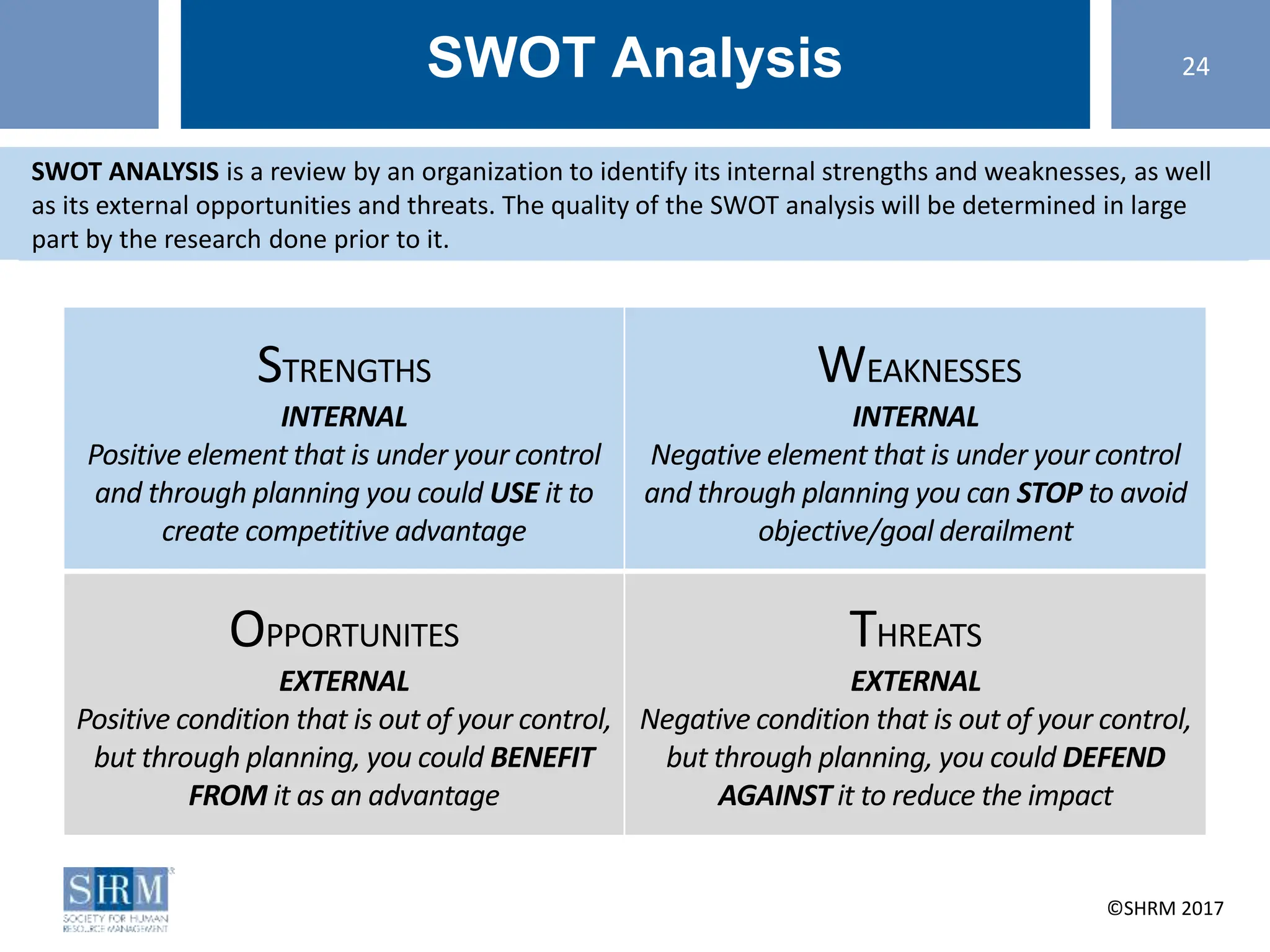
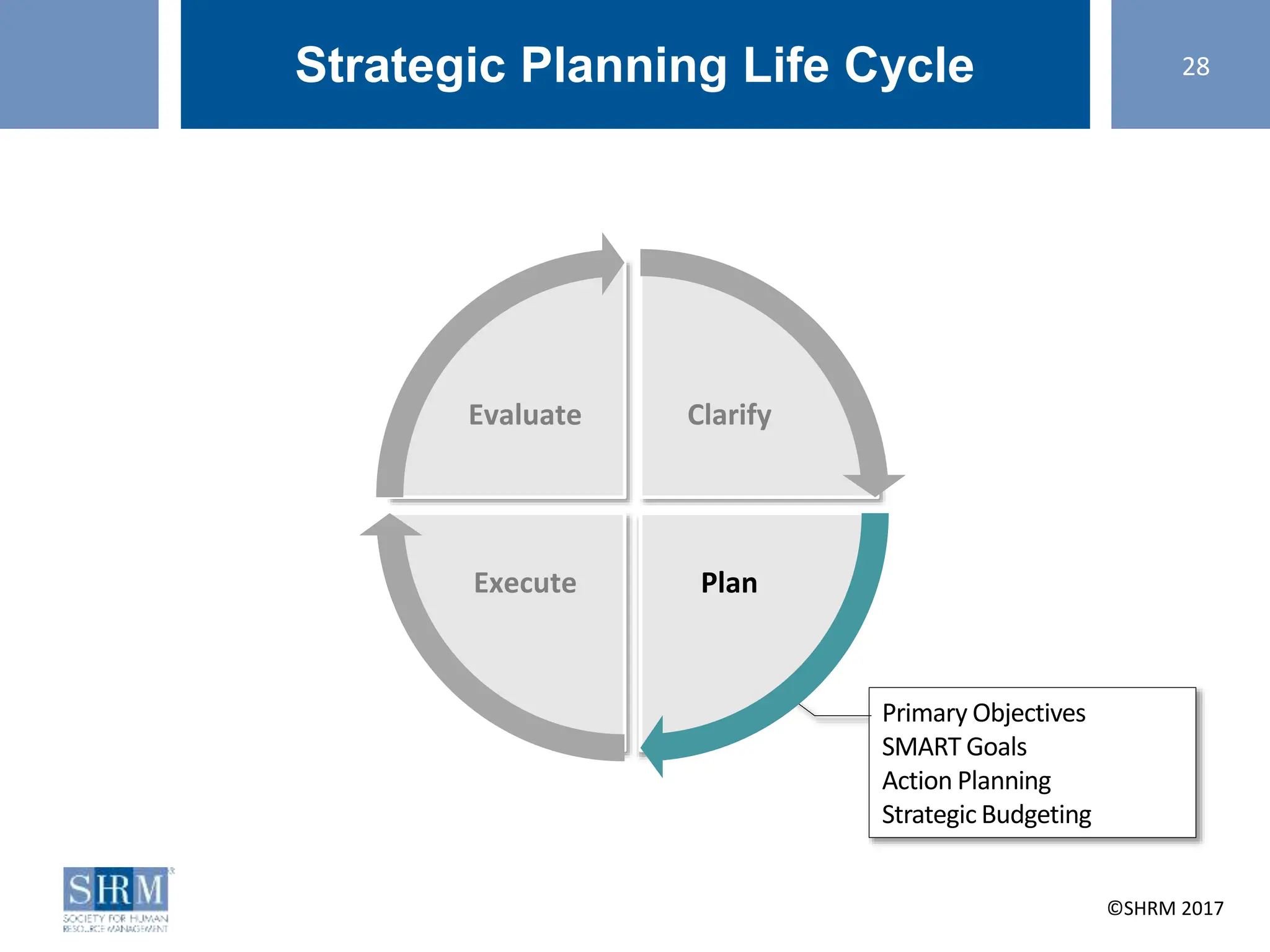
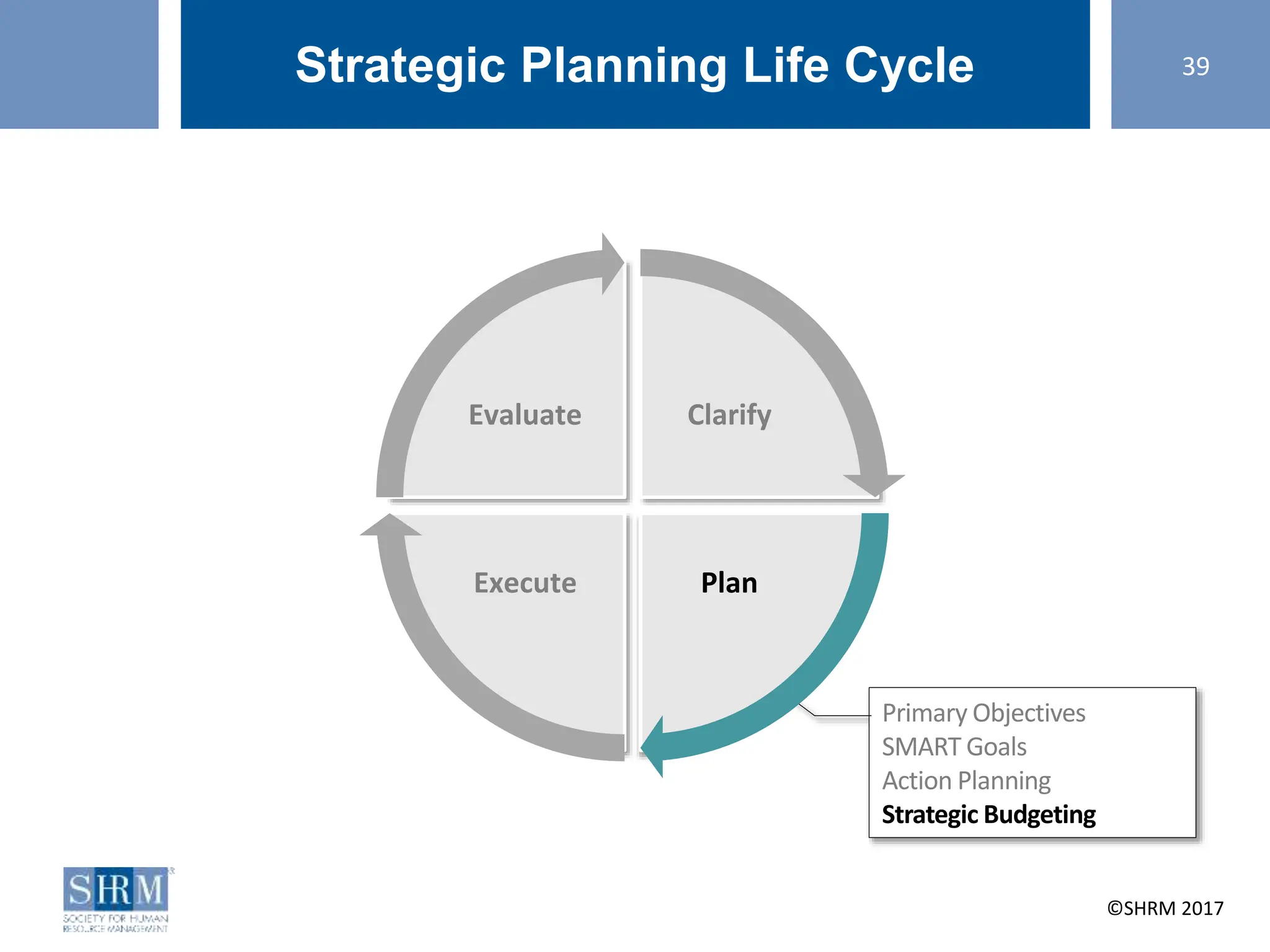
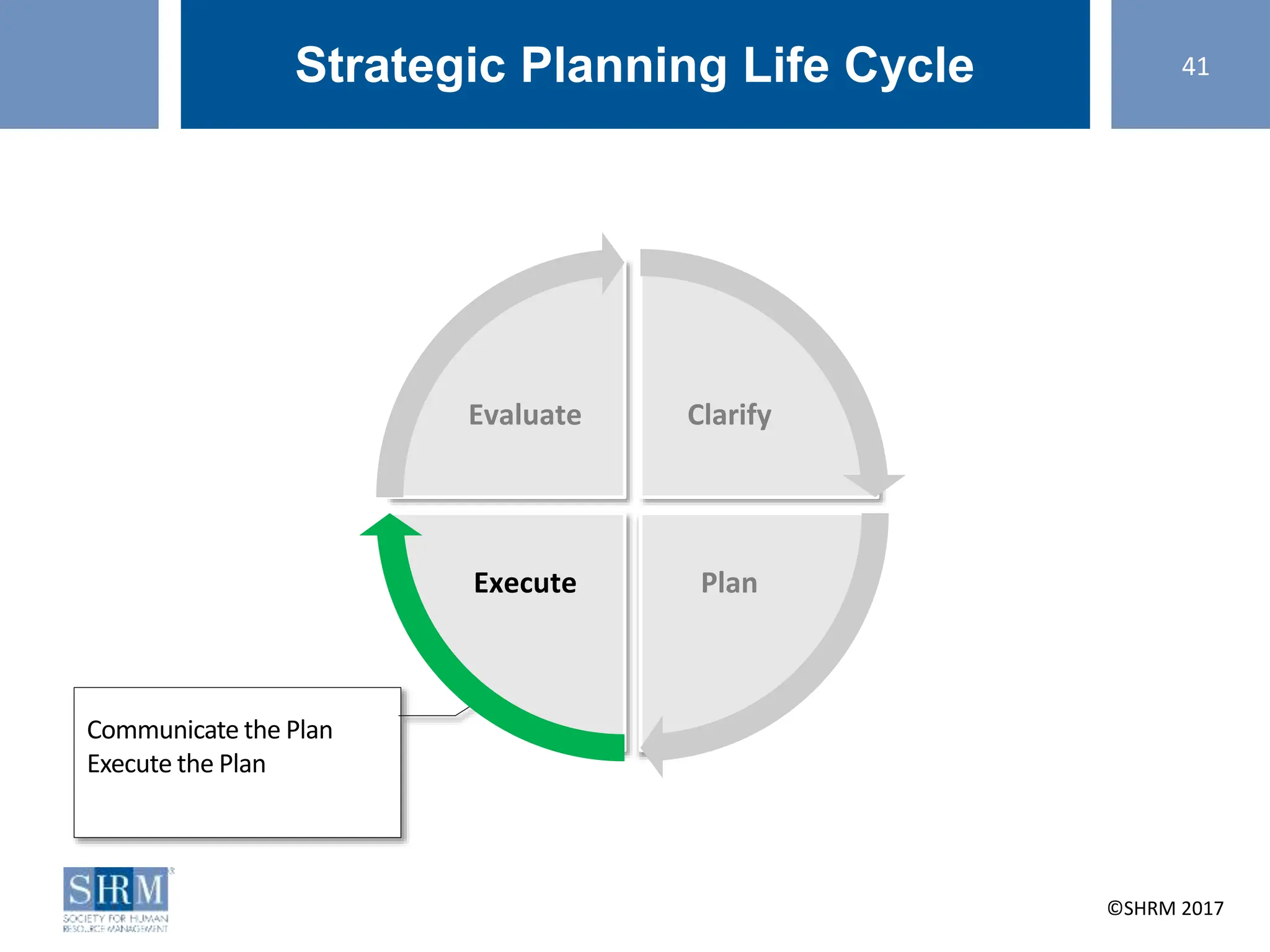
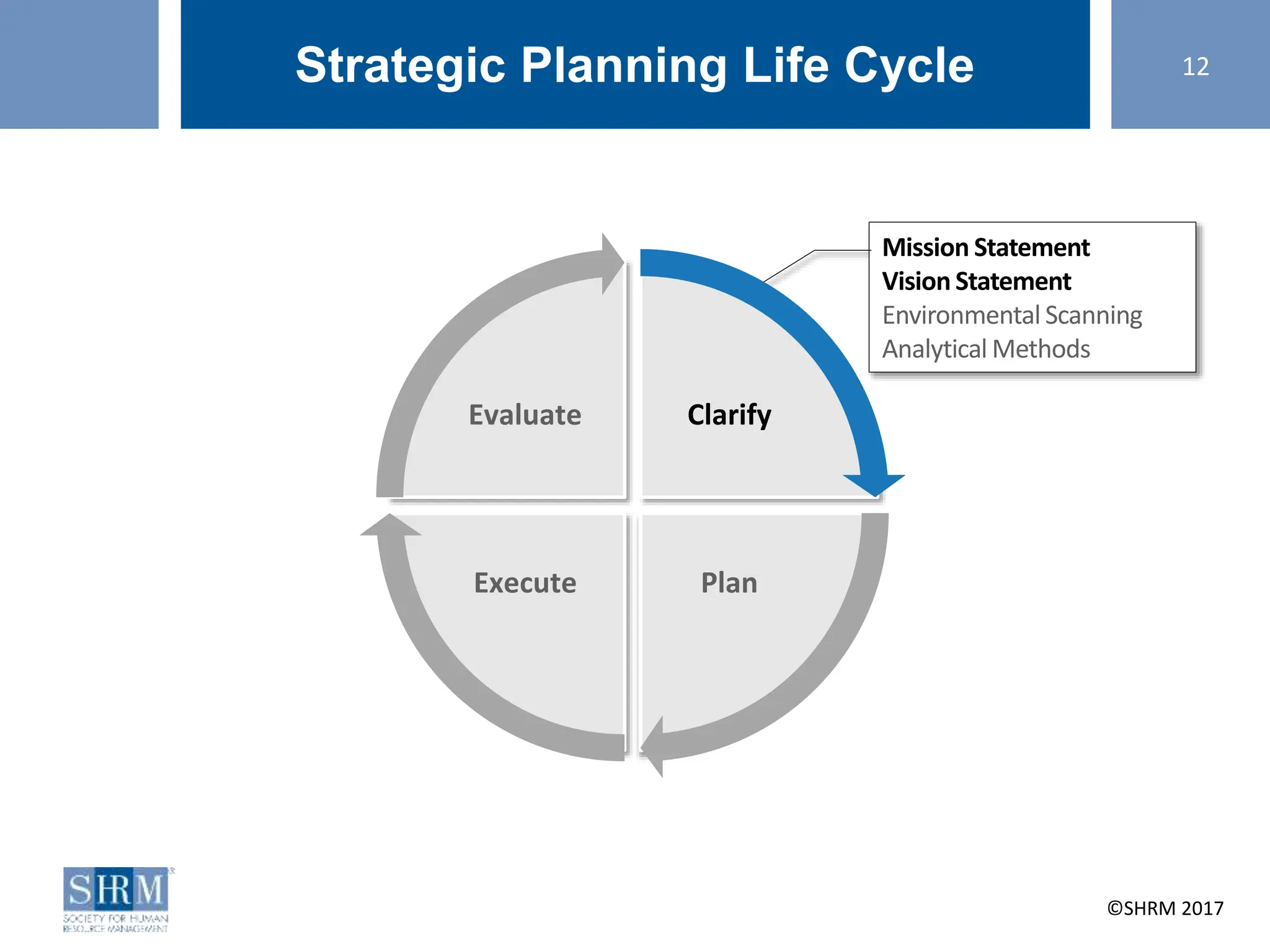
This document provides guidance on conducting a strategic planning workshop. It discusses identifying a strategic planning task force, developing mission and vision statements, conducting an environmental scan using tools like SWOT analysis and gap analysis, identifying primary objectives and SMART goals, and creating action plans. The workshop aims to walk participants through the strategic planning life cycle of clarifying the organization's direction, planning goals and initiatives, executing the plan, and evaluating results. Sample mission and vision statements are provided as examples. Activities guide participants in drafting their own mission, vision, objectives, and action plans through group discussions and exercises.
![©SHRM 2014 ©SHRM 2017
Train the Trainer:
Strategic Planning Workshop
[Insert Chapter/State Council Name]
[Insert Presenter Name]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/strategicplanningworkshoppresentation2017final-231227012942-37c7c888/75/Strategic-Planning-Workshop-Presentation_2017-FINAL-ppt-1-2048.jpg)


![©SHRM 2014 ©SHRM 2017
Getting to Know You
[Insert Chapter/State Council Name]
[Insert Getting to Know You Question ]
4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/strategicplanningworkshoppresentation2017final-231227012942-37c7c888/75/Strategic-Planning-Workshop-Presentation_2017-FINAL-ppt-4-2048.jpg)









![©SHRM 2014 ©SHRM 2017
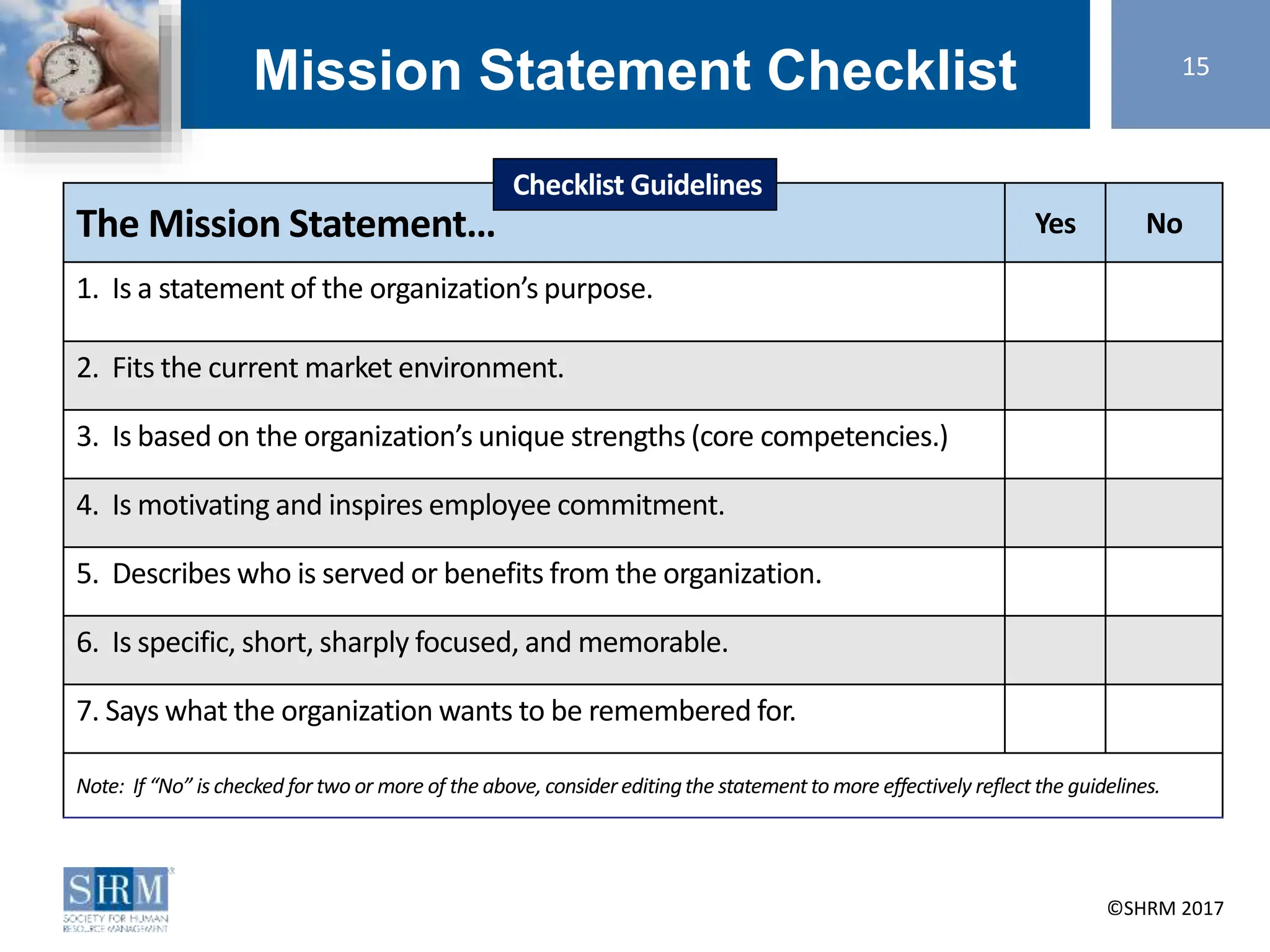
ACTIVITY: Mission Statement 16
[Insert Chapter/State Council Name] Mission
Statement:
[Insert Chapter/State Council Mission Statement]
• Review (chapter/state council) mission statement
and sample mission statements
• Draft mission statement and post mission
statement on flip chart
• Team circles words to include
• Review all circled words
• Discuss and finalize mission statement](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/strategicplanningworkshoppresentation2017final-231227012942-37c7c888/75/Strategic-Planning-Workshop-Presentation_2017-FINAL-ppt-16-2048.jpg)



![©SHRM 2014 ©SHRM 2017
ACTIVITY: Vision Statement 20
[Insert Chapter/State Council Name] Vision
Statement:
[Insert Chapter/State Council Mission
Statement]
• Review (chapter/state council) vision statement
and sample mission statements
• Draft vision statement and post vision statement
on flip chart
• Team circles words to include
• Review all circled words
• Discuss and finalize vision statement](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/strategicplanningworkshoppresentation2017final-231227012942-37c7c888/75/Strategic-Planning-Workshop-Presentation_2017-FINAL-ppt-20-2048.jpg)