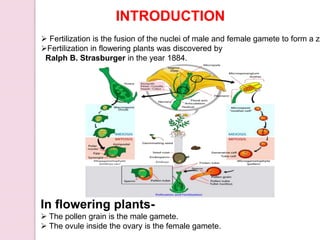
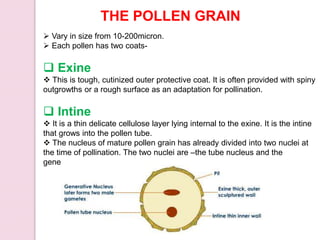
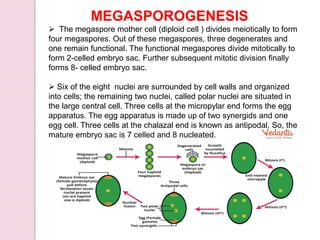
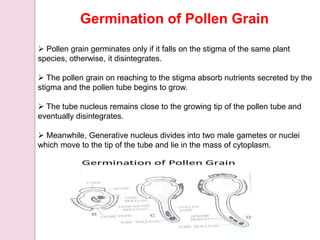
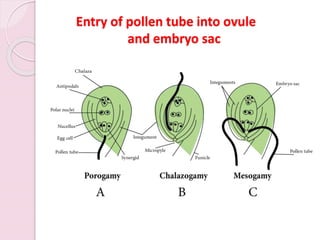
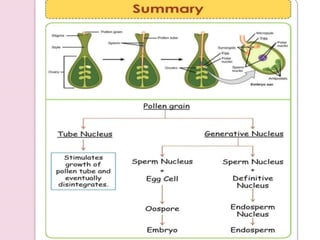
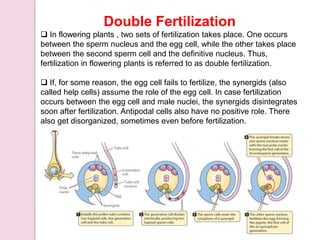
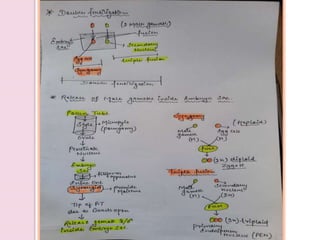
Fertilization in flowering plants involves a double fertilization process. The pollen grain contains two sperm cells that travel down the pollen tube. One sperm cell fertilizes the egg cell to form a zygote, while the second sperm cell fertilizes the two polar nuclei to form the endosperm. This double fertilization results in the formation of an embryo from the zygote and endosperm to nourish the developing seed. The ovary then develops into a fruit containing one or more seeds formed from the fertilized ovules.