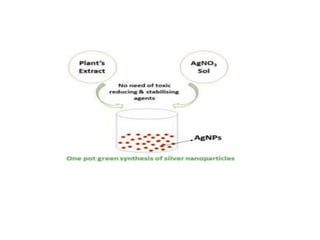
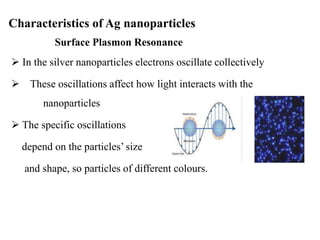
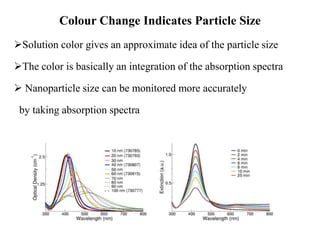
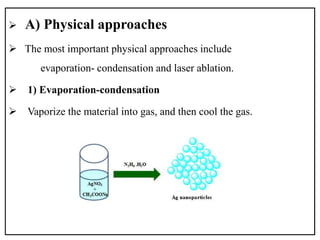
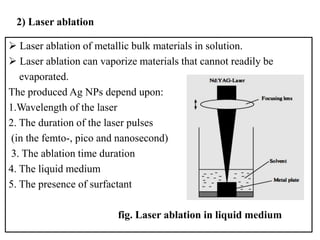
The document discusses the synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles (Ag NPs), detailing various approaches including physical, chemical, and biological methods, with a focus on environmentally friendly techniques. It highlights the applications of Ag NPs in medical, dental, and consumer products, noting their historical use and modern relevance. Key characteristics like surface plasmon resonance and the correlation between particle size and color are also explored.










![chemical approach
Tollens method
It involves the reduction of
[Ag(NH3)2]+ (as a Tollens reagent)
by an aldehyde.
In the modified Tollens procedure,
silver ions are reduced by saccharides
in the presence of ammonia.
[Ag(NH3)2]+(aq) + RCHO(aq)
Ag(s) +RCOOH(aq)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pptag-181031052732/85/introduction-to-silver-nanoparticles-and-characterization-13-320.jpg)