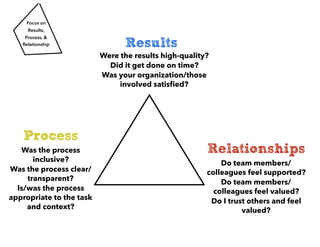
This document provides guidance for facilitators on managing group processes and discussions. It discusses key facilitation skills like setting expectations, maintaining focus, and helping groups build agreements. The core of facilitation involves opening discussion of a topic, narrowing considerations, and closing or transitioning. Techniques are presented for each phase like brainstorming, prioritizing, and defining next steps. Effective facilitation requires balancing attention to results, relationships, and process. The document also discusses facilitative leadership and practices like sharing vision, maximizing appropriate involvement, and celebrating accomplishments.