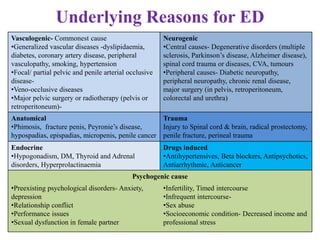
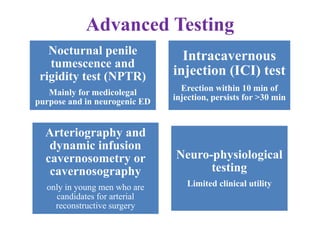
Dr. Sujoy Dasgupta, a gold medalist with extensive qualifications, provides a comprehensive overview of erectile dysfunction (ED), detailing its causes, evaluation, and treatment options. The document discusses various underlying factors contributing to ED, including psychological, physical, and pharmacological causes, as well as diagnostic tools like the International Index of Erectile Function questionnaire. Furthermore, it outlines a range of treatments from lifestyle changes and medications to advanced procedures such as penile implants, highlighting the need for tailored approaches in managing ED.