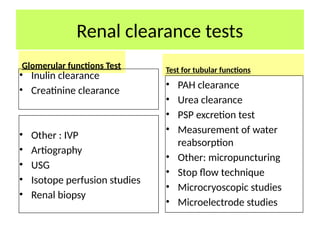
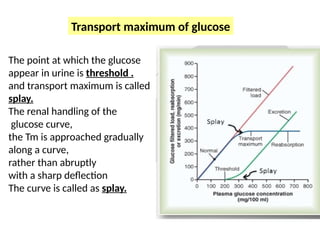
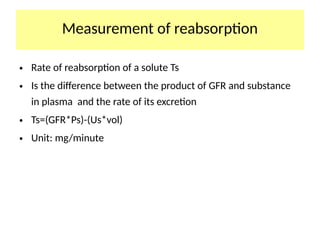
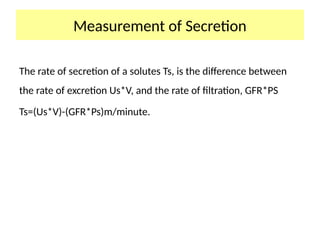
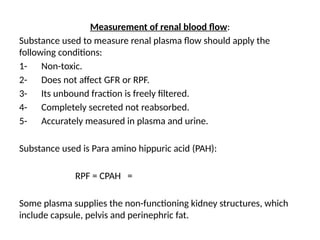
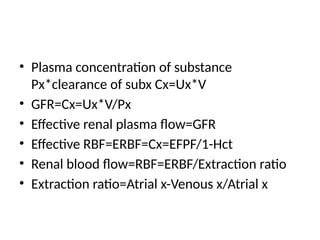
The document discusses various factors affecting glomerular filtration rate (GFR) and renal function tests, including the components and functions of nephrons, the impact of arterial diameter and blood pressure on nephron function, and processes like reabsorption and clearance. It outlines specific tests to assess glomerular and tubular functions, measurement techniques for substances like glucose, and methods for calculating GFR using inulin and creatinine. Additionally, it covers the conditions required for substances used to evaluate GFR and renal plasma flow, emphasizing the significance of the clearance ratio in determining the renal handling of substances.