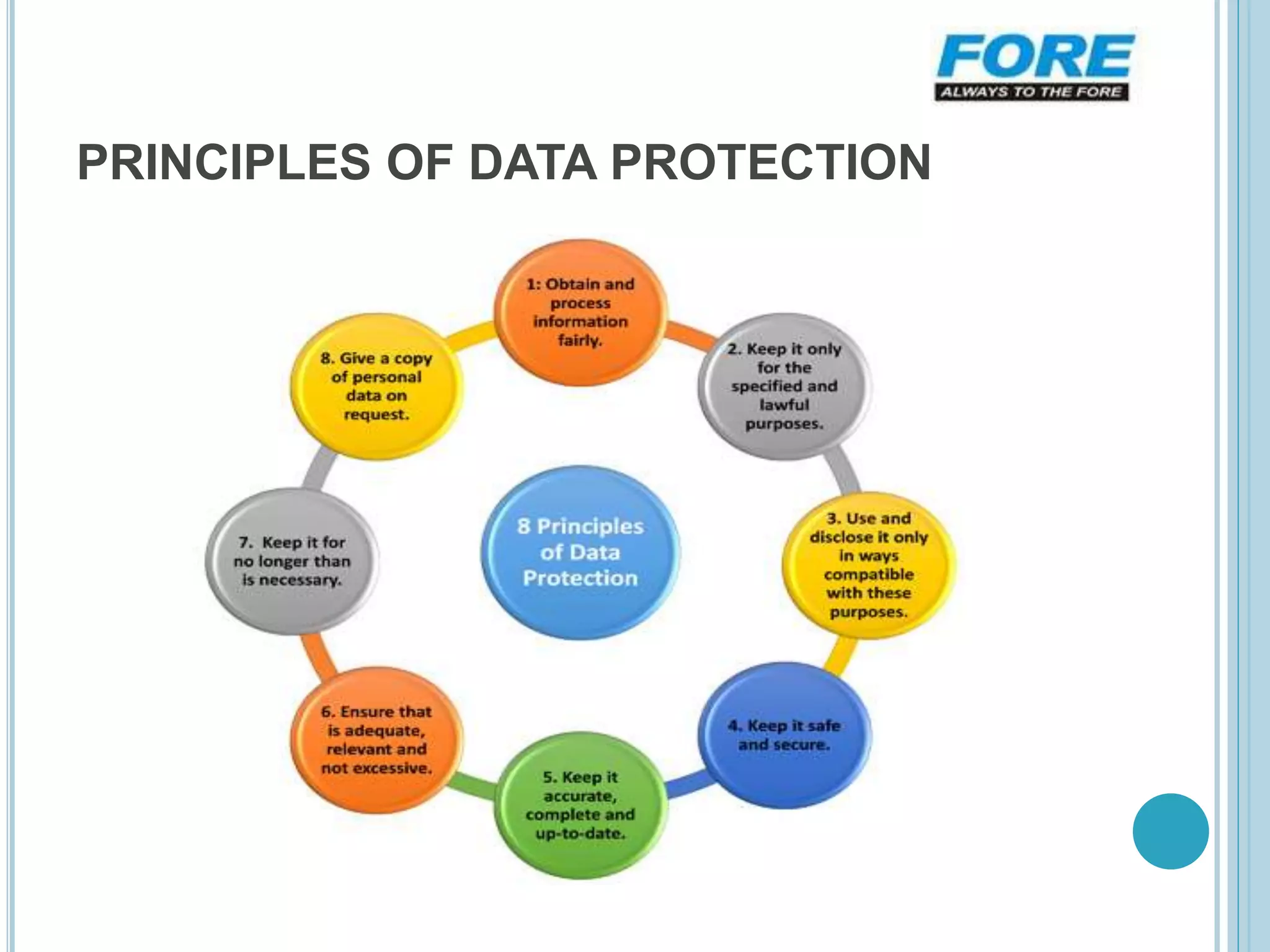
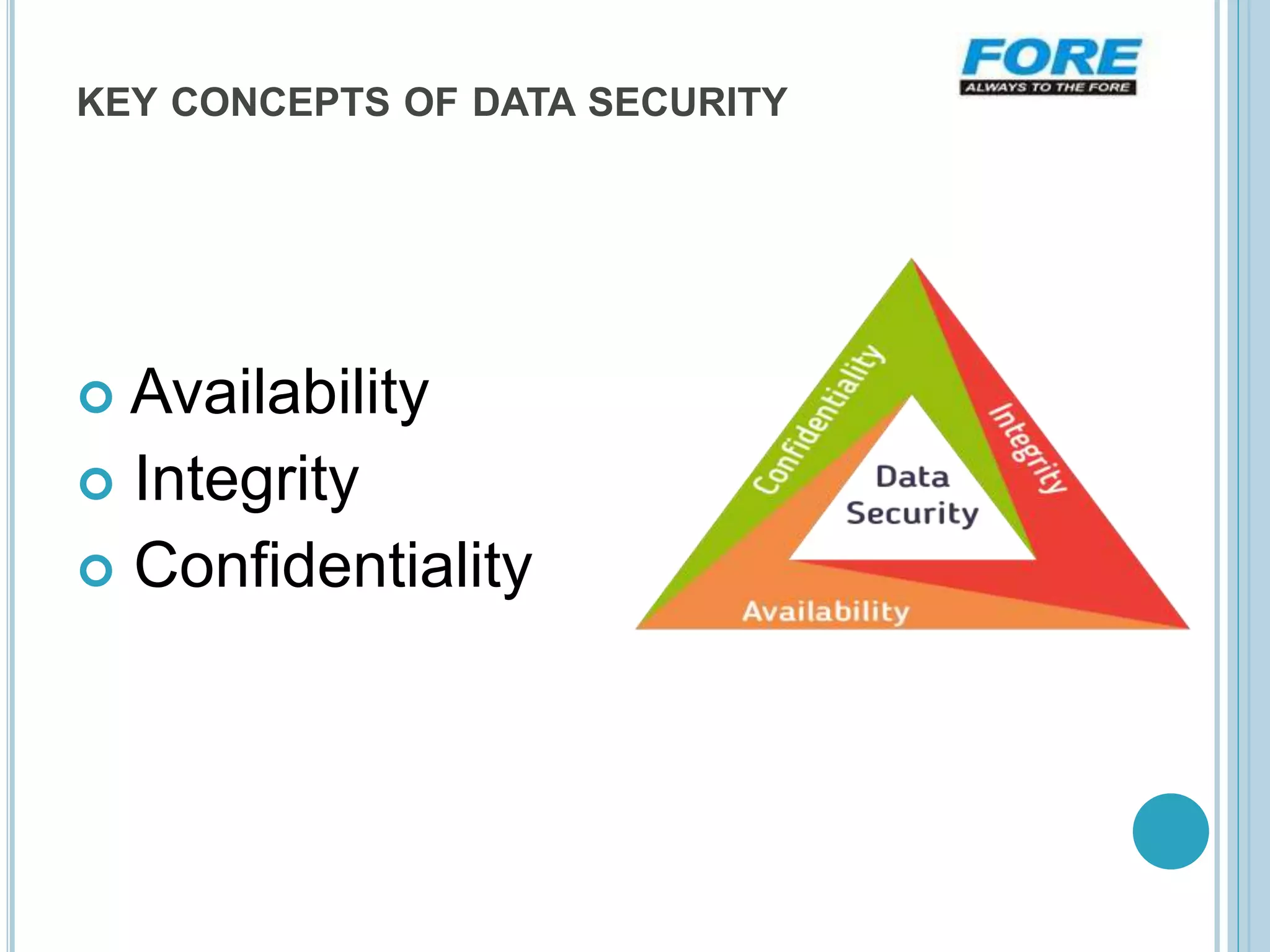
This document discusses the importance of data security. It introduces data as information stored in computers in binary format. Data can be transferred between devices via networks. The document emphasizes providing advanced email security, threat protection, data loss prevention, and endpoint protection to keep data secure. Data loss prevention ensures sensitive information is not sent outside a company's network without authorization. Key concepts of data security include availability, integrity, and confidentiality of data. Data should be accessible to authorized users, protected from unauthorized access and modification, and kept confidential to the intended recipients. Proper data security is crucial for businesses and individuals to protect sensitive information.