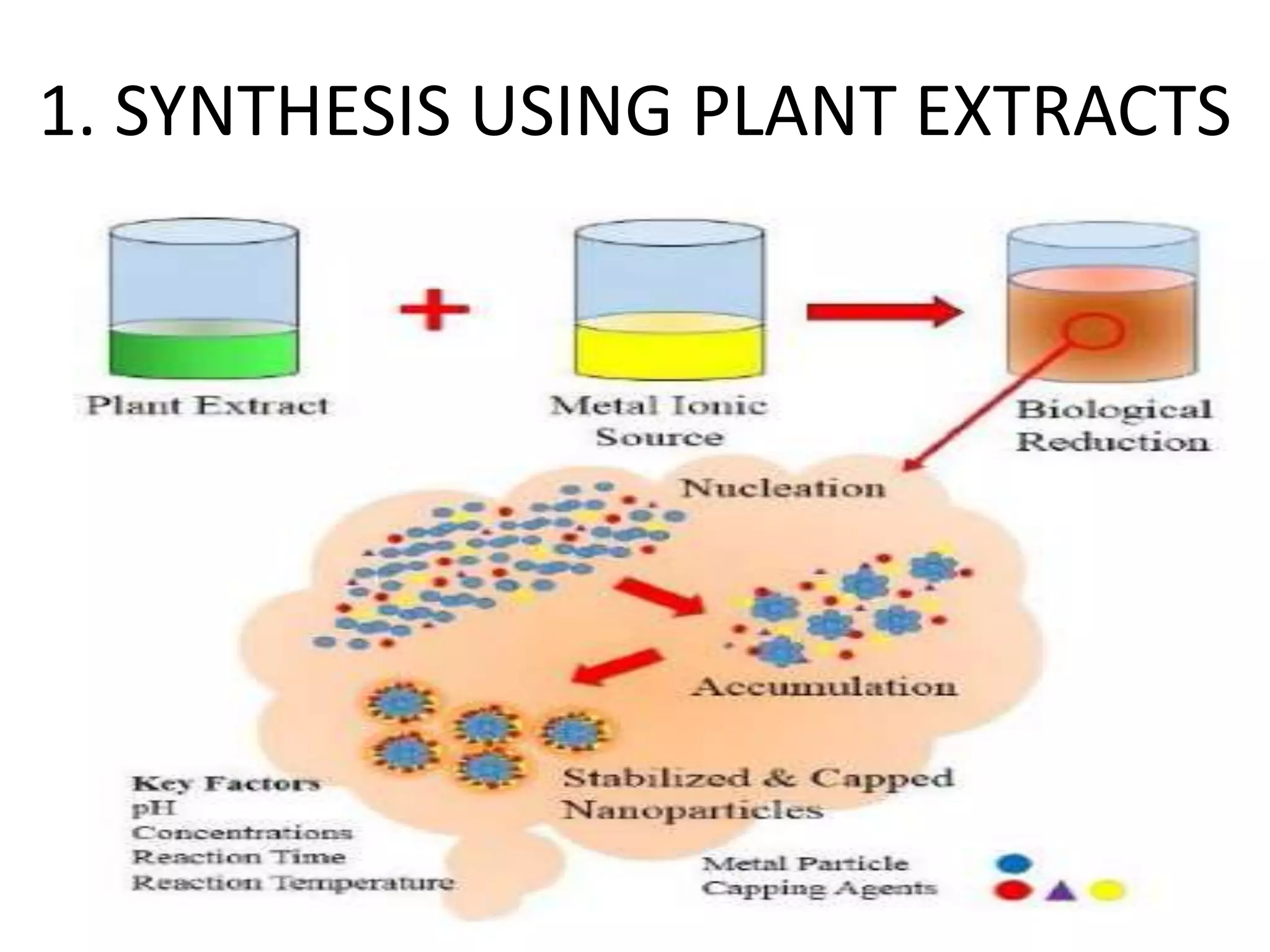
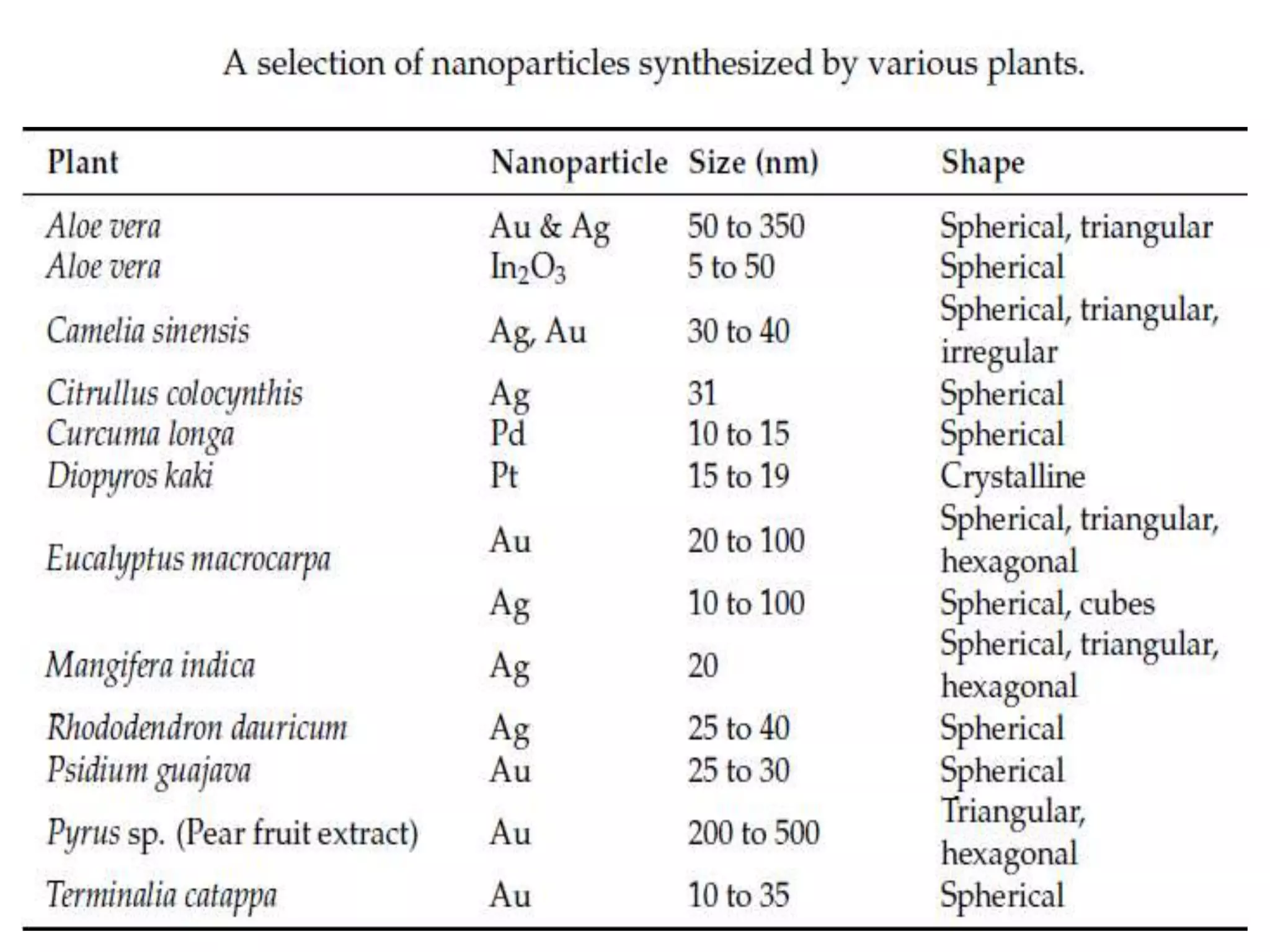
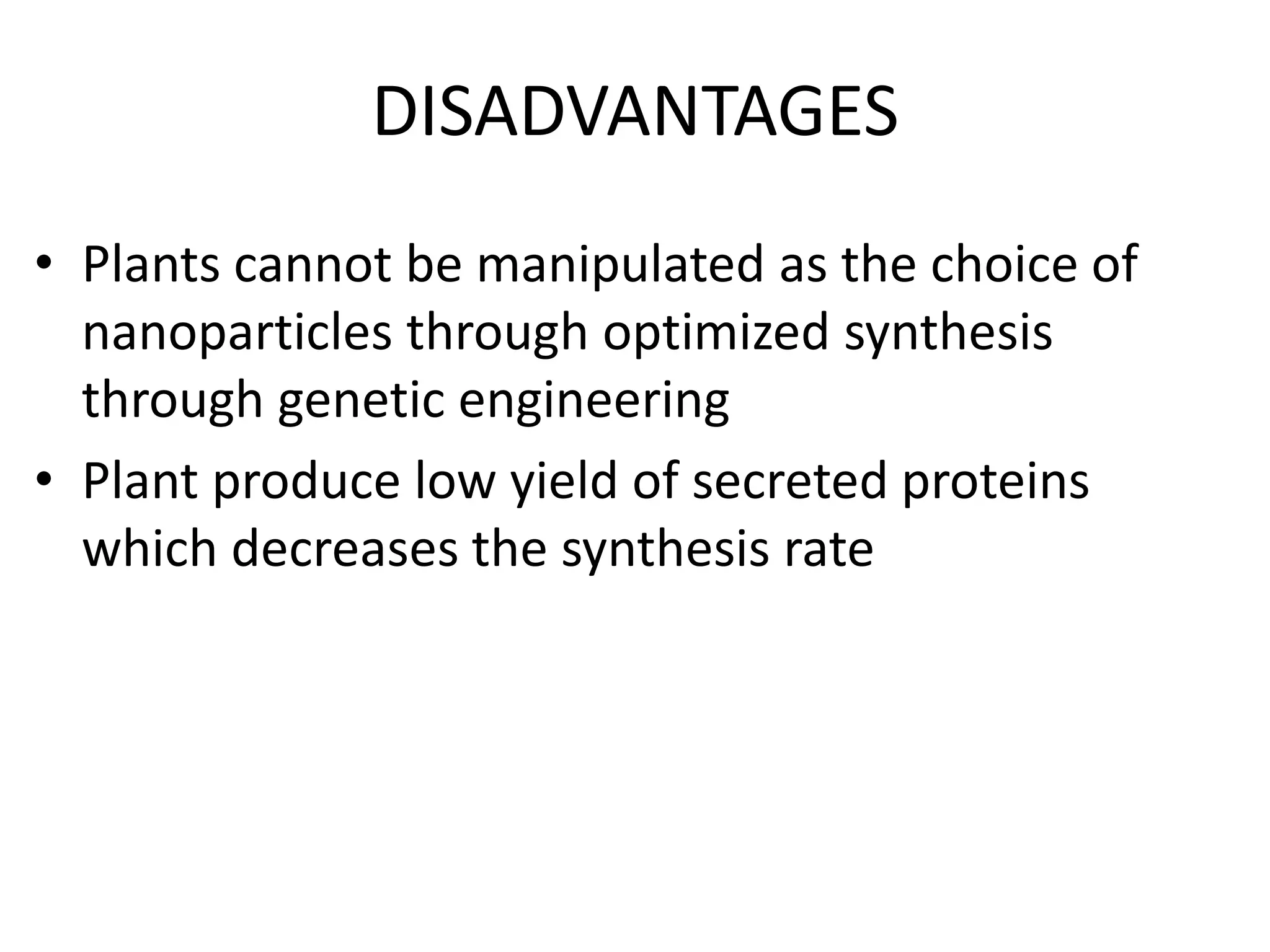
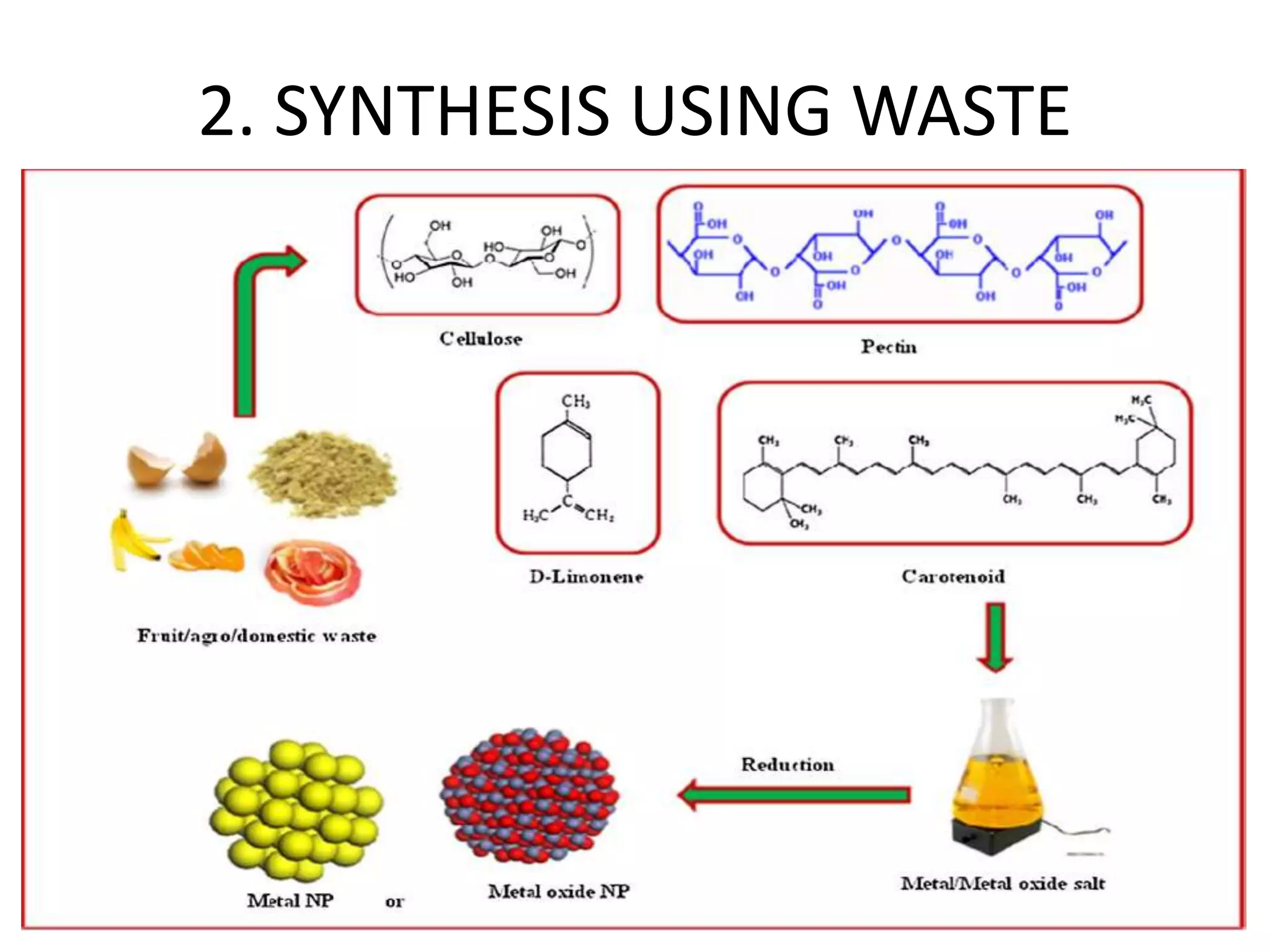
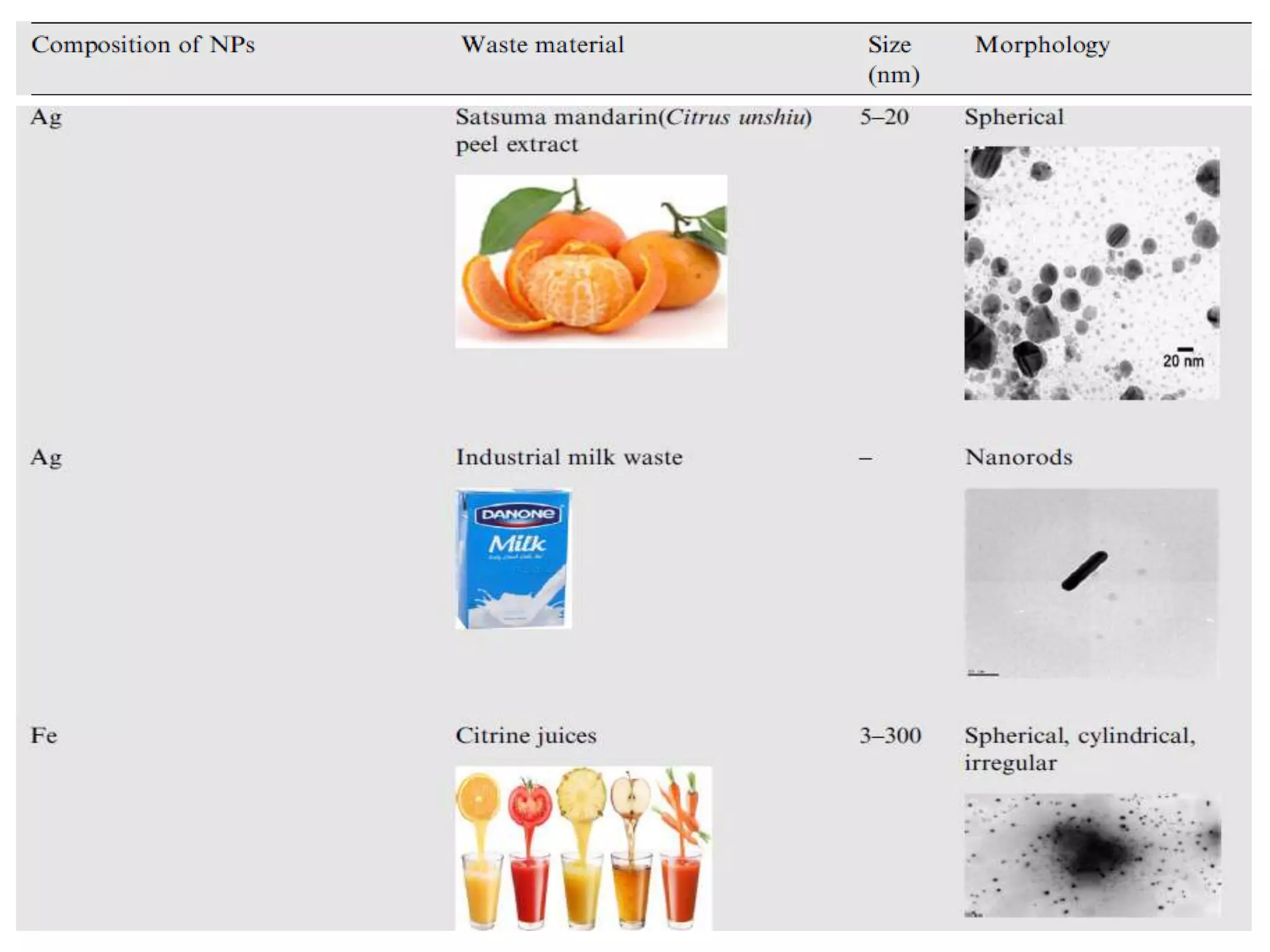
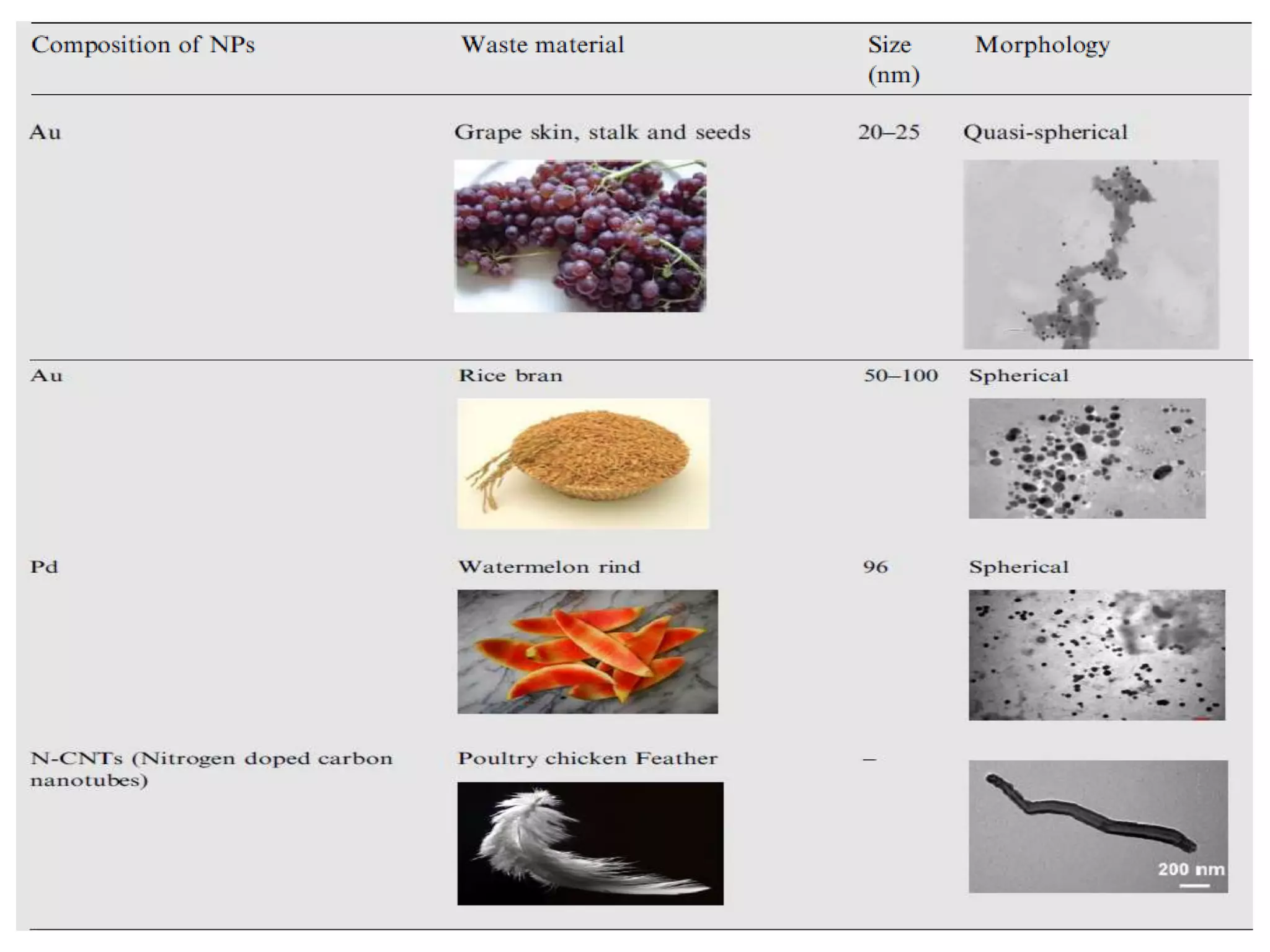
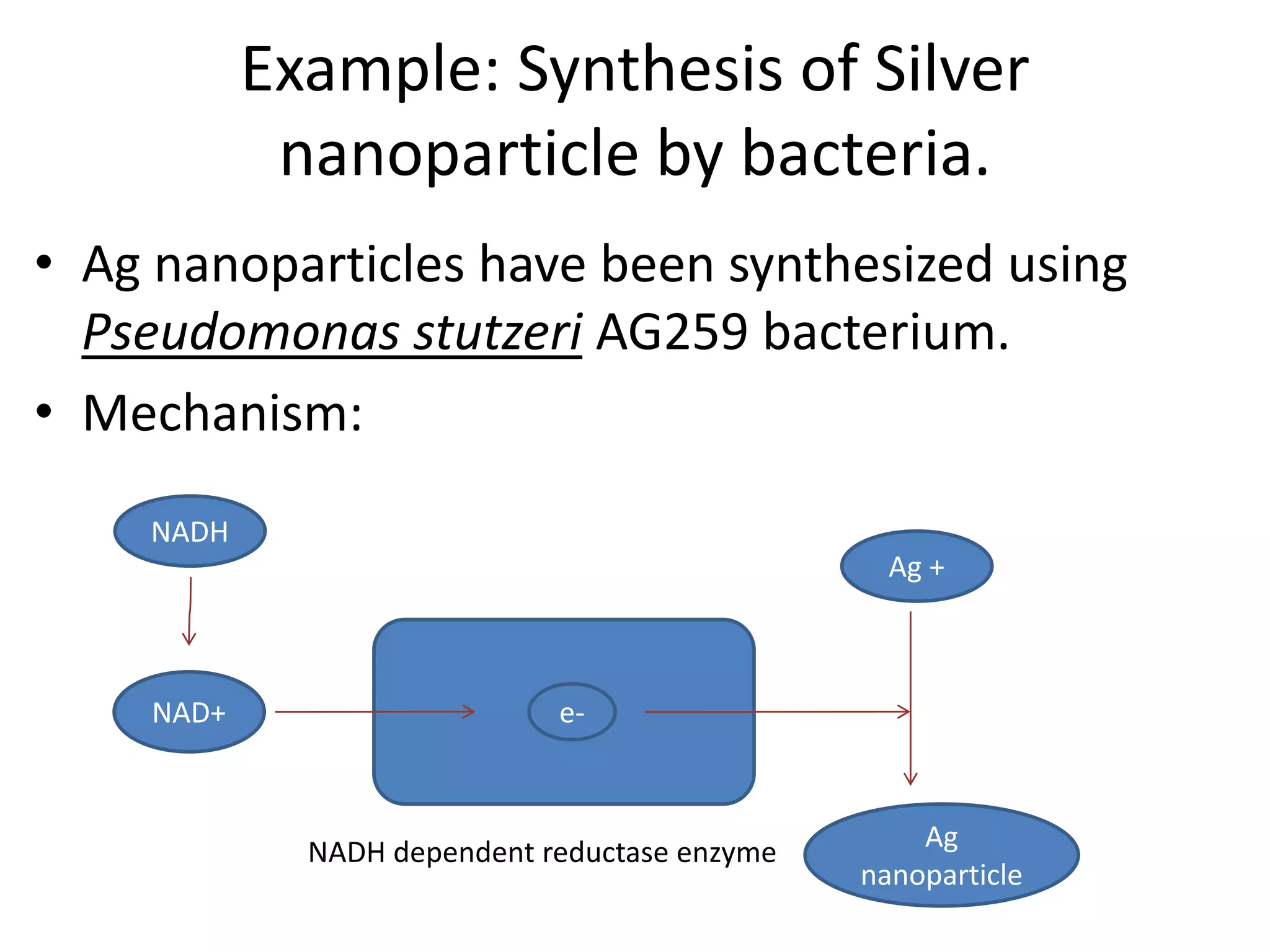
This document discusses green synthesis of nanoparticles using biological methods. It describes how nanoparticles can be synthesized using plant extracts, agricultural waste, microorganisms and enzymes in an environmentally friendly way. This is advantageous over chemical and physical methods as it is cost-effective, produces non-toxic nanoparticles and does not require high temperature or pressure. Specific examples discussed include using bacteria to synthesize silver nanoparticles and controlling factors like pH and temperature to regulate nanoparticle size and shape during microbial synthesis. Overall, the document presents biological methods as a green alternative for nanoparticle production.