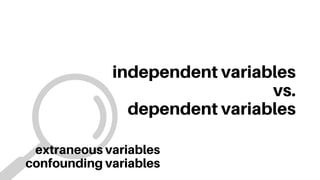
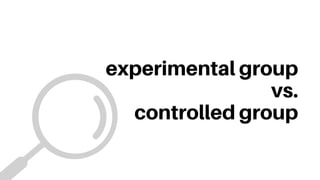
This document discusses experimental and non-experimental research methods. Experimental research involves manipulating an independent variable and measuring its effects on a dependent variable, while controlling for other influences. It uses random assignment to experimental and control groups. Quasi-experimental research has less control and randomization. Non-experimental research observes relationships through methods like surveys and case studies but cannot prove causation. Surveys are a common non-experimental method used in fields like sociology to understand opinions, conditions, and social issues in a timely manner, though they have weaknesses in establishing variable relationships.



!["[It] utilizes the principle of
manipulation of the independent
variables and examines its cause-
and-effect relationship on the
dependent variables by
controllingtheeffectsofother
variables."
(SAGE)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lesson2-230110130705-a2468e32/85/Experimental-and-non-experimental-research-4-320.jpg)



!["Non-experimental research
...[finds] out truths about a
subject by describing the
collected data about such subject
and determining their
relationships or connections with
one another."
(Barraceros 2018)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lesson2-230110130705-a2468e32/85/Experimental-and-non-experimental-research-9-320.jpg)



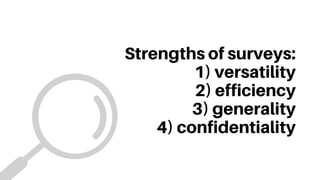
!["[Surveys] aim at knowing
what a big number of people
think and feel about some
sociological issues."
Surveys are mostly used in the
fields of sociology, psychology,
and the humanities.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lesson2-230110130705-a2468e32/85/Experimental-and-non-experimental-research-13-320.jpg)