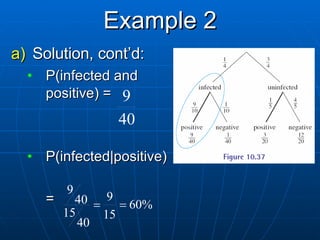
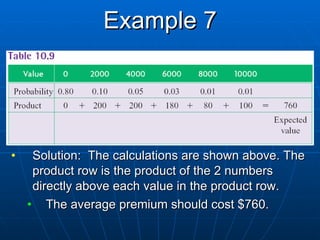
This document provides examples and explanations of key concepts in probability, including:
1) Probability is a number between 0 and 1 that indicates the likelihood of an event. Experimental probability is calculated from observations, while theoretical probability uses the composition of a sample space.
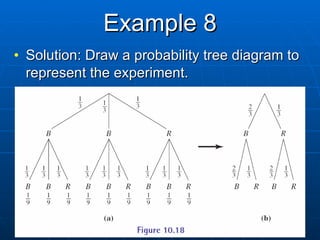
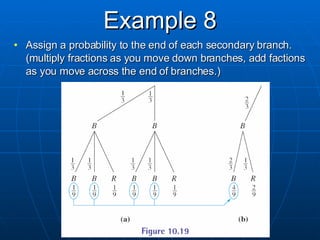
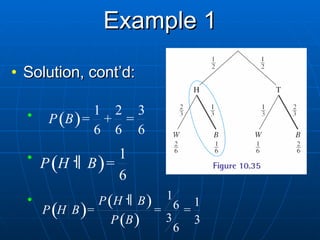
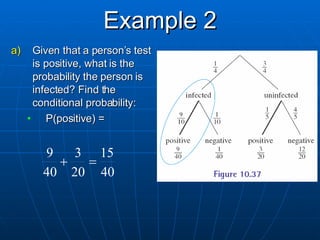
2) Tree diagrams and the fundamental counting principle can be used to determine the number of possible outcomes and probabilities in multi-stage experiments.
3) Union, intersection, and complements of events are probability concepts used to calculate probabilities of combined events.