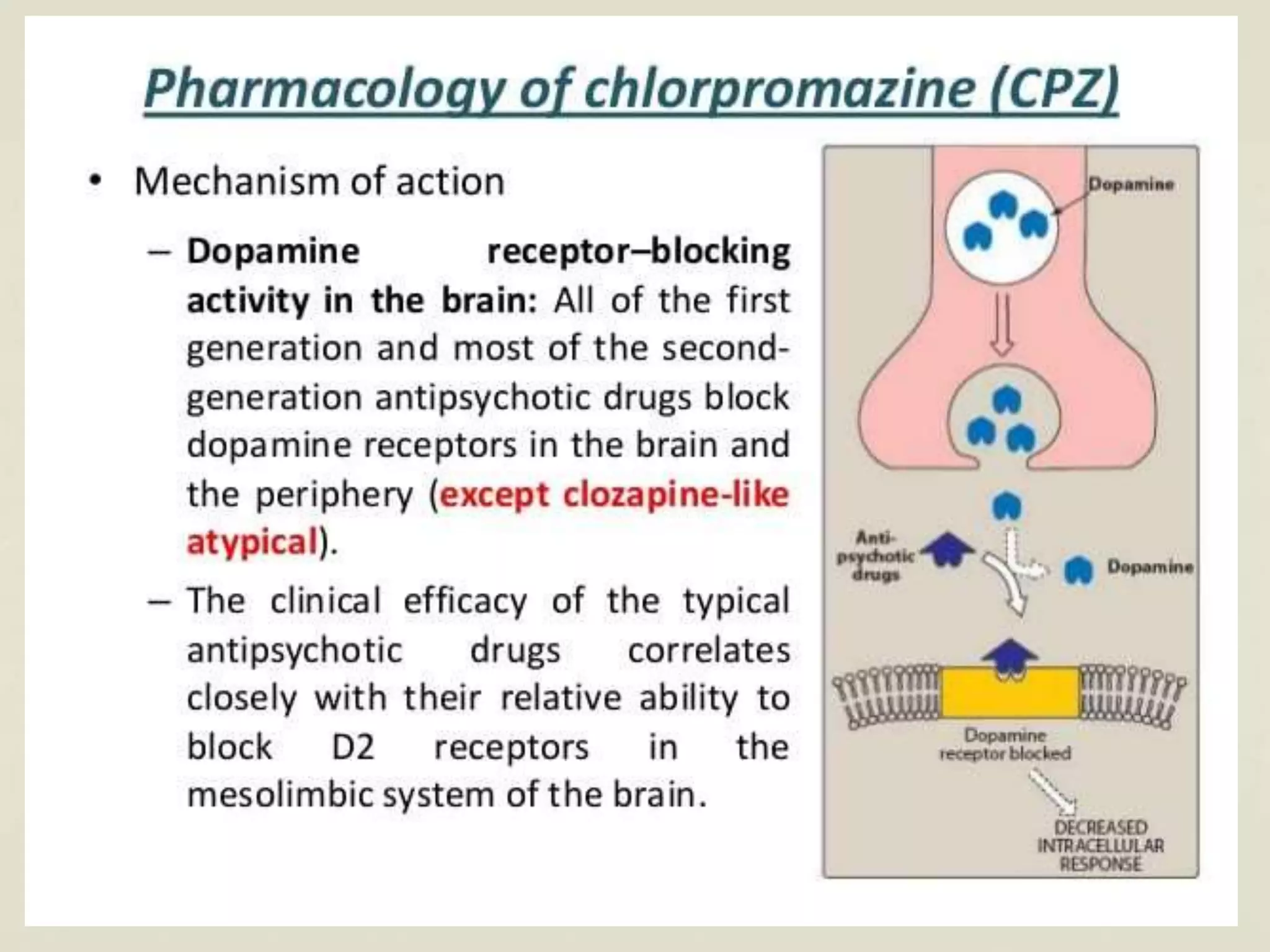
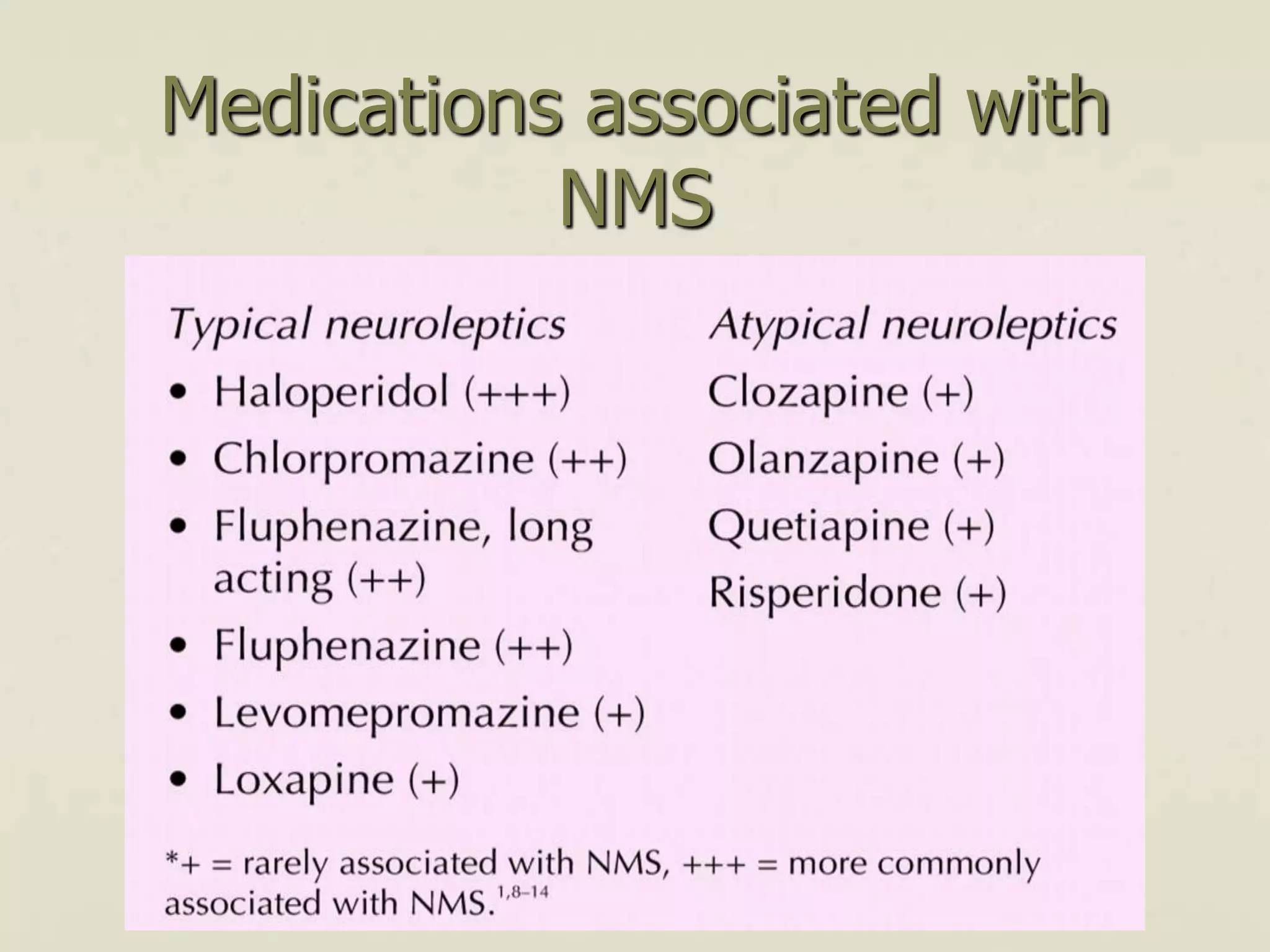
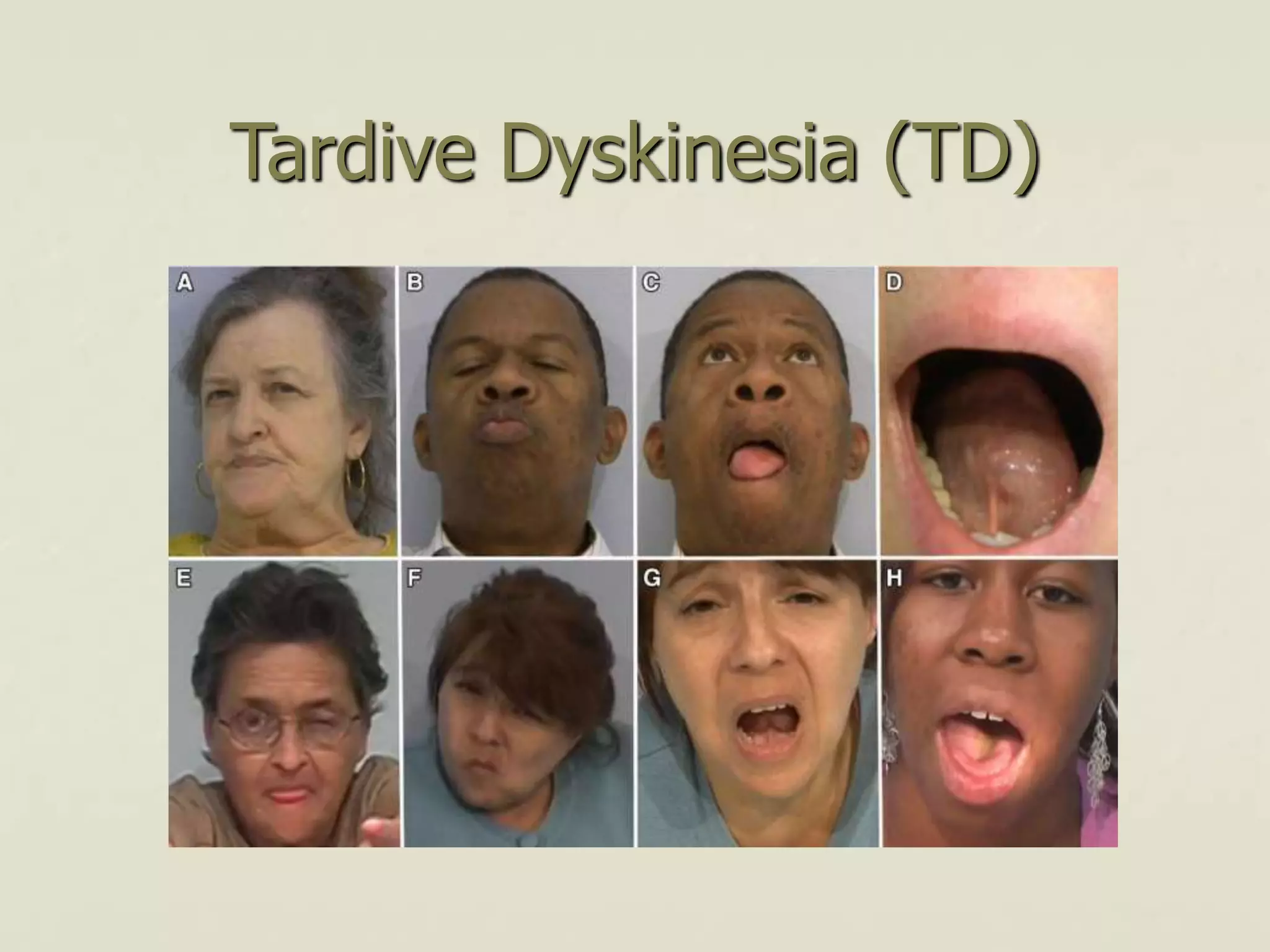
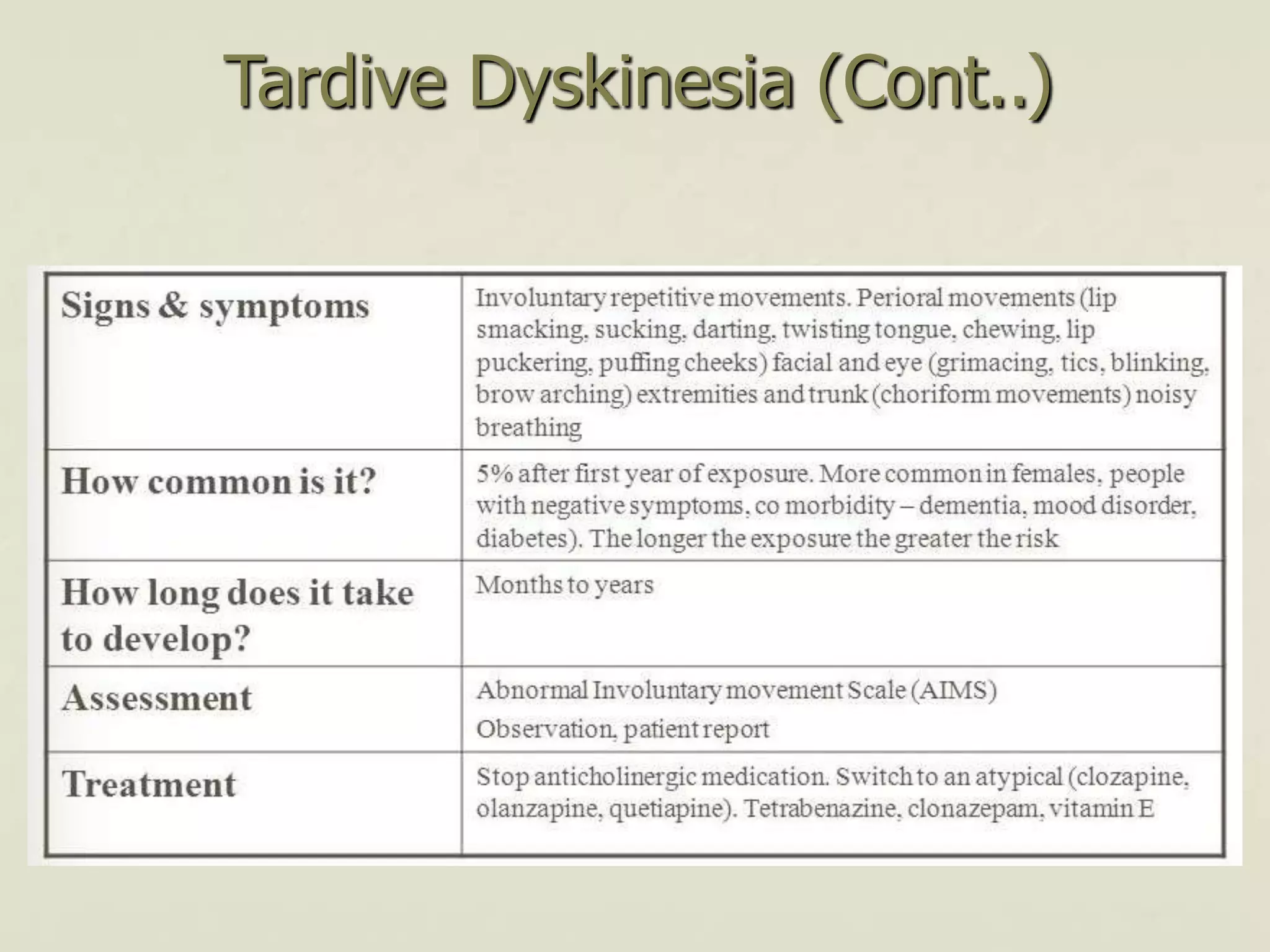
This document discusses extrapyramidal symptoms, which are movement disorders that result from disruption of the basal ganglia network in the brain. It provides an overview of the anatomy of the basal ganglia and their role in motor control. It then presents a case scenario of a 16-year-old boy who developed acute dystonia after taking an unspecified nausea medication, likely causing the extrapyramidal symptom. The document outlines different extrapyramidal symptoms like parkinsonism, acute dystonia, neuroleptic malignant syndrome, and tardive dyskinesia. It provides recommendations for treating each condition, such as using procyclidine or benztropine for acute dystonia.