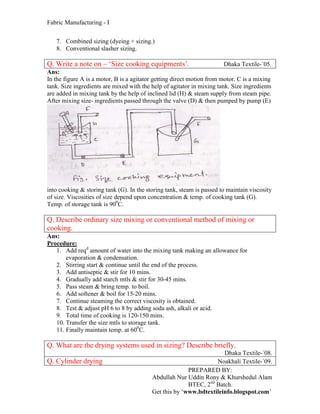
The document discusses sizing, which is the process of applying a protective coating to yarn surfaces to improve weaving efficiency. It defines sizing and describes why it is done for weaving. Various types of sizing are described, such as light, pure, medium and heavy sizing. Key factors to consider for size ingredients and properties of size ingredients are outlined. Common size ingredients for different fiber types like cotton, jute and polyester are listed. The functions of size ingredients and technological changes in yarn properties due to sizing are summarized. Different sizing faults and their causes are described. Finally, drying systems for sized yarn including cylinder drying are briefly discussed.