The document discusses Expressionist architecture and provides details about the Einstein Tower designed by Erich Mendelsohn. Some key points:
- Expressionist architecture developed in early 20th century Europe in parallel with Expressionist visual and performing arts, especially in Germany. It emphasized emotional effects through distorted forms, symbolic meanings over realism, and conceiving architecture as art.
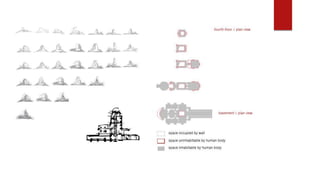
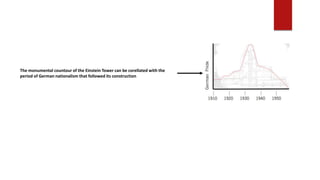
- The Einstein Tower in Potsdam (1921) was Mendelsohn's renowned first major work. Its complex shapes reflected artistic freedom and "functional dynamics." The tower isolated experiments from external light/temperature changes by thickening its base and using mirror systems to redirect light.
- The tower merged opposing concepts through relating mass and motion to