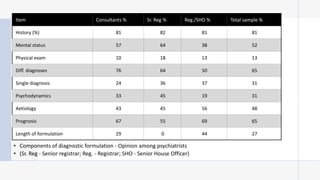
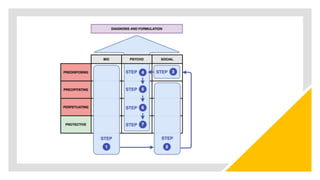
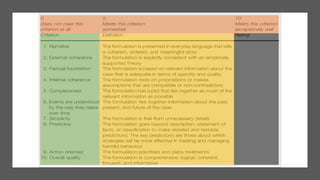
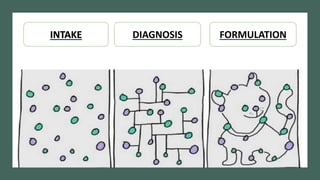
The document discusses the history and evolution of case formulation in psychiatry. It originated from Adolf Meyer's holistic approach in the early 1900s and was further developed by George Kelly in the 1950s. Key figures like George Engel promoted biopsychosocial formulations. While important, formulations are still confusing and not uniformly understood. The document outlines core components and functions of formulations, including guiding treatment and integrating diverse clinical information.