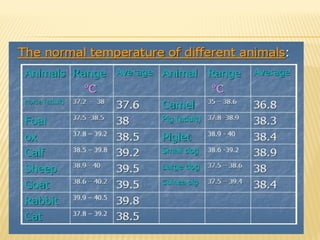
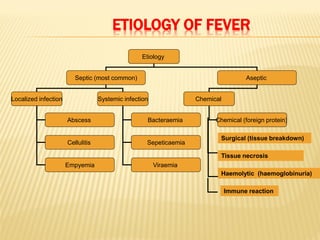
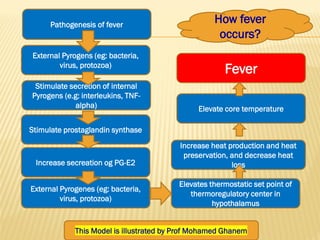
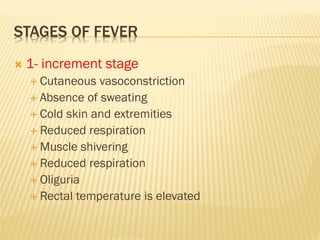
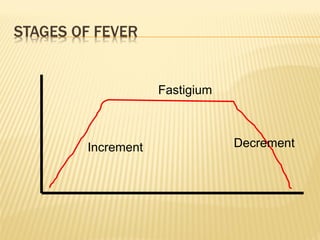
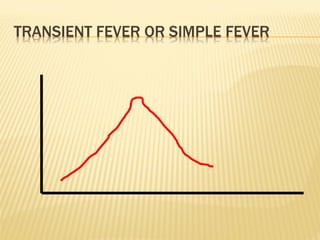
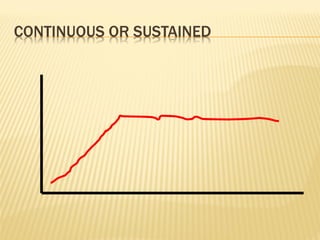
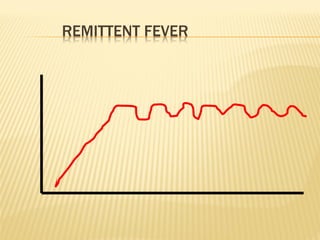
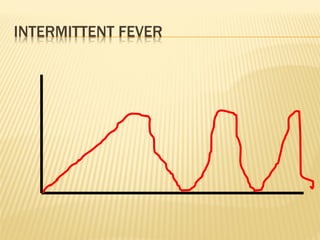
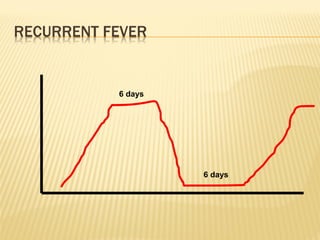
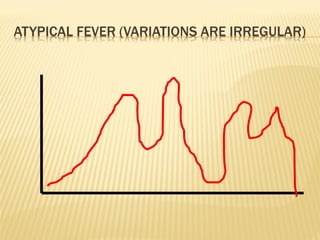
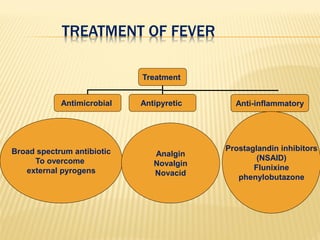
This document discusses fever (pyrexia), including its etiology, pathogenesis, stages, clinical findings, forms, and treatment. It explains that fever is caused by external pyrogens like bacteria and viruses stimulating the production of internal pyrogens like interleukins and TNF-alpha by the body. These internal pyrogens elevate the hypothalamus' thermoregulatory set point, increasing heat production and conservation to raise core body temperature. Fever progresses through increment, fastigium, and decrement stages. Treatment involves antimicrobials to combat external pyrogens, antipyretics like NSAIDs to inhibit prostaglandin synthesis and reduce the fever, and anti-inflammatories.