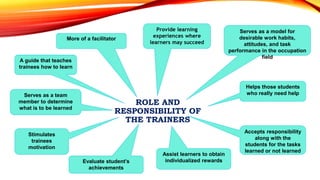
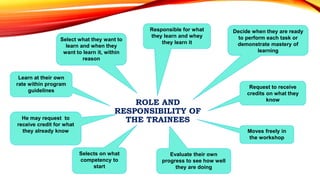
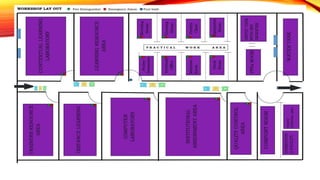
This document provides information about Masbate Polytechnic and Development College, Inc. It discusses how the college was established in 2009 and transformed from a technical vocational school into a college in 2014. It offers the bachelor of agricultural technology as its first degree program. The college aims to continuously produce graduates with skills, knowledge, and attitudes to become productive citizens through entrepreneurship or employment. It recognizes supporters who have helped the college continue its mission of providing education, training, and human resource development.