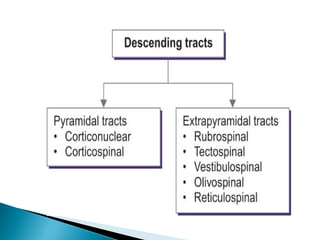
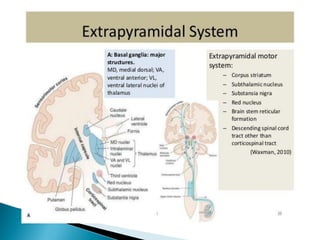
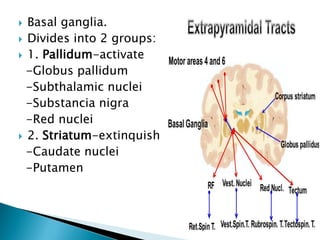
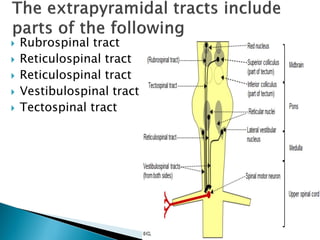
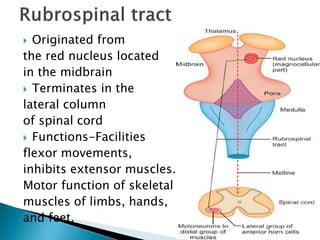
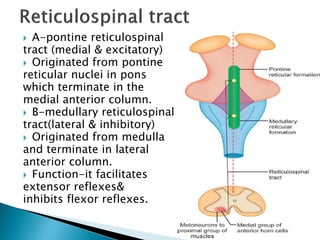
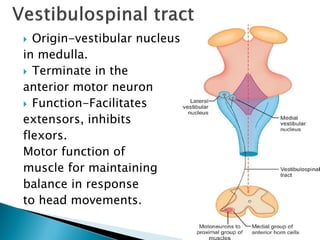
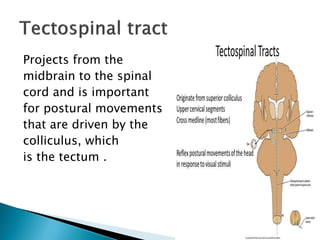
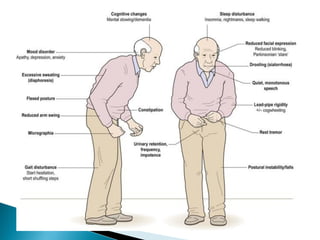
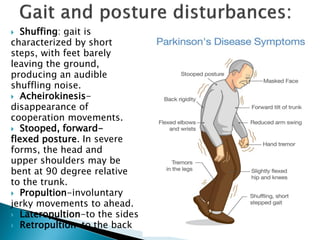
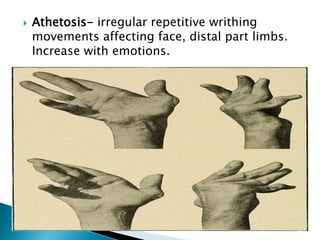
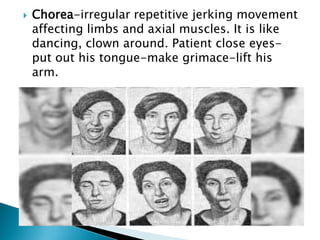
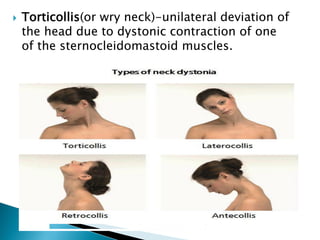
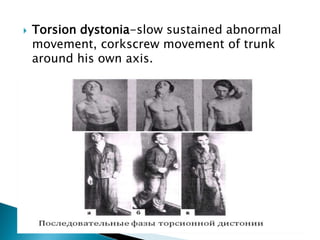
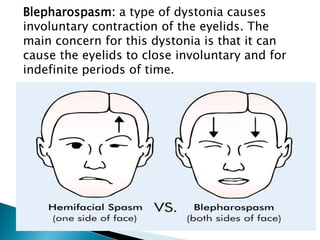
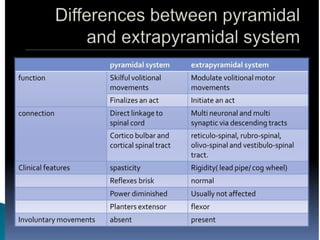
The extrapyramidal system is a neural network located in the brain that is part of the motor system and centers around the indirect control of movement. It responds to purposive, nonvoluntary movements and regulates muscle tone. The basal ganglia are nuclei that are part of complex regulatory circuits connected to the motor cortex and exert excitatory and inhibitory effects on movement and muscle tone. Lesions can cause excess or deficiency of movement. Parkinson's disease is the most common basal ganglia disease.