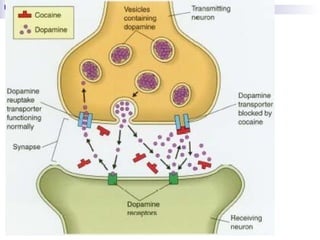
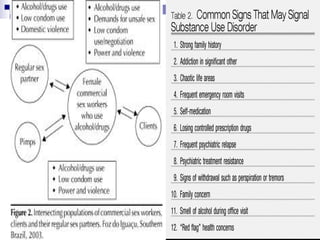
This document summarizes substance use disorders. It defines substances such as alcohol, opioids, cannabinoids, sedatives/hypnotics, cocaine, caffeine, hallucinogens, and tobacco. It describes how to identify substance use disorders through self-report data, analysis of bodily fluids, clinical signs and symptoms, and informant history. It then explains different classifications of substance use disorders including acute intoxication, harmful use, dependence syndrome, tolerance, withdrawal states, psychotic disorders, amnesic syndromes, and residual/late onset psychotic disorders. It provides examples of each classification.