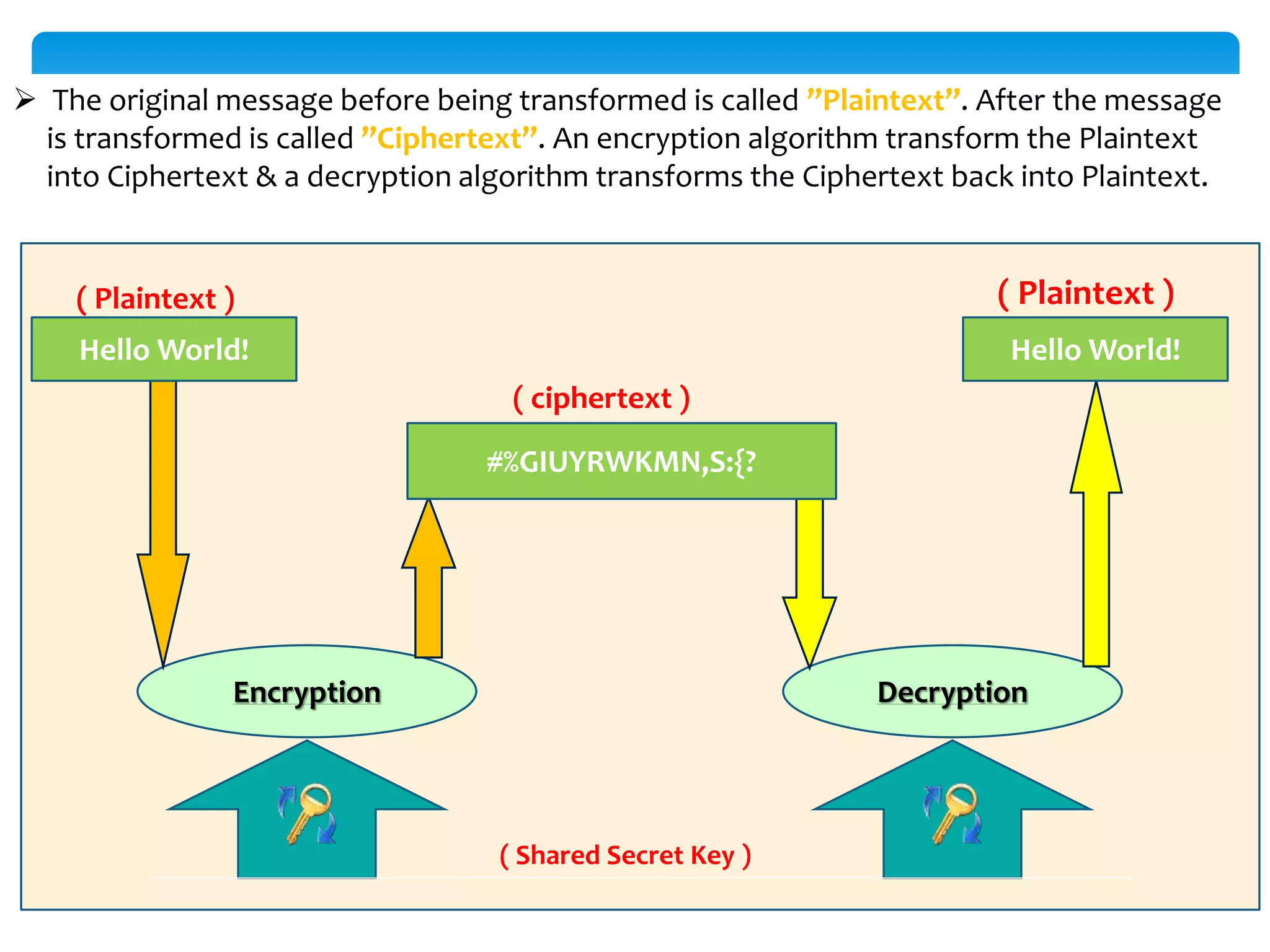
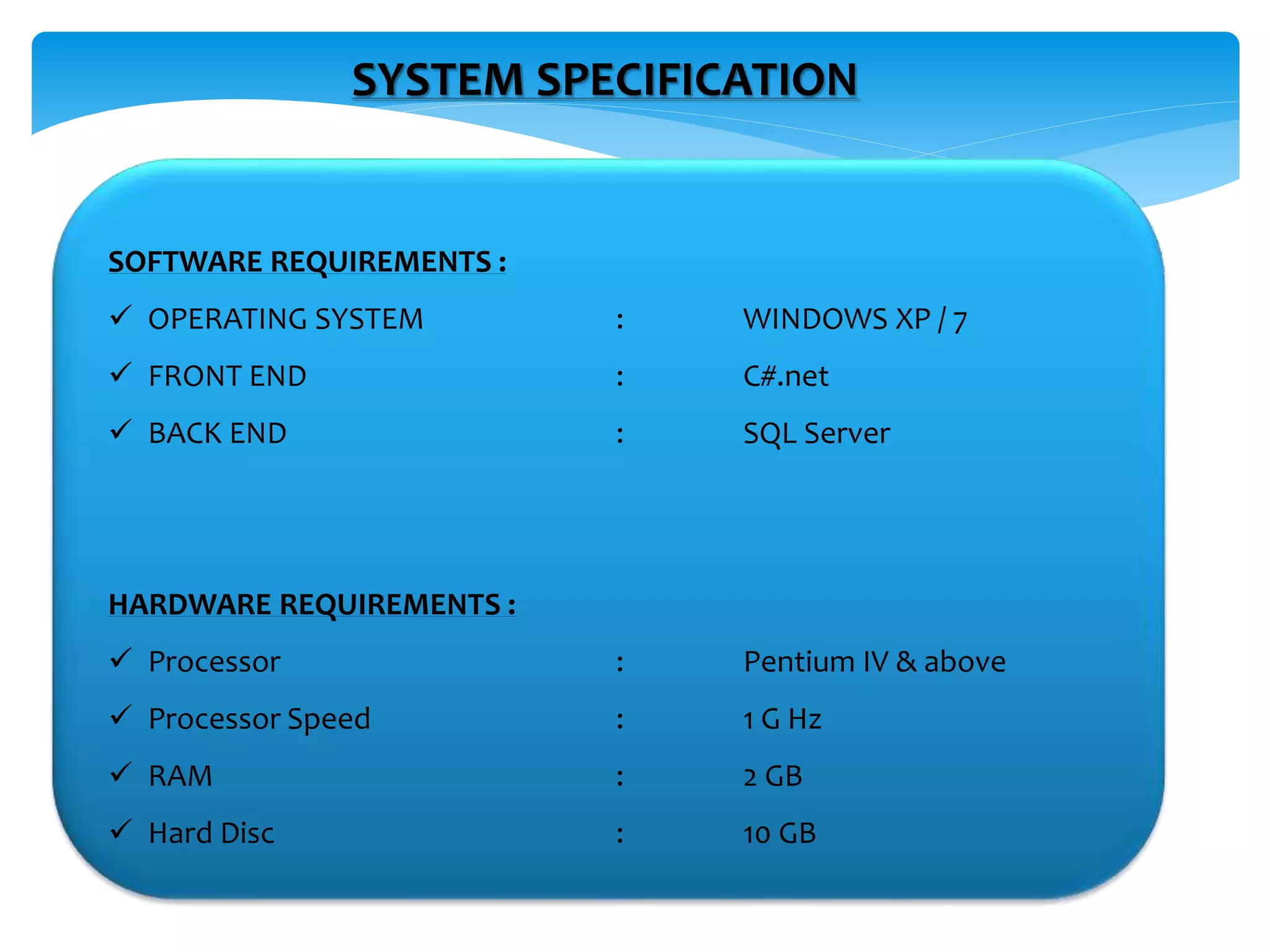
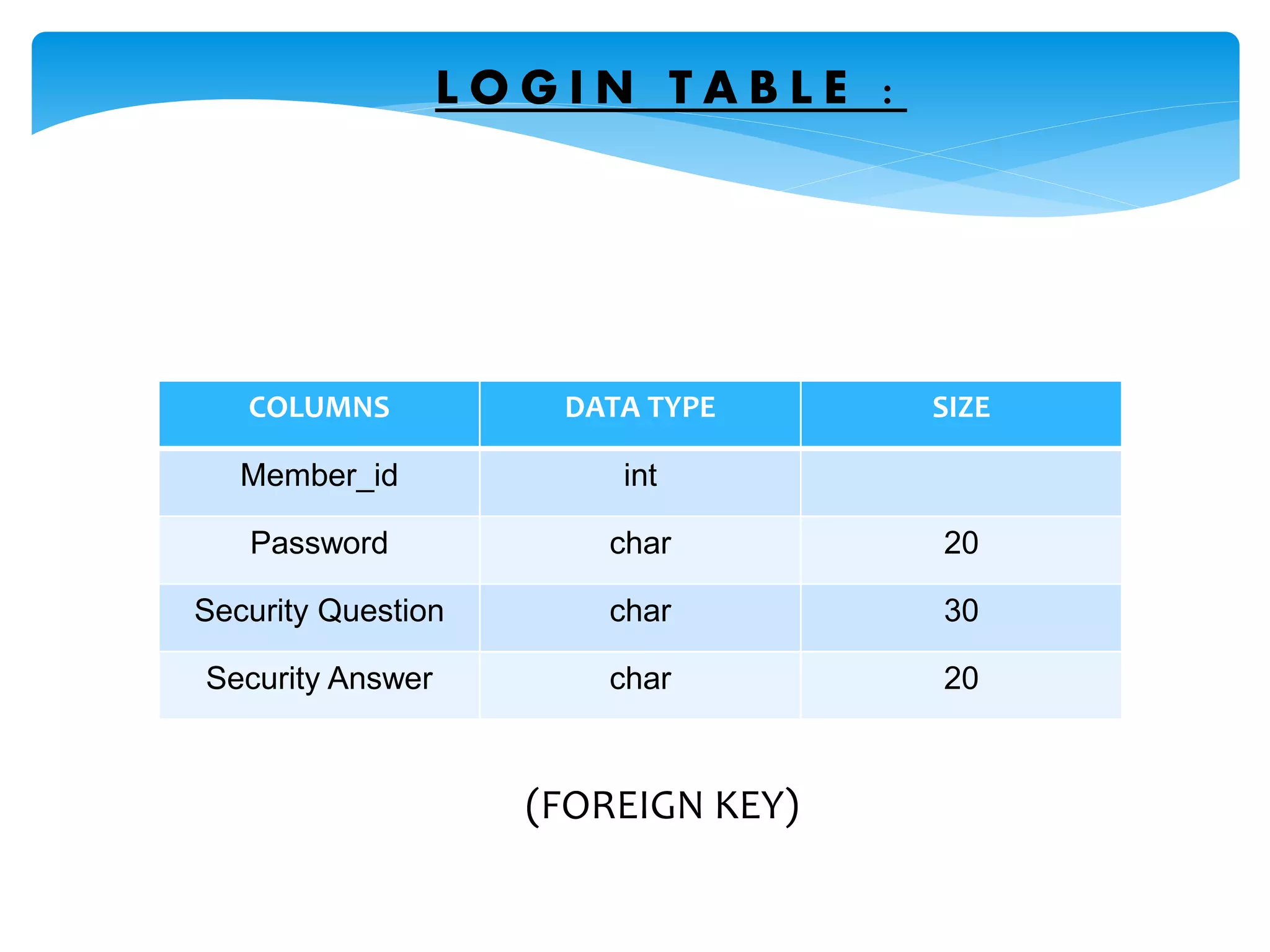
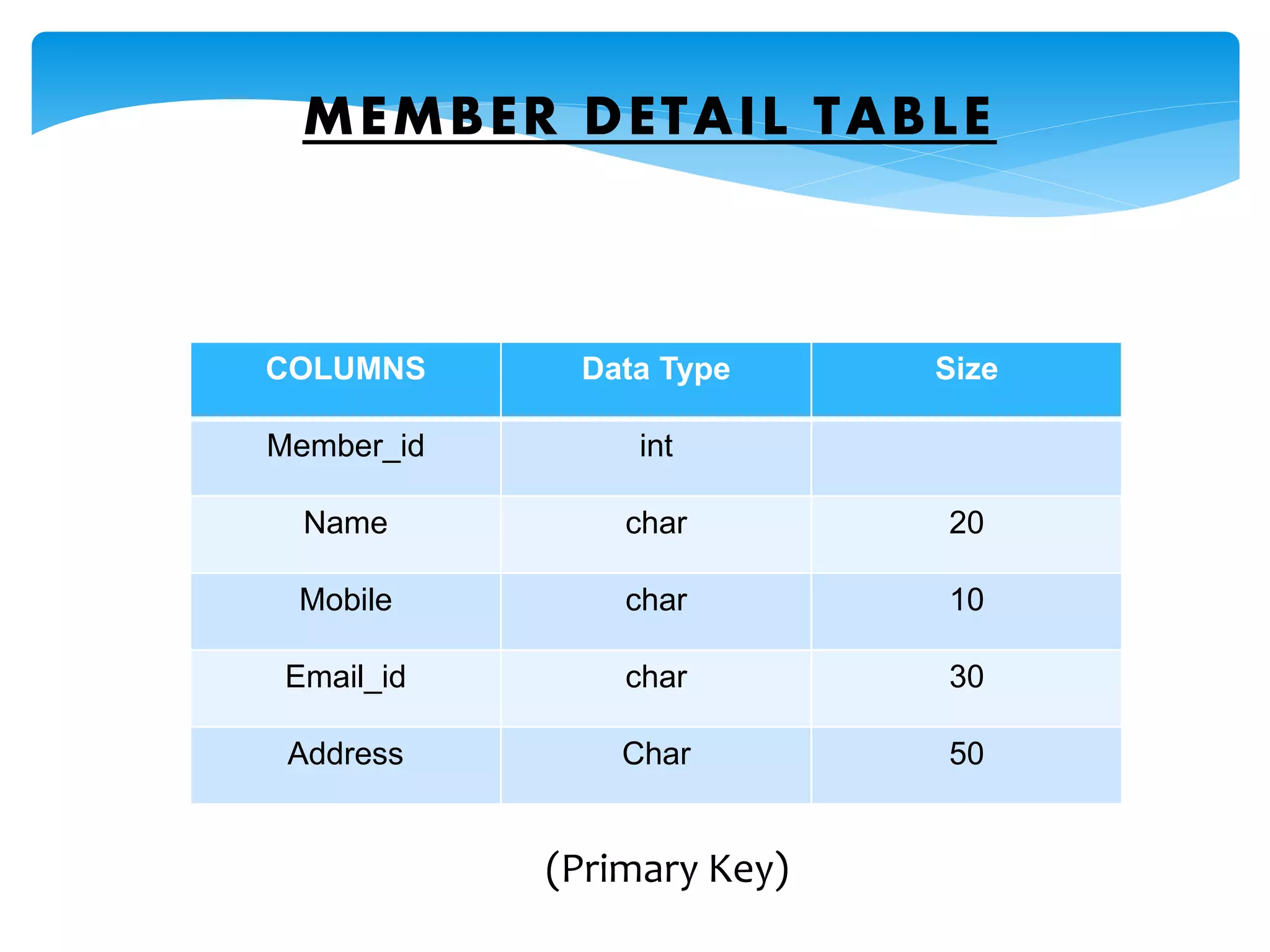
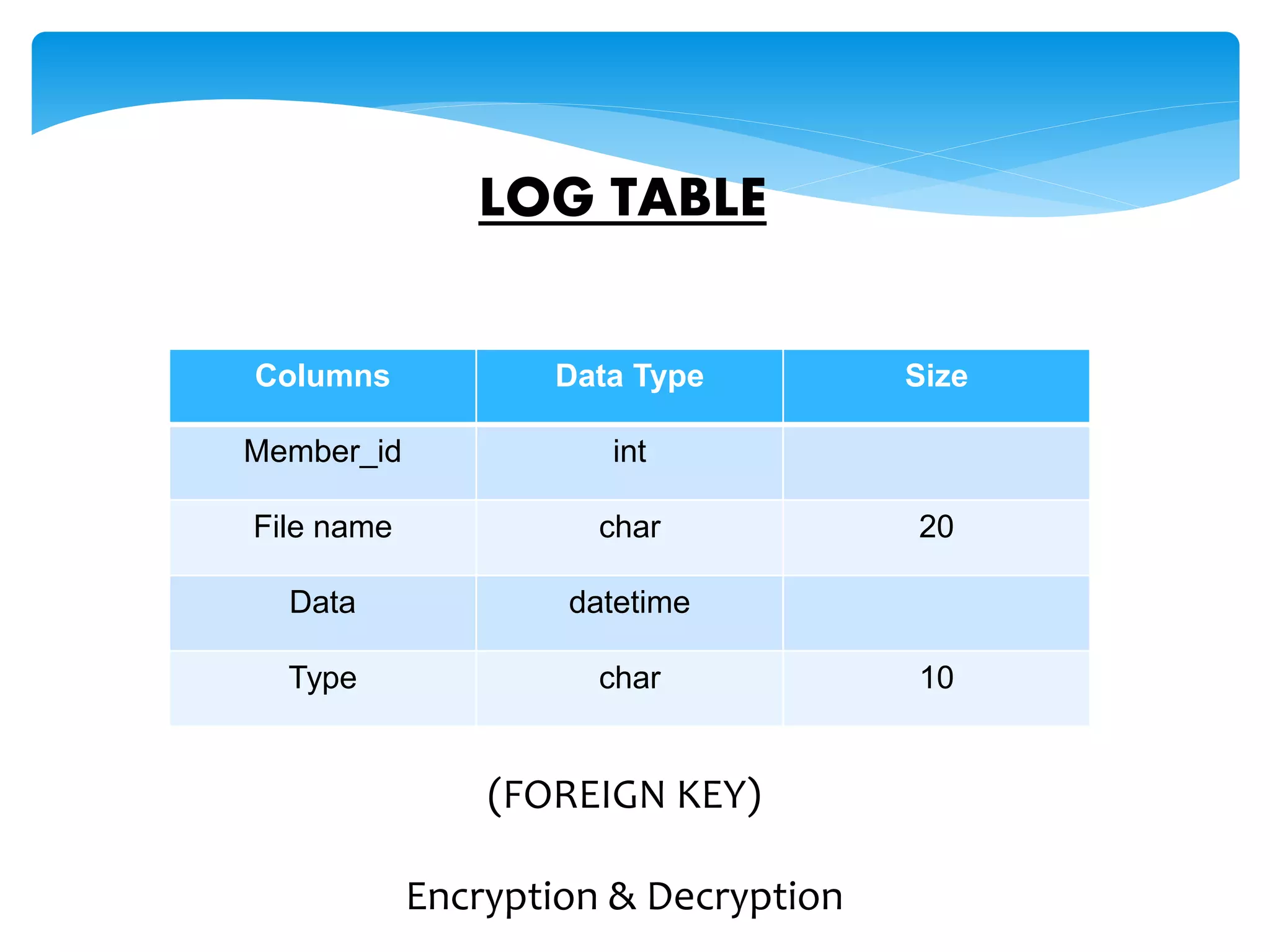
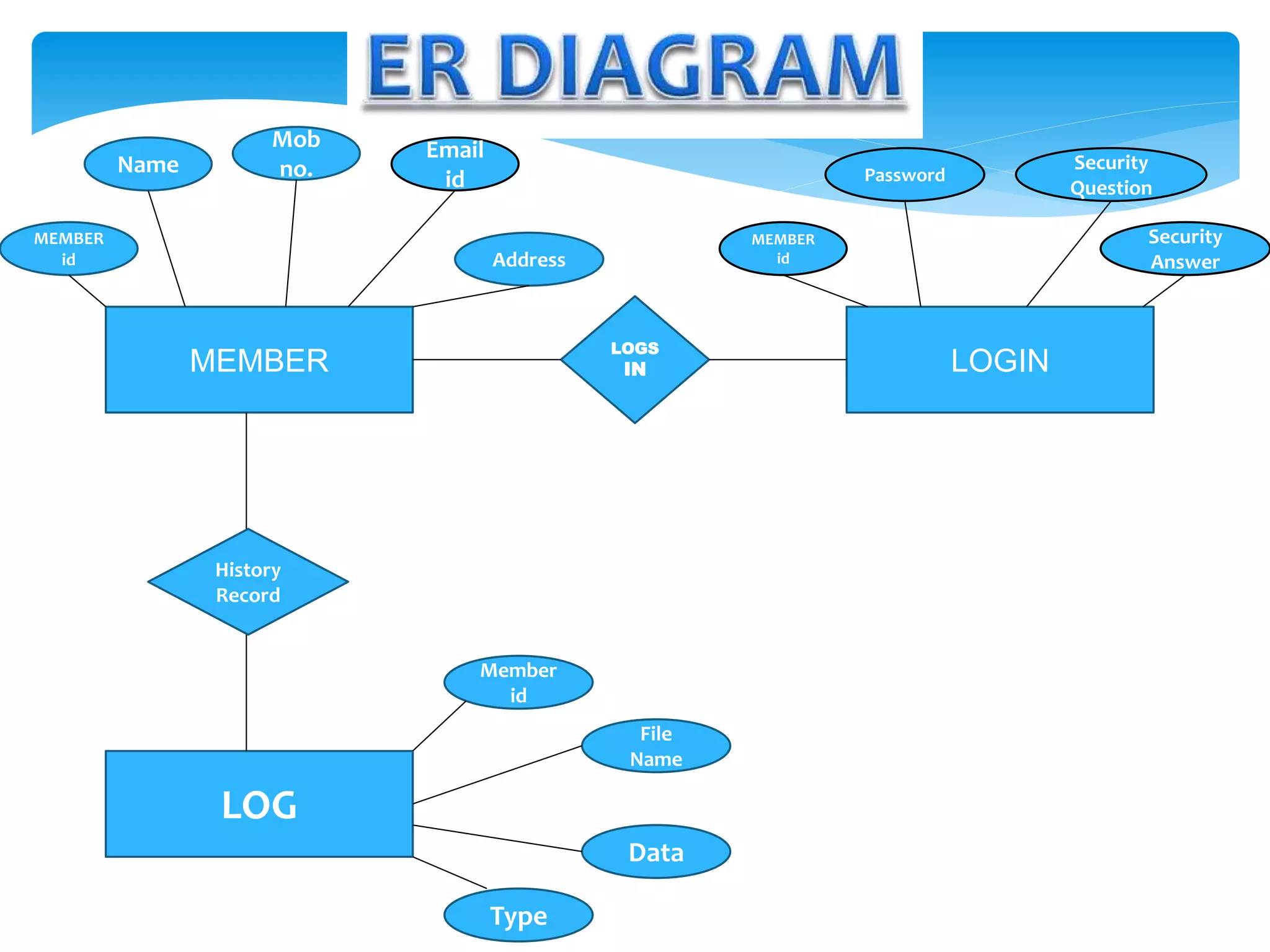
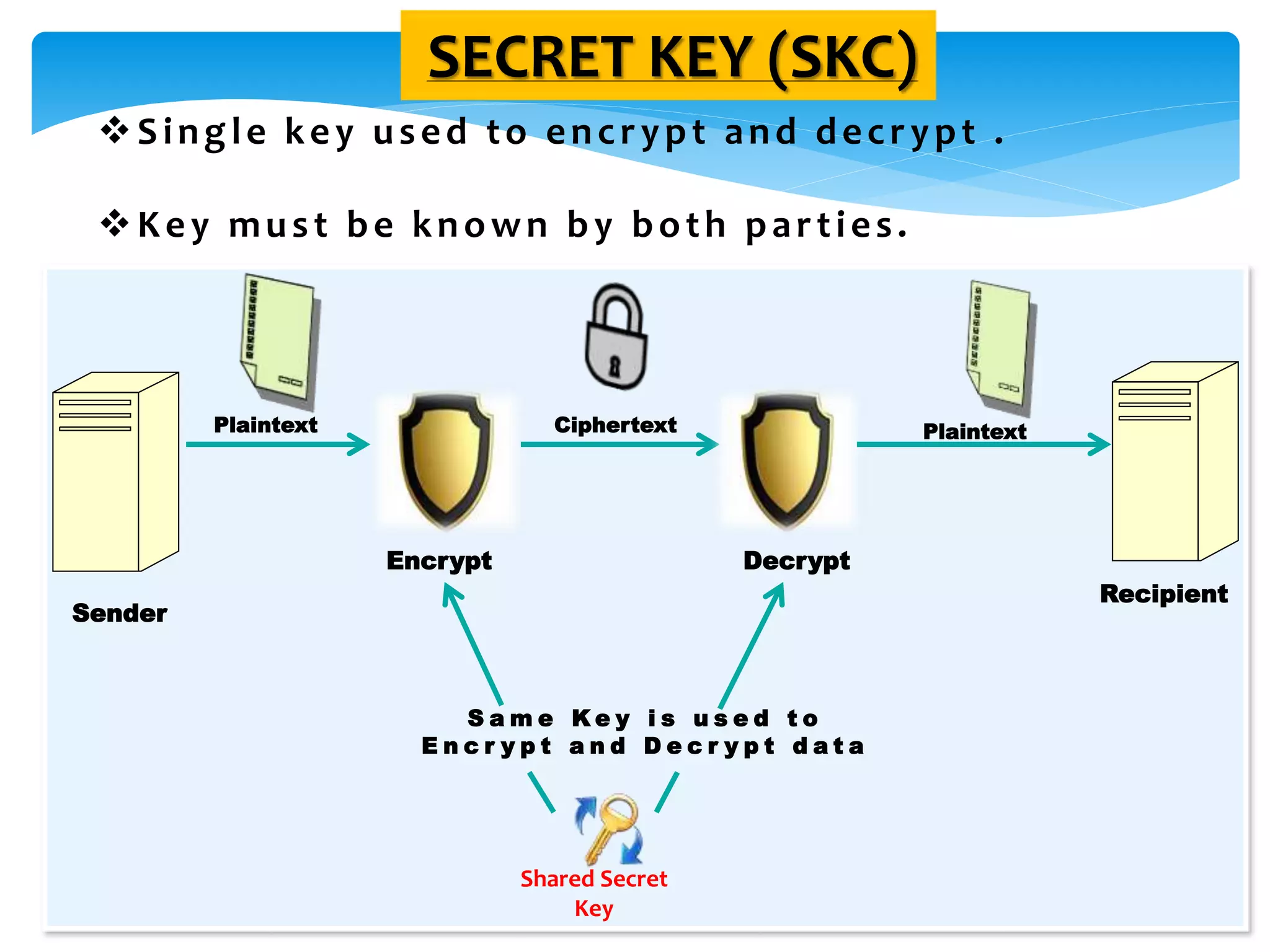
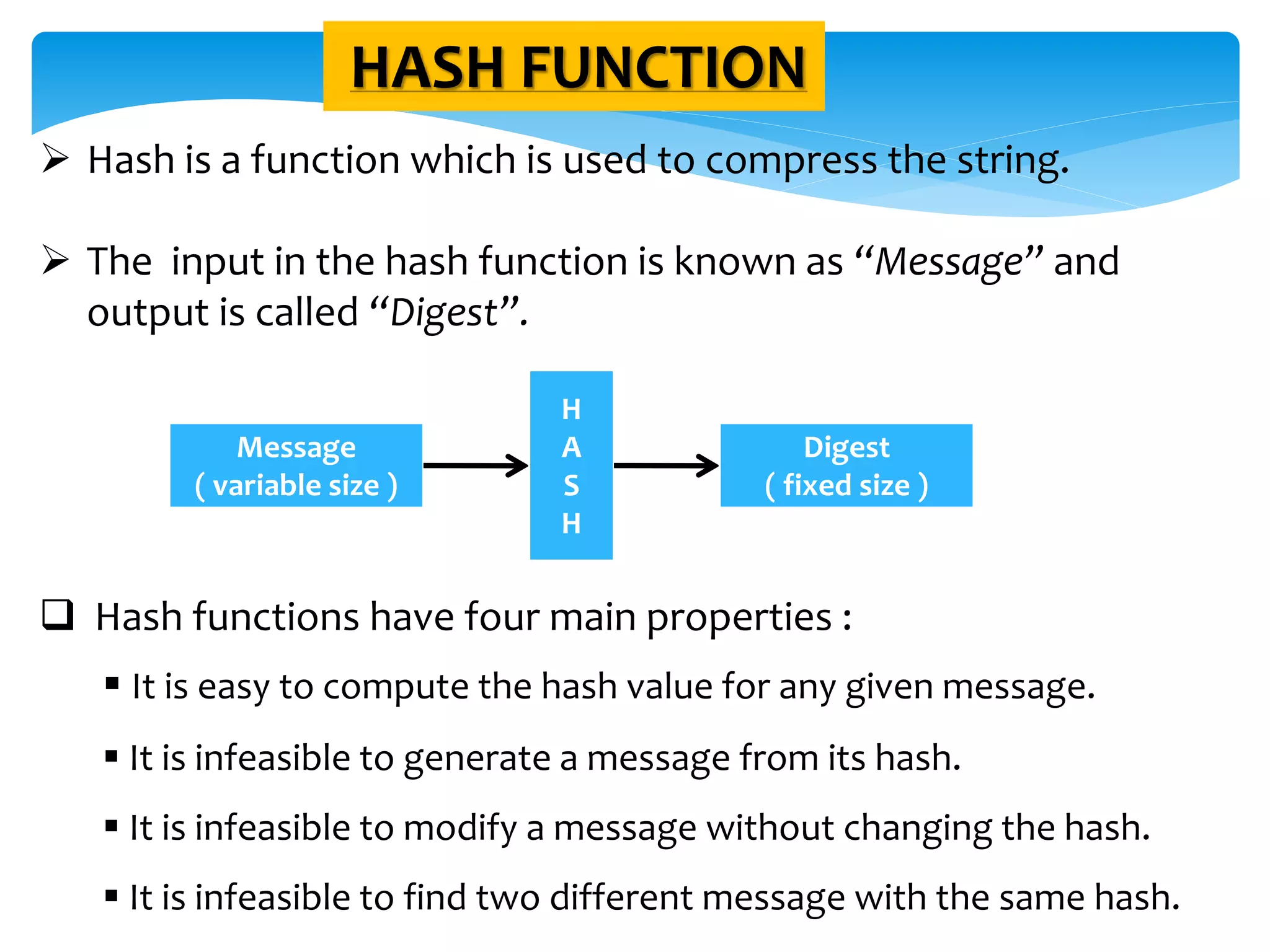
The document discusses the significance of cryptography in securing communication over networks, emphasizing its role in protecting sensitive data from unauthorized access or alteration. It outlines various encryption techniques, such as symmetric and asymmetric cryptography, and highlights key concepts like plaintext and ciphertext. The project aims to develop a software solution for encrypting and decrypting messages and files, ensuring secure data transfer among users.