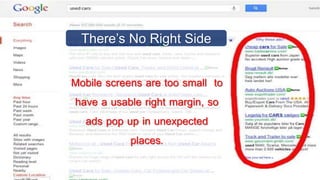
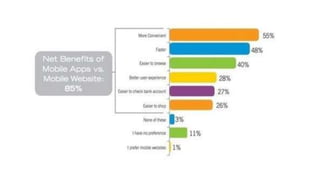
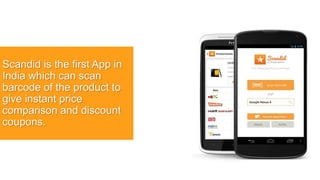
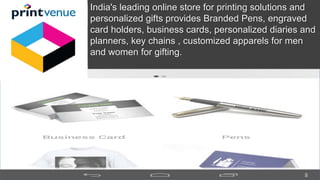
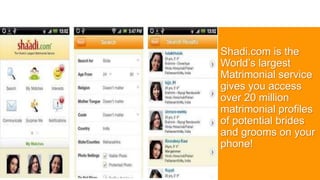
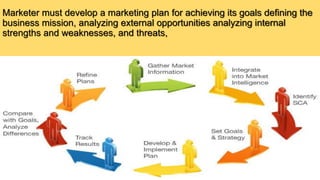
The document outlines insights from various modules on marketing management, emphasizing the importance of mobile advertising and the need for apps over traditional ads. It discusses strategies for enhancing customer engagement by creating value through convenience, unique functionalities, and social interaction. Additionally, it includes case studies demonstrating effective marketing strategies and pricing decisions for companies in different industries.