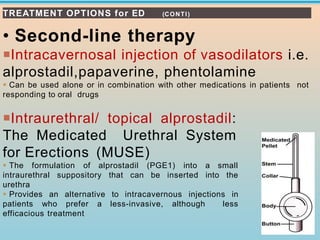
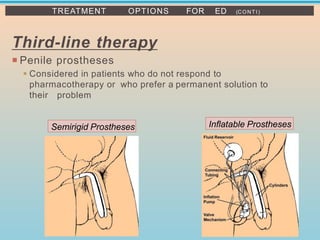
1. The document discusses erectile dysfunction (ED), including its anatomy, physiology, etiology, evaluation, and treatment. It defines ED and describes the neurovascular processes underlying erection.
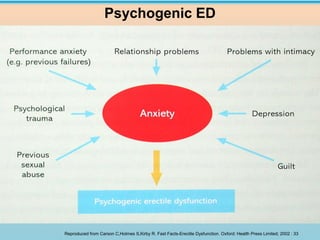
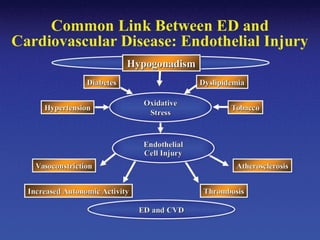
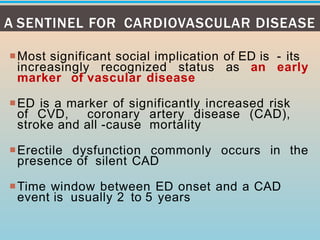
2. Common organic, psychogenic, and mixed causes of ED are outlined. Evaluation involves history, physical exam, and investigations.
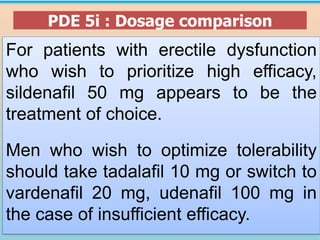
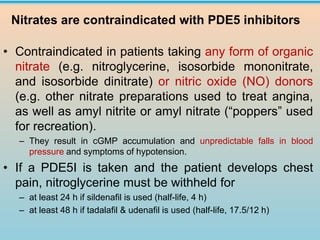
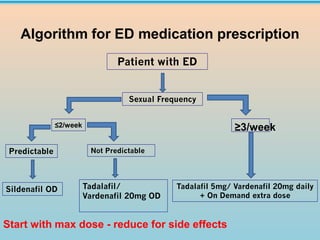
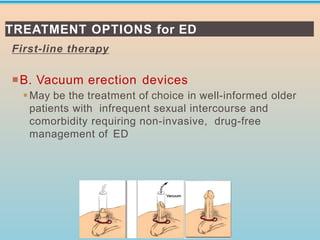
3. Treatment options discussed include lifestyle modifications and first-line oral phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors like sildenafil, tadalafil, and vardenafil. Guidelines on their use and dosing are provided.









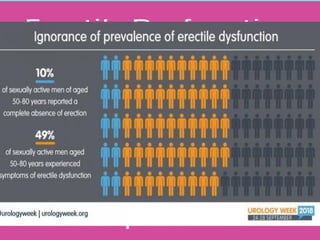
![• Several studies accessed the prevalence of ED. The
Massachusetts Male Aging Study reported a prevalence of 52%
[1].
• The study demonstrated that ED is increasingly prevalent with
age: approximately 40% of men are affected at age 40 and
nearly 70% of men are affected at age 70.
• The prevalence of complete ED increased from 5% at age 40 to
15% at age 70 [2].
1. Feldman HA et al. Impotence and its medical and psychosocial correlates: Results of the Massachusetts Male Aging Study. J Urol 1994; 151:54–61.
2. Johannes CB et al. Incidence of erectile dysfunction in men 40 to 69 years old: Longitudinal results from the Massachusetts Male Aging Study. J Urol 2000; 163:460–463.
Prevalence](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/edeavualtionmx-drselim-210225163720/85/Erectile-Dysfunction-Evaluation-and-Management-by-Dr-Shahjada-Selim-15-320.jpg)


![Treatment
Lifestyle Modification
Erectile dysfunction is known to be associated with
general health status, thus, lifestyle modification
improves erectile function and decreases the rate of
decline of function with aging.
✓ One year after discontinuation of smoking, patients
were found to have a 25% improvement in erectile
quality [1].
✓ In addition, multivariate analysis found obesity is
associated with erectile dysfunction with an
approximately 50% increase in ED in obese men as
compared with normal weight men [2].
1. Pourmand G, Alidaee MR, Rasuli S, Maleki A, Mehrsai A. Do cigarette smokers with erectile dysfunction benefit from stopping?: A prospective study. BJU Int 2004; 94:1310–1313).
2.. Janiszewski PM, Janssen I, Ross R. Abdominal obesity and physical inactivity are associated with erectile dysfunction independent of body mass index. J Sex Med 2009; 6:1990–1998](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/edeavualtionmx-drselim-210225163720/85/Erectile-Dysfunction-Evaluation-and-Management-by-Dr-Shahjada-Selim-22-320.jpg)
![Treatment
….Lifestyle Modification
✓ Little evidence supports that increased physical activity alone
improves erectile quality; however, the strong association
between physical activity and lower BMI is well described, and
therefore recommended for men with erectile dysfunction and
without a contraindication to physical activity.
✓ The Massachusetts Male Aging Study demonstrated
increased risk of ED among heavy alcohol users though the
impact of alcohol use on erection quality is not well
understood [3].
3 Feldman HA, Goldstein I, Hatzichristou DG, Krane RJ, McKinlay JB. Impotence and its medical and psychosocial correlates: Results of the Massachusetts Male Aging Study. J Urol 1994; 151:54–61.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/edeavualtionmx-drselim-210225163720/85/Erectile-Dysfunction-Evaluation-and-Management-by-Dr-Shahjada-Selim-23-320.jpg)