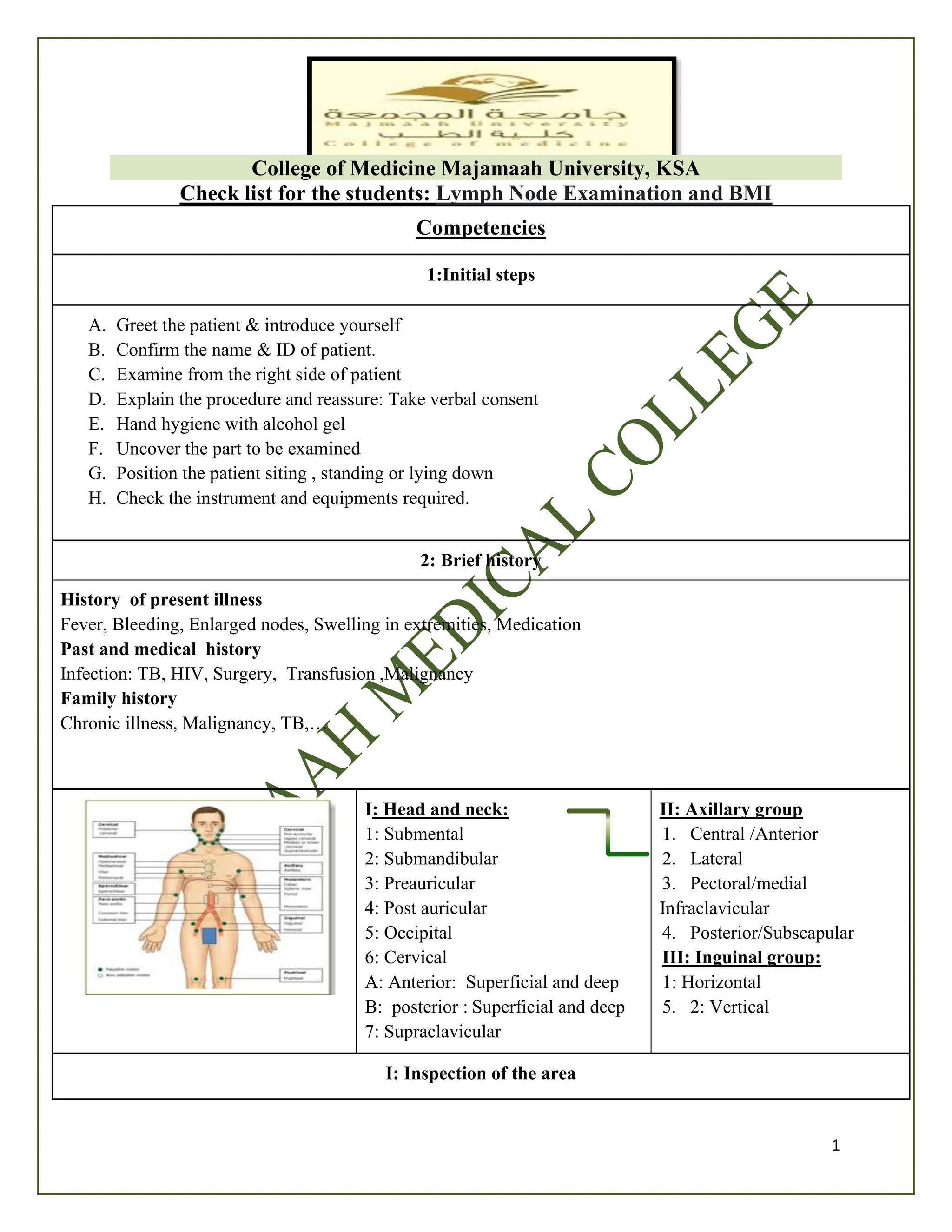
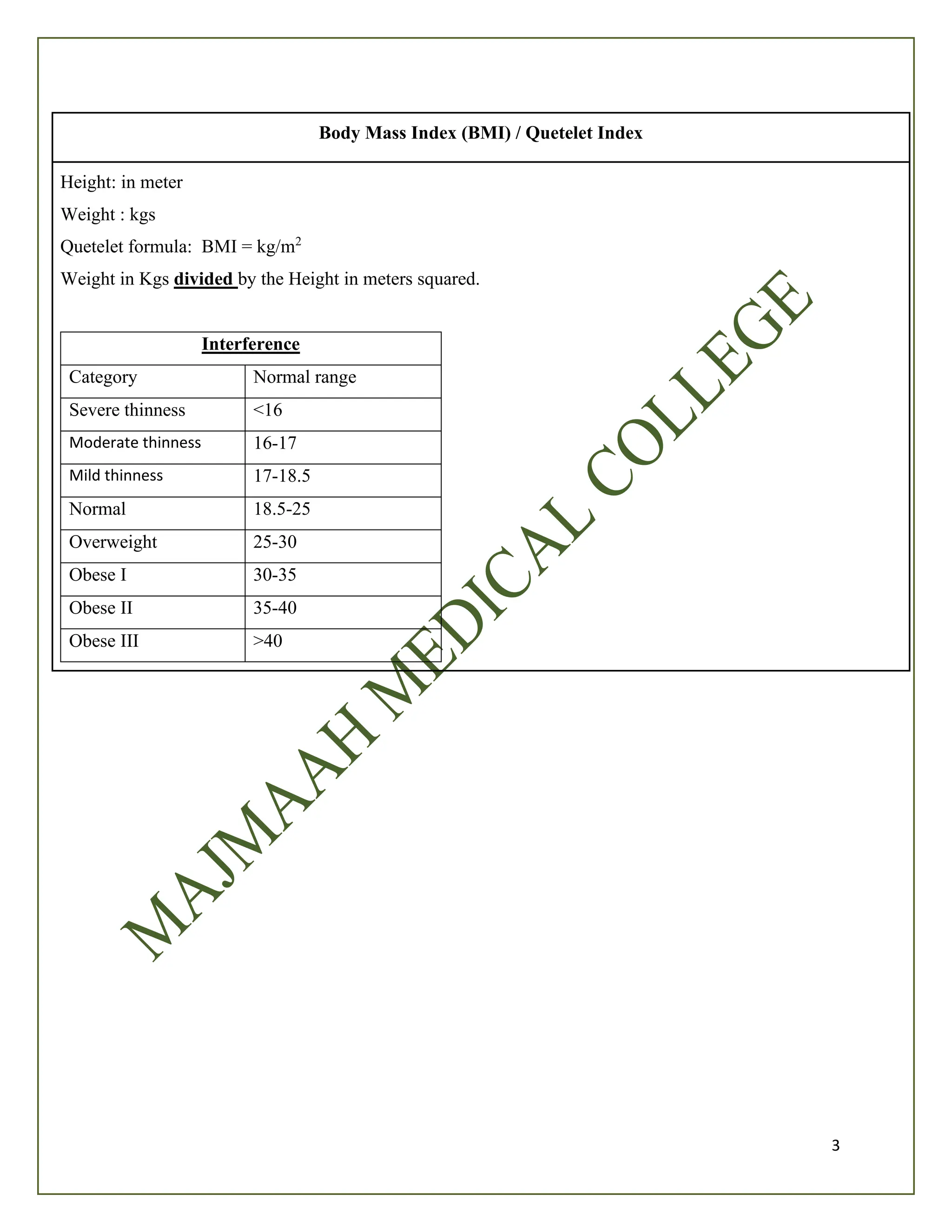
The document outlines a checklist for medical students at Majmaah University regarding lymph node examination and Body Mass Index (BMI) competencies. It includes initial examination steps, a guide for taking patient history, techniques for inspecting and palpating lymph nodes, as well as the interpretation of findings. Additionally, it provides the formula for calculating BMI and categorizes weight status based on BMI values.