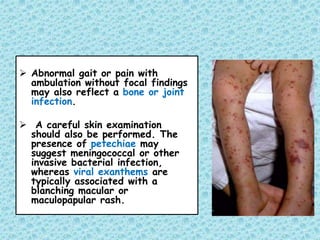
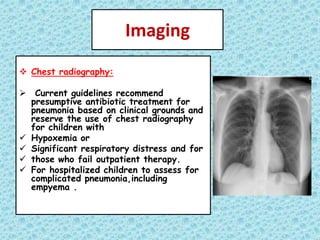
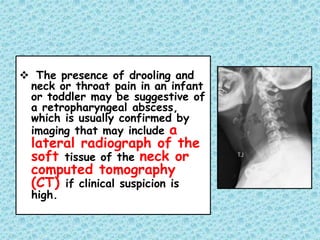
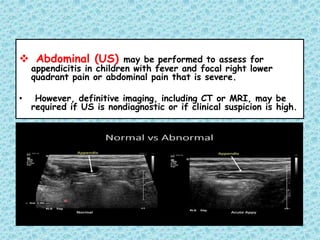
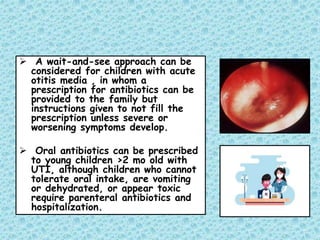
This document discusses fever without a focus in older children. It notes that while most fevers in children are due to benign viral infections, some may be caused by more serious bacterial infections. A thorough history, physical exam, and diagnostic testing when indicated can help establish the cause. Common viral infections include respiratory and gastrointestinal viruses. Potential bacterial infections include otitis media, strep throat, and urinary tract infections. Occult bacteremia must also be considered. Treatment involves supportive care for viral infections and antibiotics only for confirmed or suspected bacterial infections.