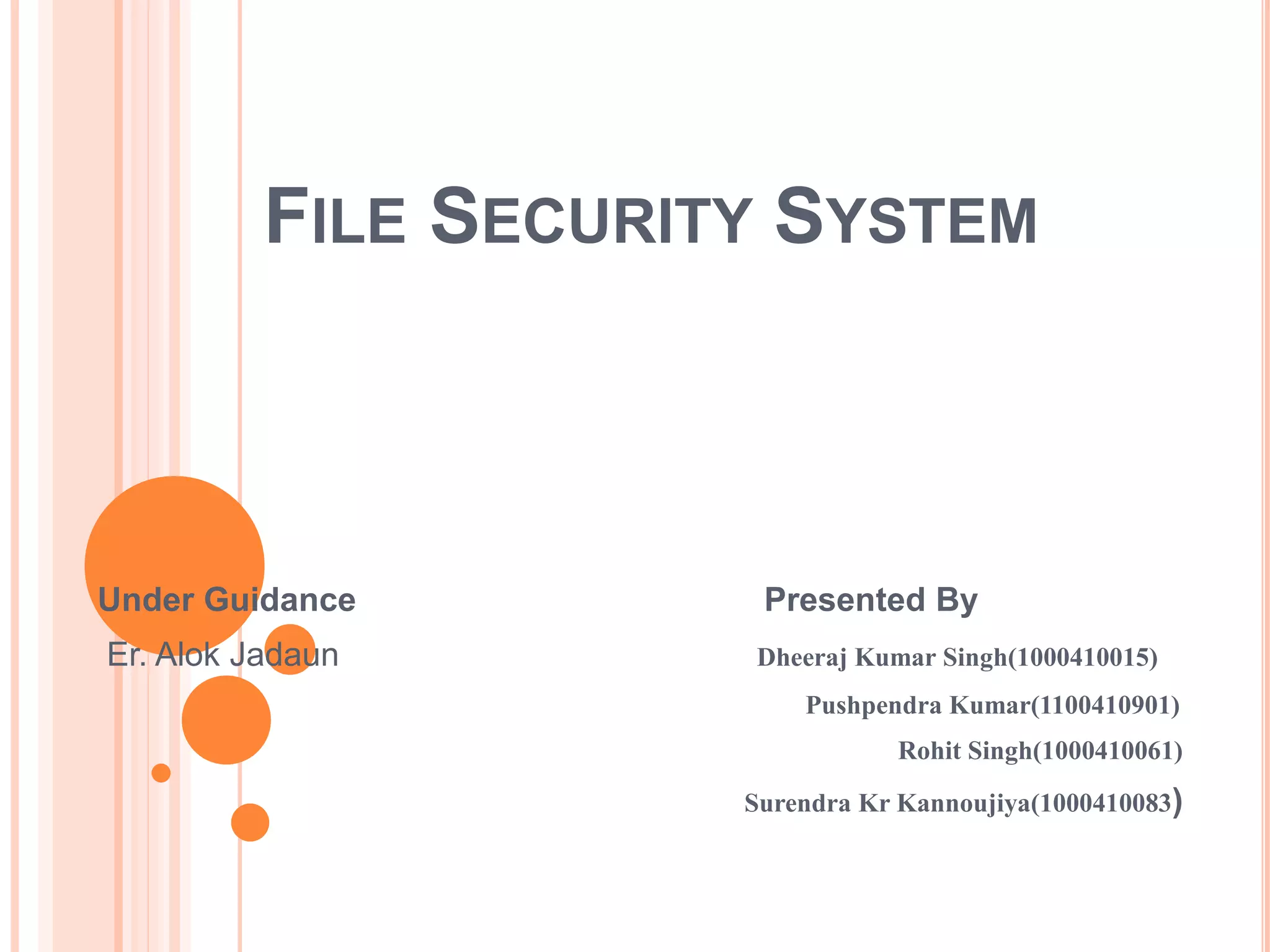
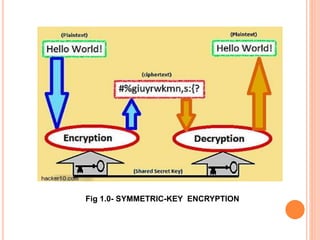
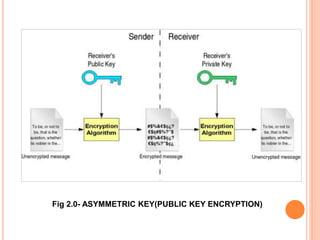
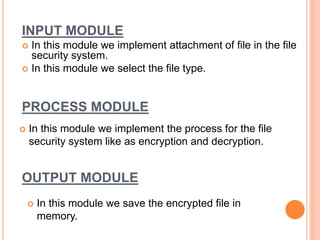
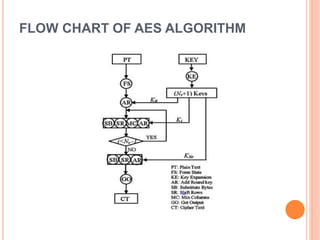
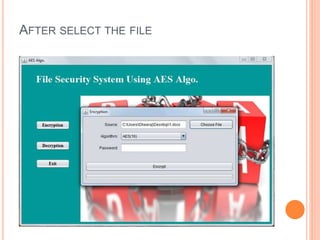
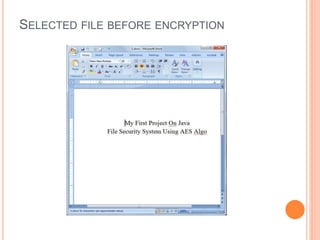
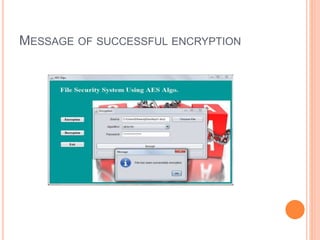
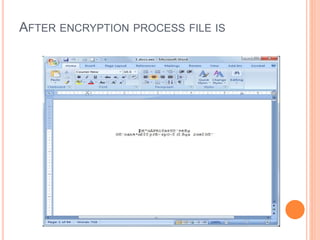
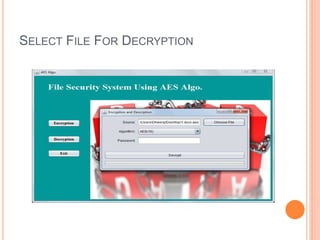
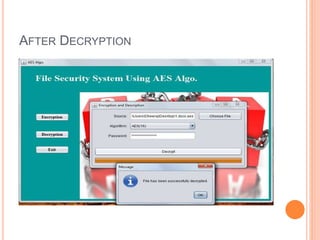
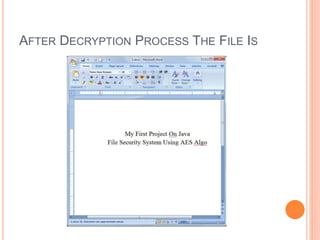
This document describes a file security system that uses encryption to secure files. It discusses the objectives of securing files from unauthorized users and maintaining confidentiality. The system uses encryption and decryption techniques, including symmetric-key and asymmetric-key encryption. It implements these techniques across three modules: input, process, and output. The system encrypts files using the AES encryption algorithm before outputting the encrypted file.













![REFERENCES
NVIDIA. High Performance Computing GPU
[EB/OL].(2010-01-09).
http://www.nvidia.cn/object/tesla_computing_solutio
ns_cn.html.
Sara Tedmori, Nijad Al-Najdawi ” Lossless Image
Cryptography Algorithm Based on Discrete Cosine
Transform” IAJIT First Online Publication
vol.3,2011.
Dariusz Stanislawek , “Free Software copyright
1997 - 2006 ”
http://members.ozemail.com.au/~nulifetv/freezip/fre
eware](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/57777d06-bd23-4cb8-8c4a-842a5abbb76a-150605161831-lva1-app6892/85/File-Security-System_2-29-320.jpg)

