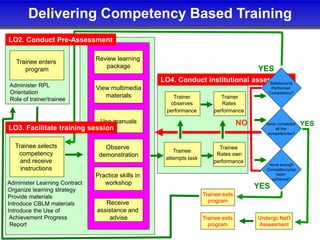
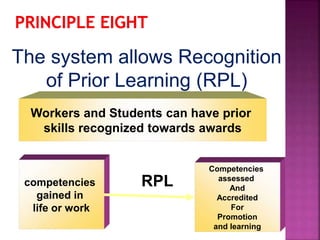
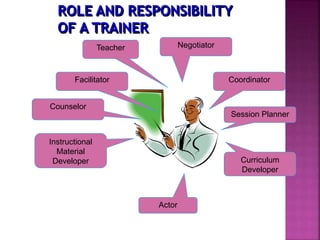
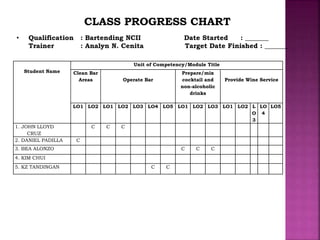
The document outlines the competency-based training program for bartending, detailing the structured approach to achieve competencies through individualized and self-paced learning. It highlights the training methodology, assessment processes, and resources available for both trainers and trainees, ensuring all materials are aligned with industry standards for effective skill acquisition. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of flexible entry and exit points in the training programs, accommodating various learning needs and prior experiences.