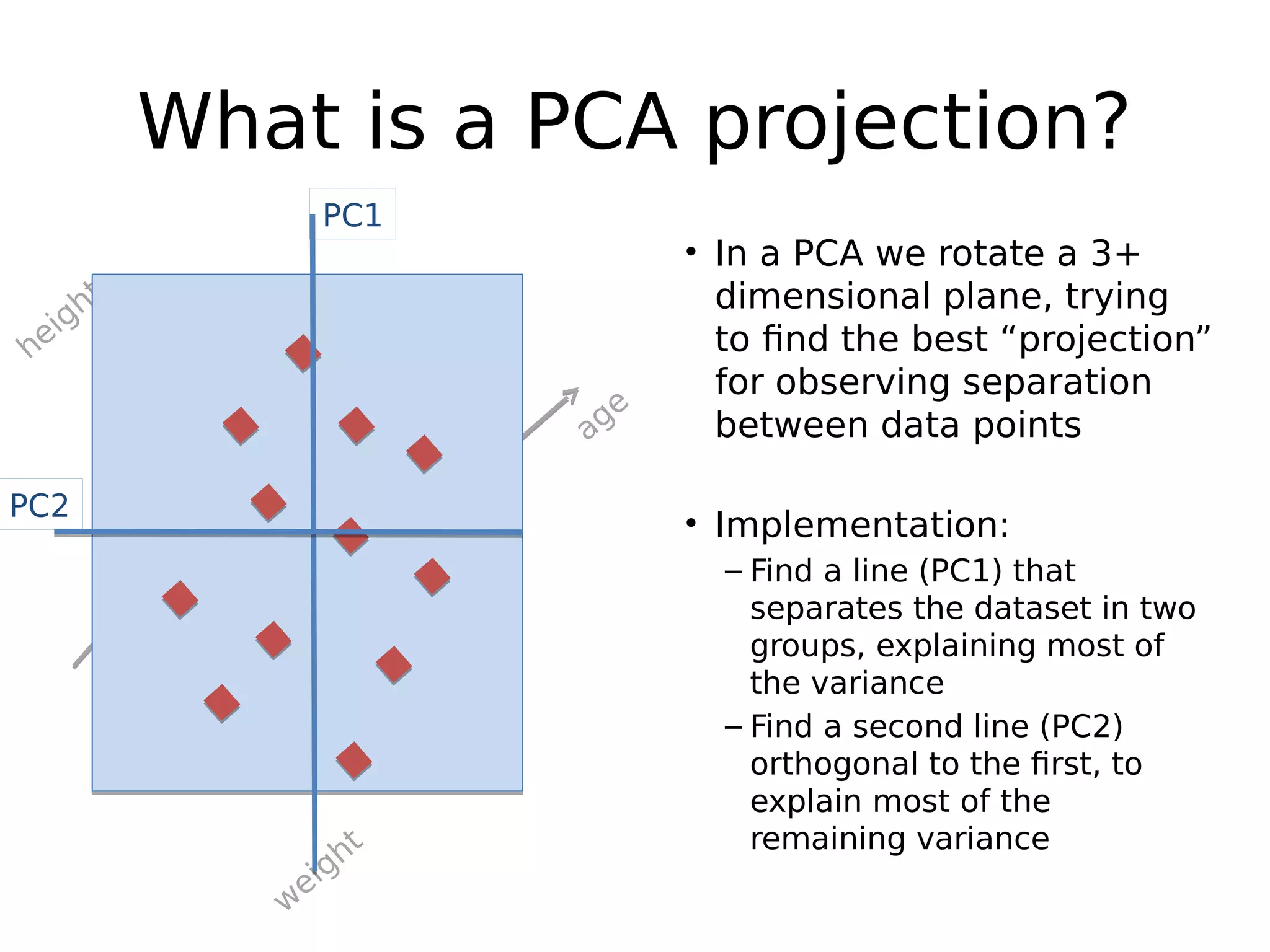
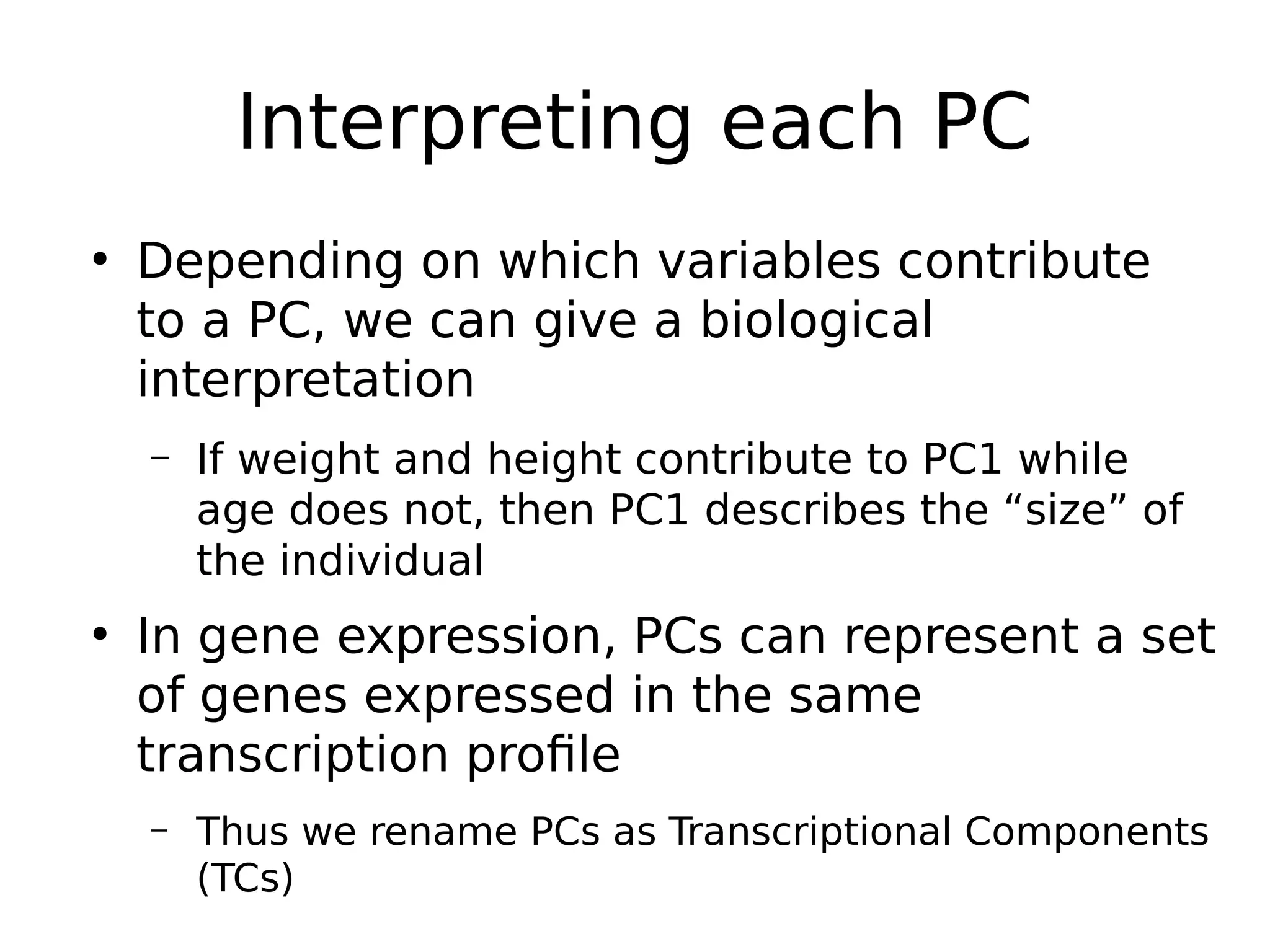
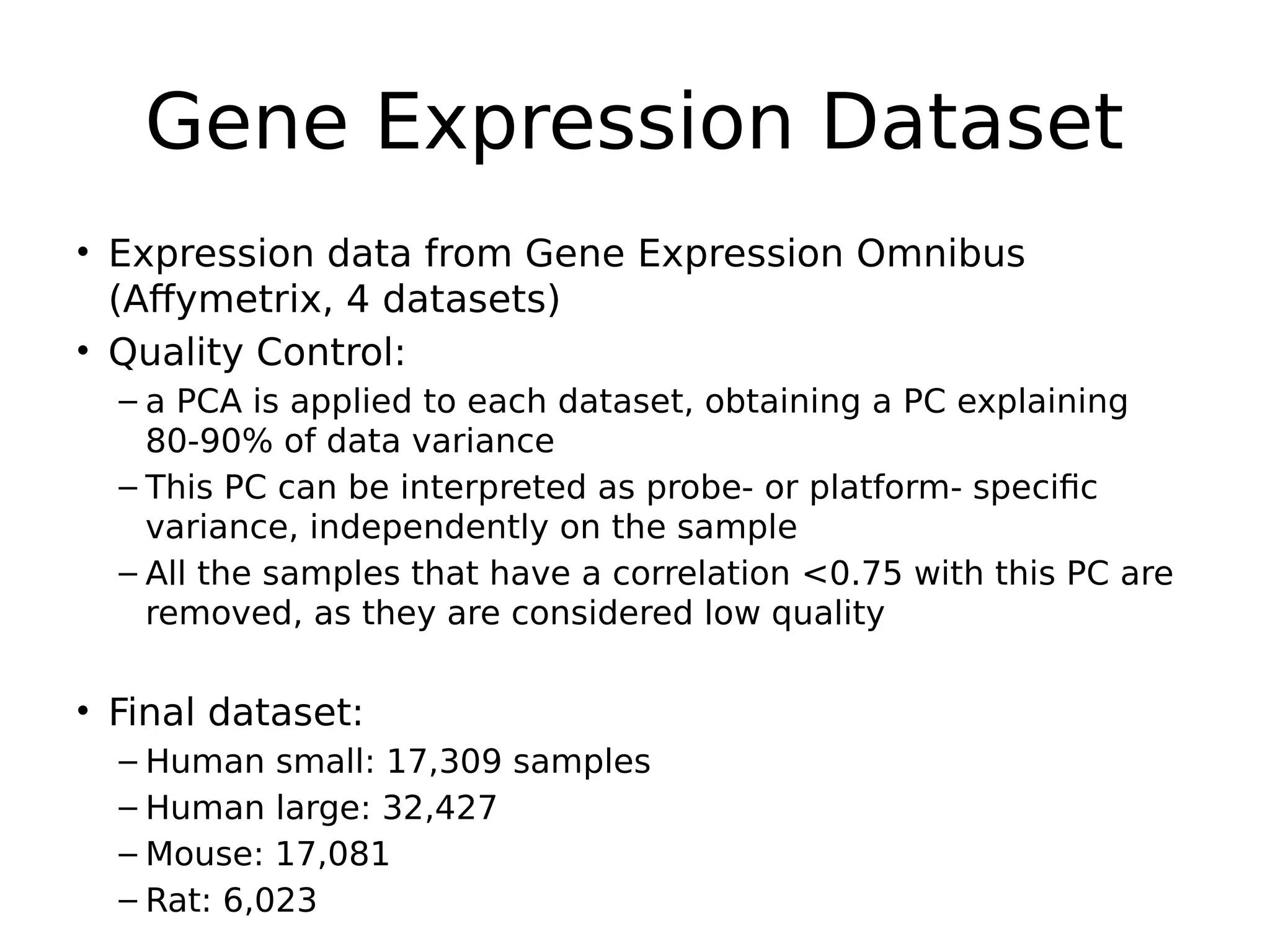
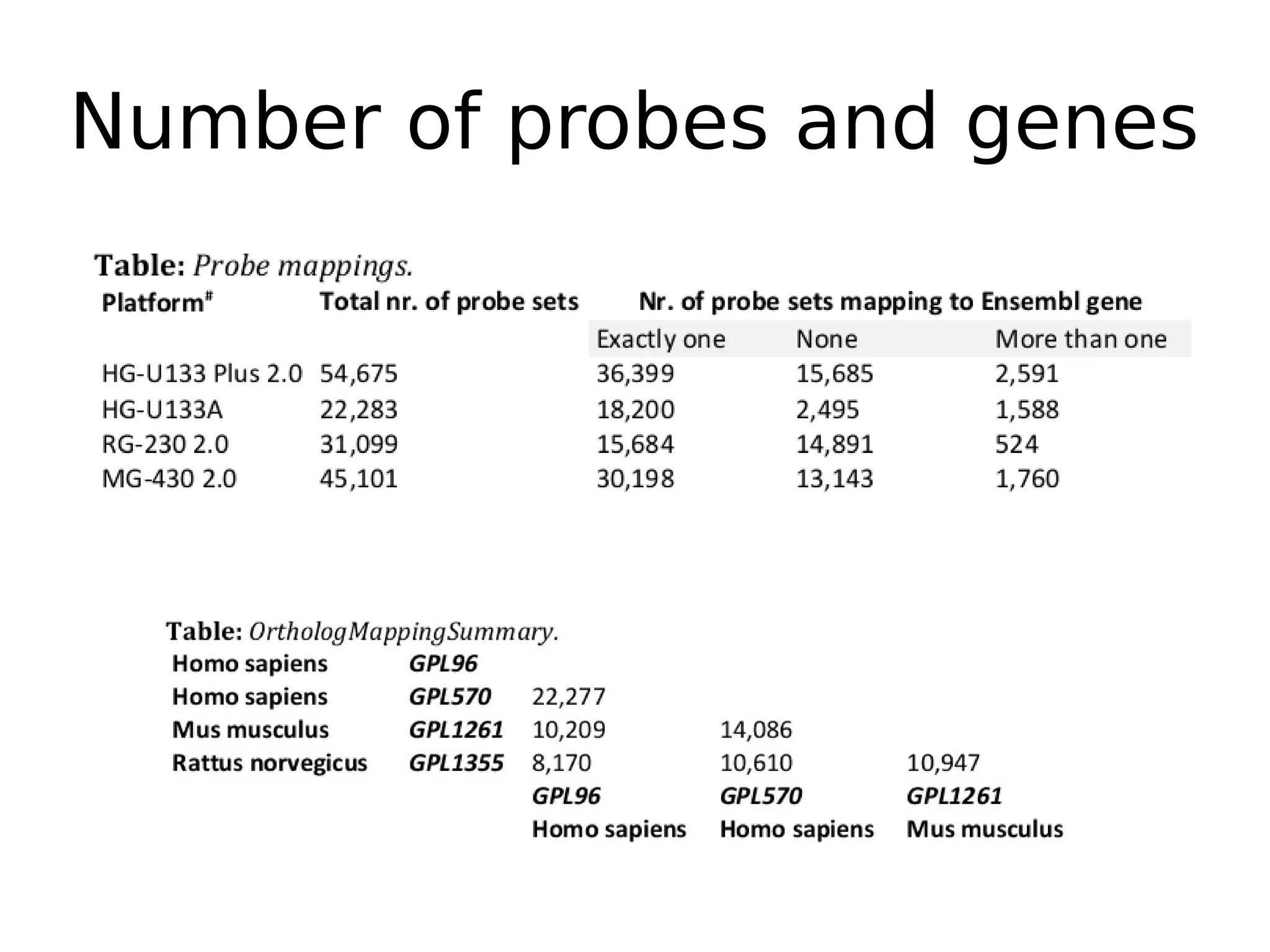
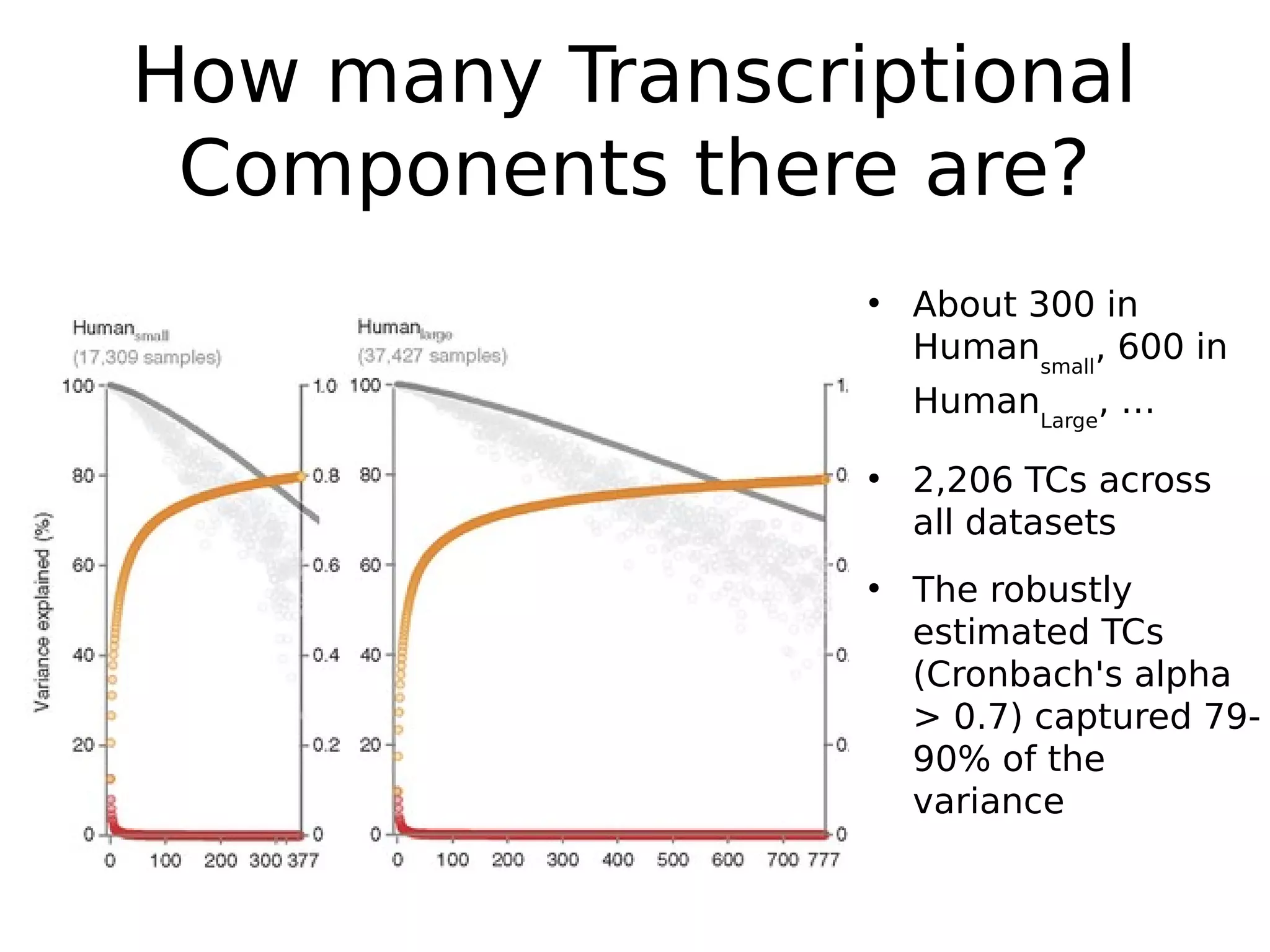
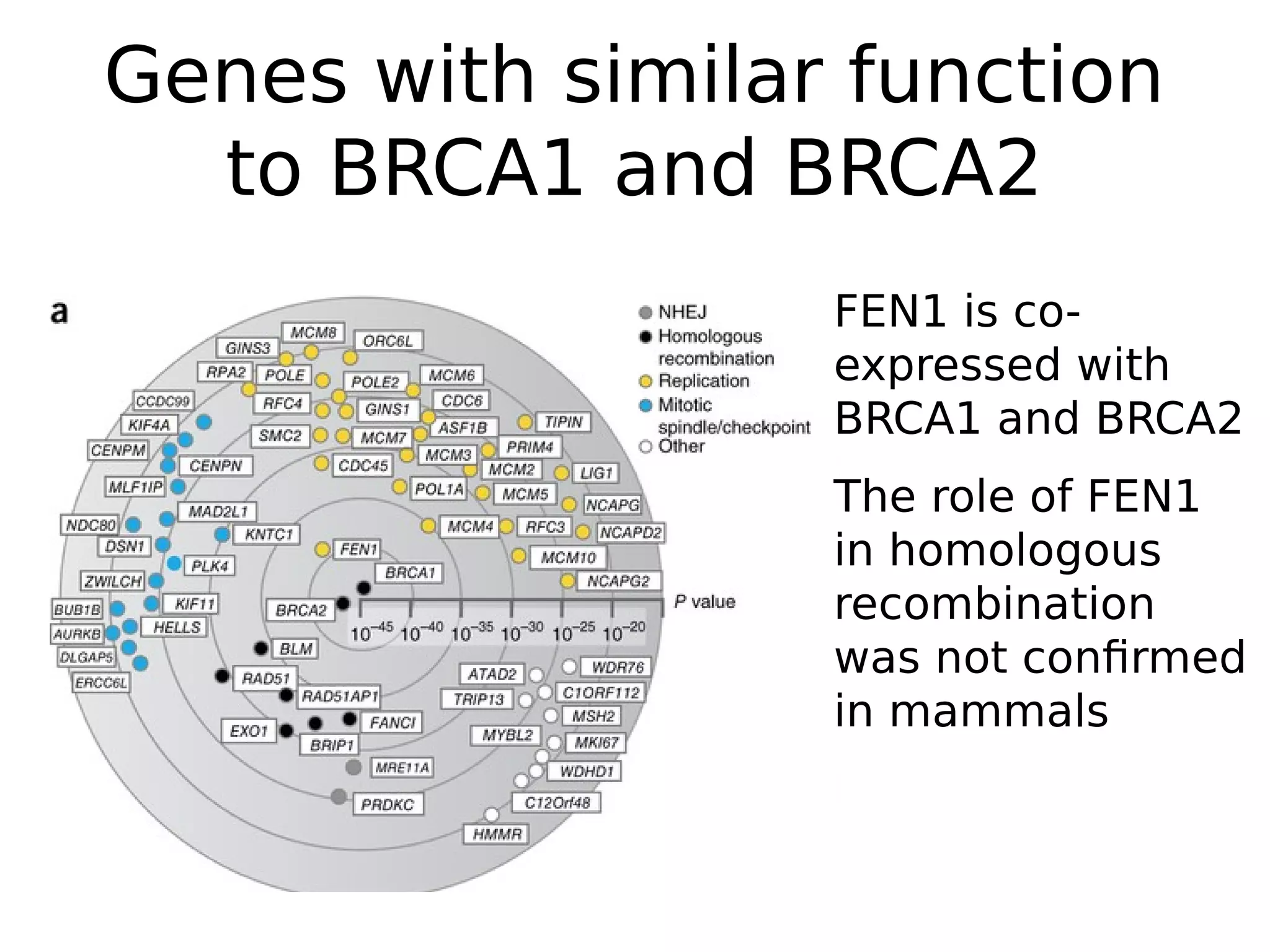
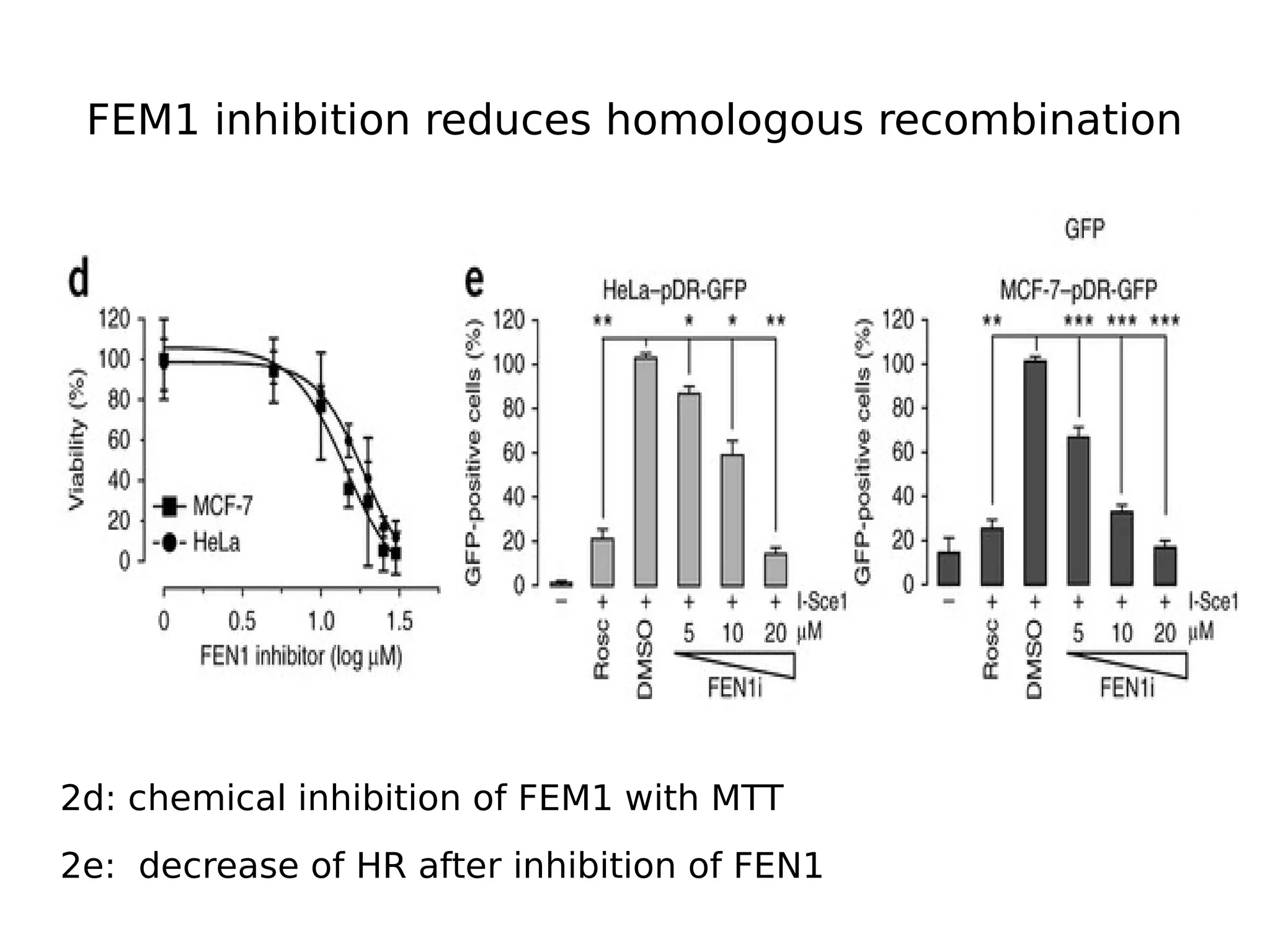
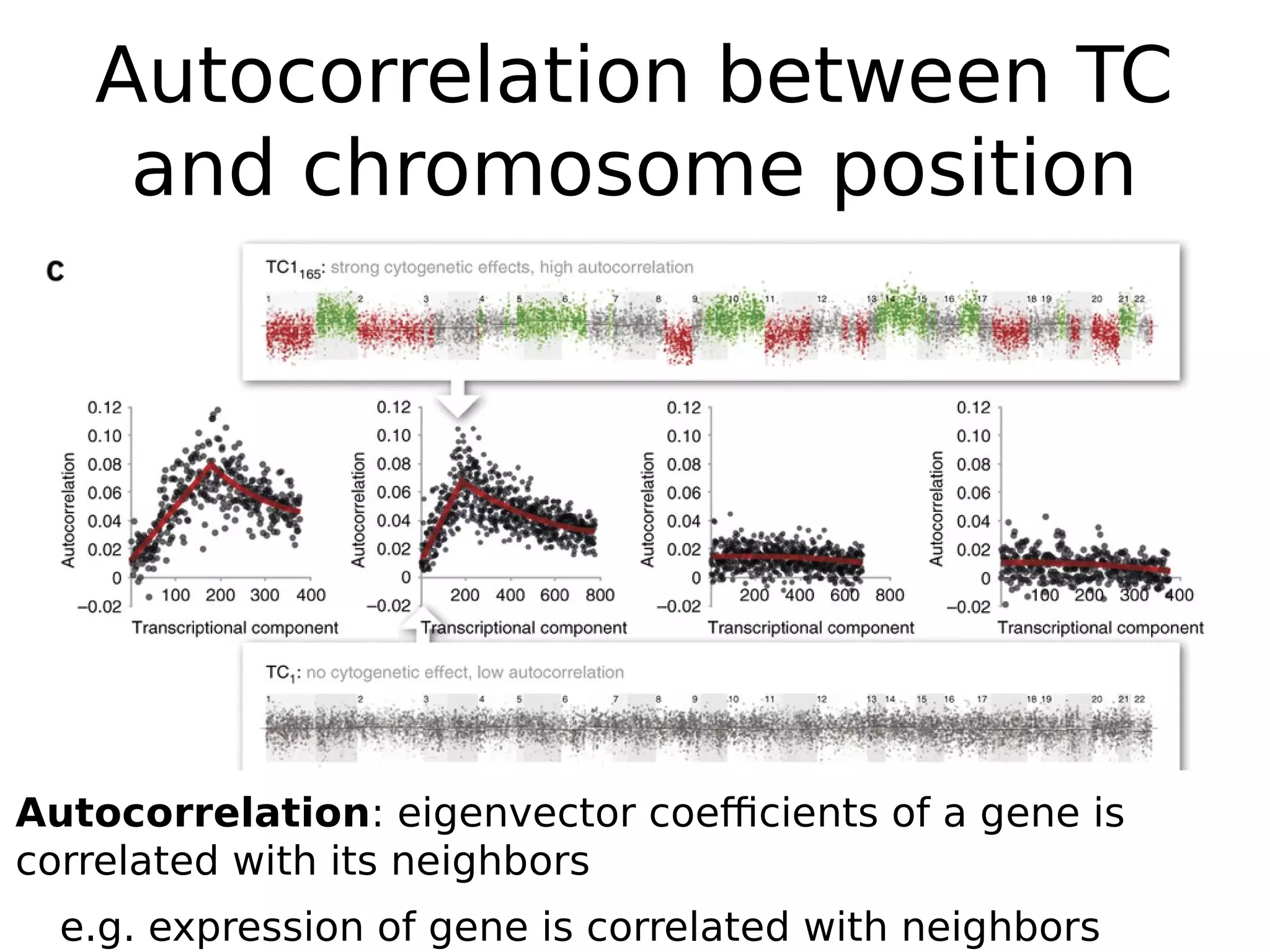
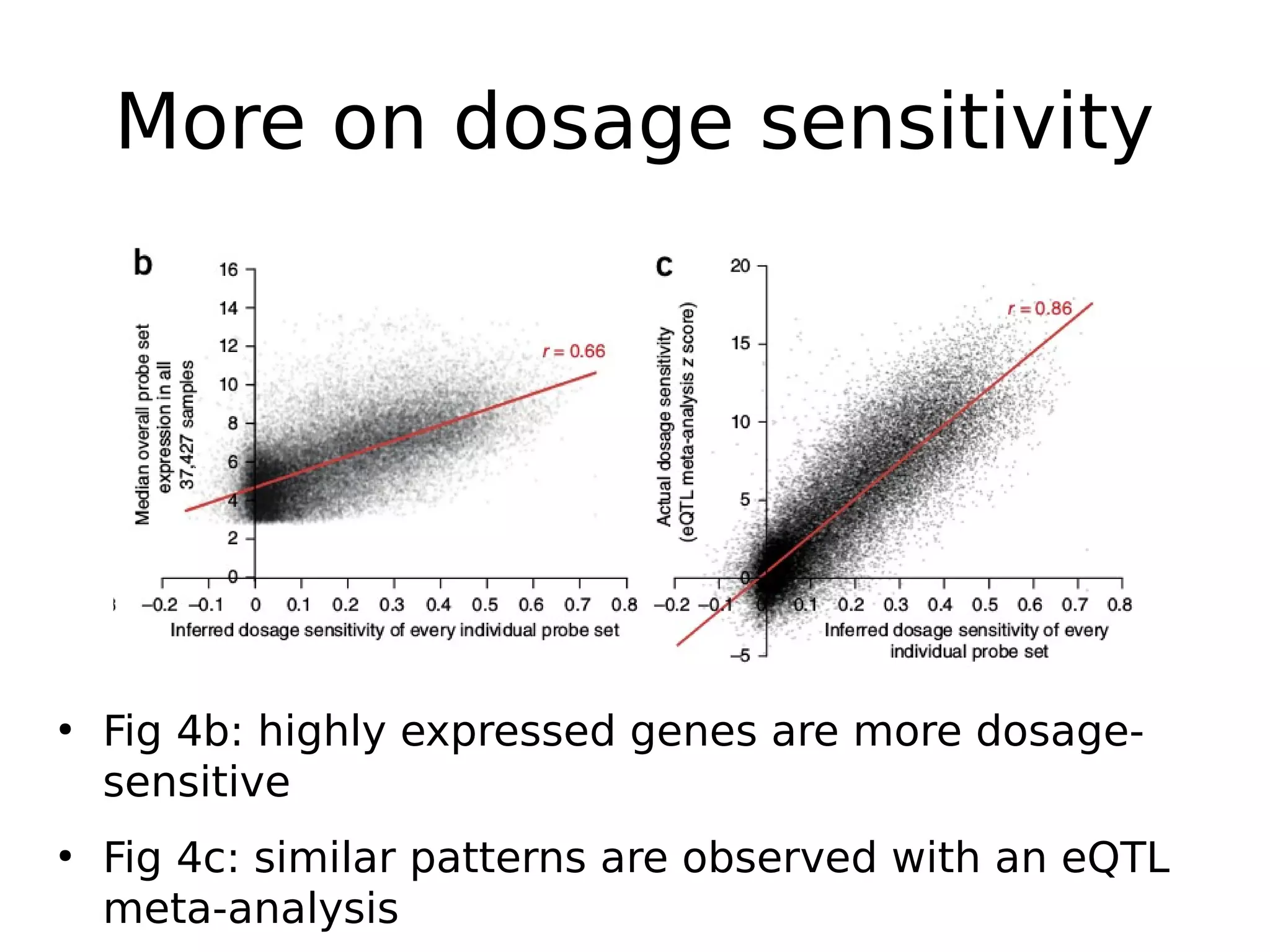
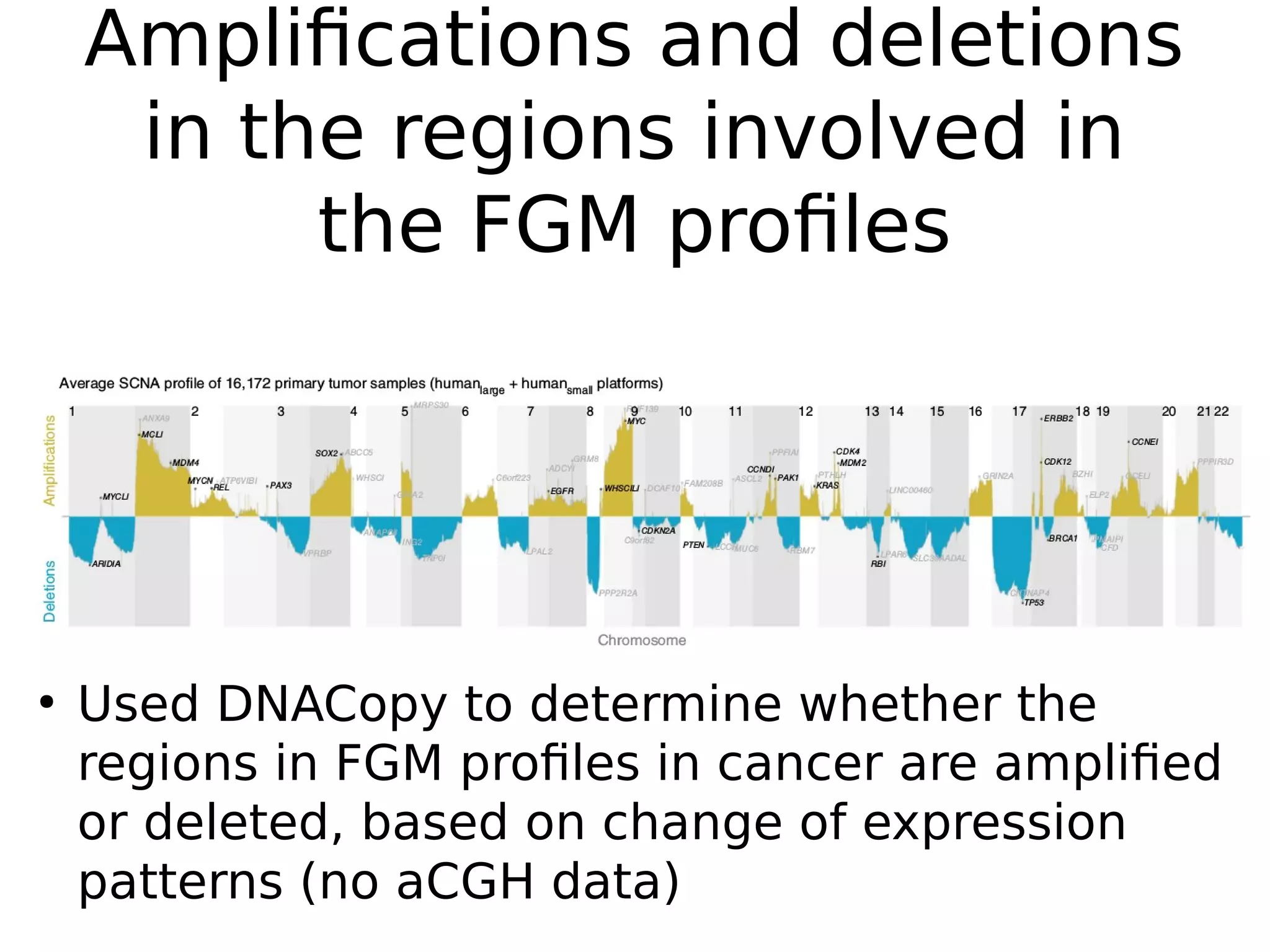
The document discusses a study that uses PCA to analyze gene expression data across various datasets, identifying 2,206 transcriptional components, with 718 representing physiological non-genetic profiles. It highlights the correlation between gene expression variations and structural genomic alterations (SCNAs) in cancer, revealing that most genes are dosage-sensitive to chromosome arm duplications or deletions. Additionally, the research emphasizes the importance of gene regulation networks and their potential for predicting gene functions based on co-expression with other genes.