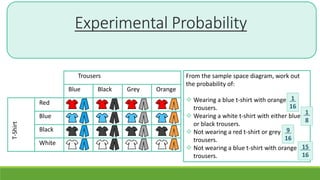
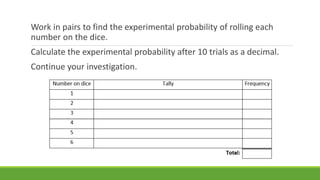
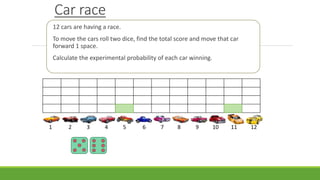
The document discusses experimental probability and how it is calculated by performing trials of an experiment and recording the number of successful outcomes. It provides examples of calculating experimental probability based on rolling dice and cars moving in a race based on dice rolls. The document aims to help students understand what experimental probability means, become familiar with experimenting with chance, and compare experimental and actual probability.