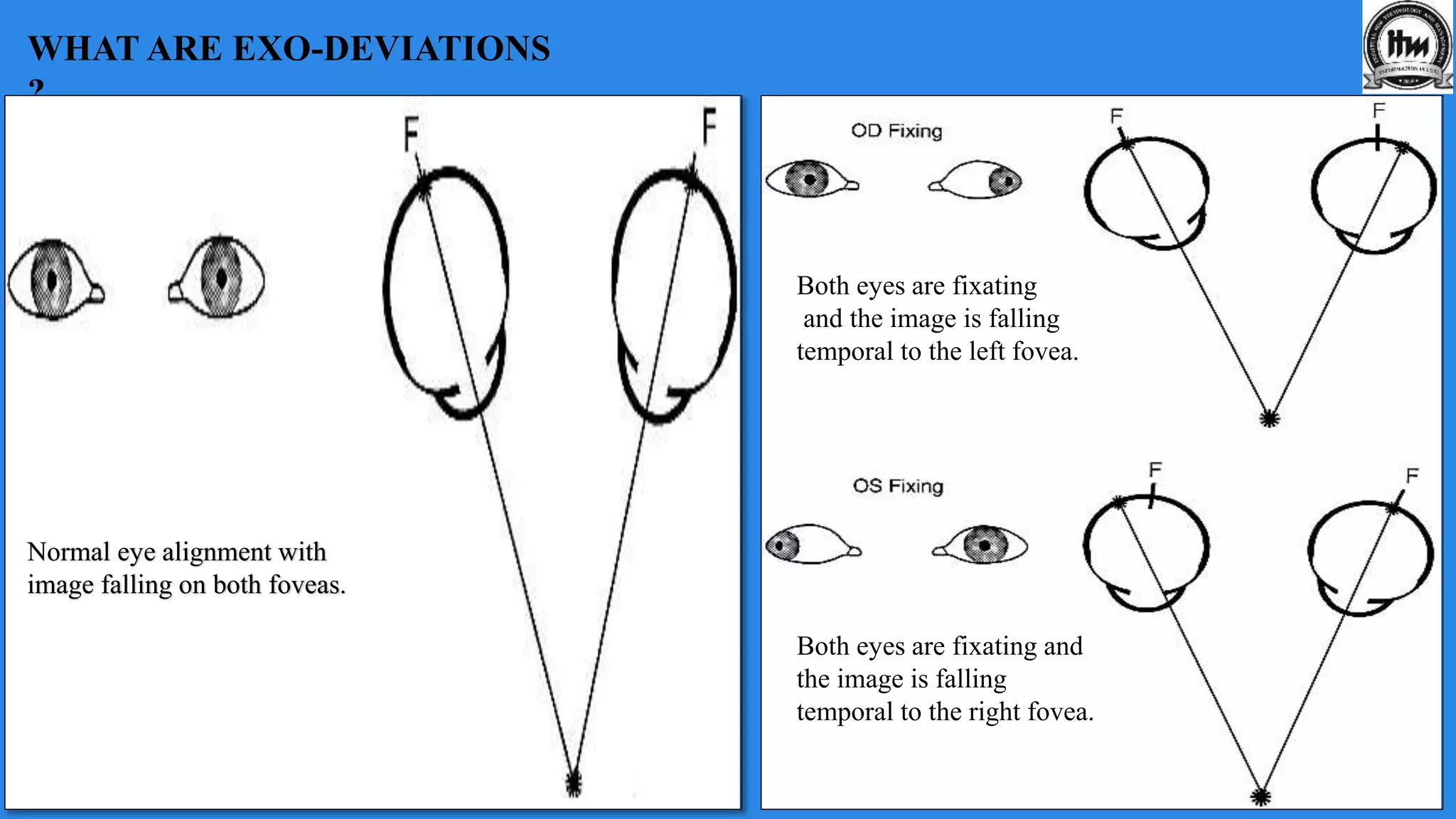
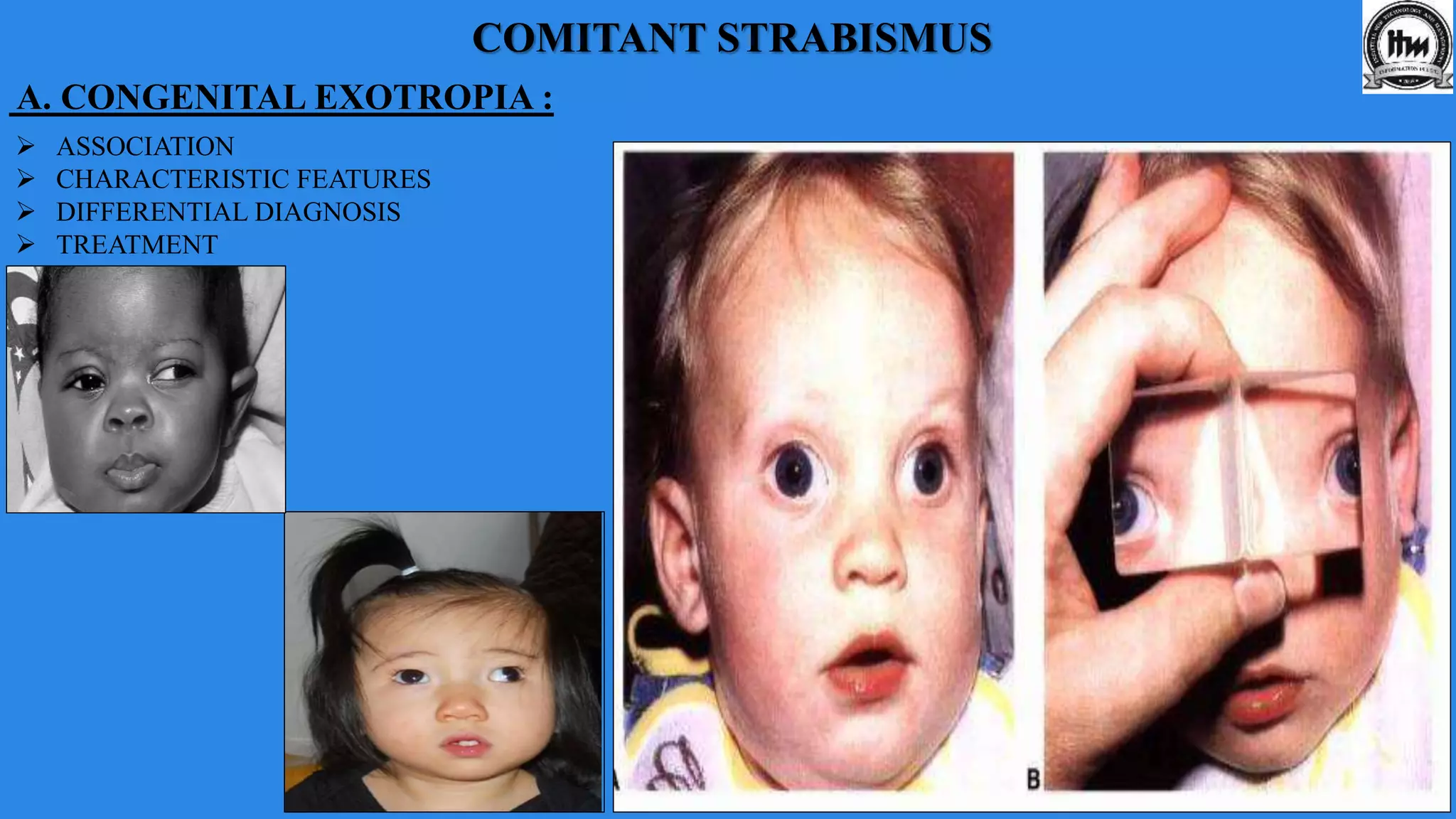
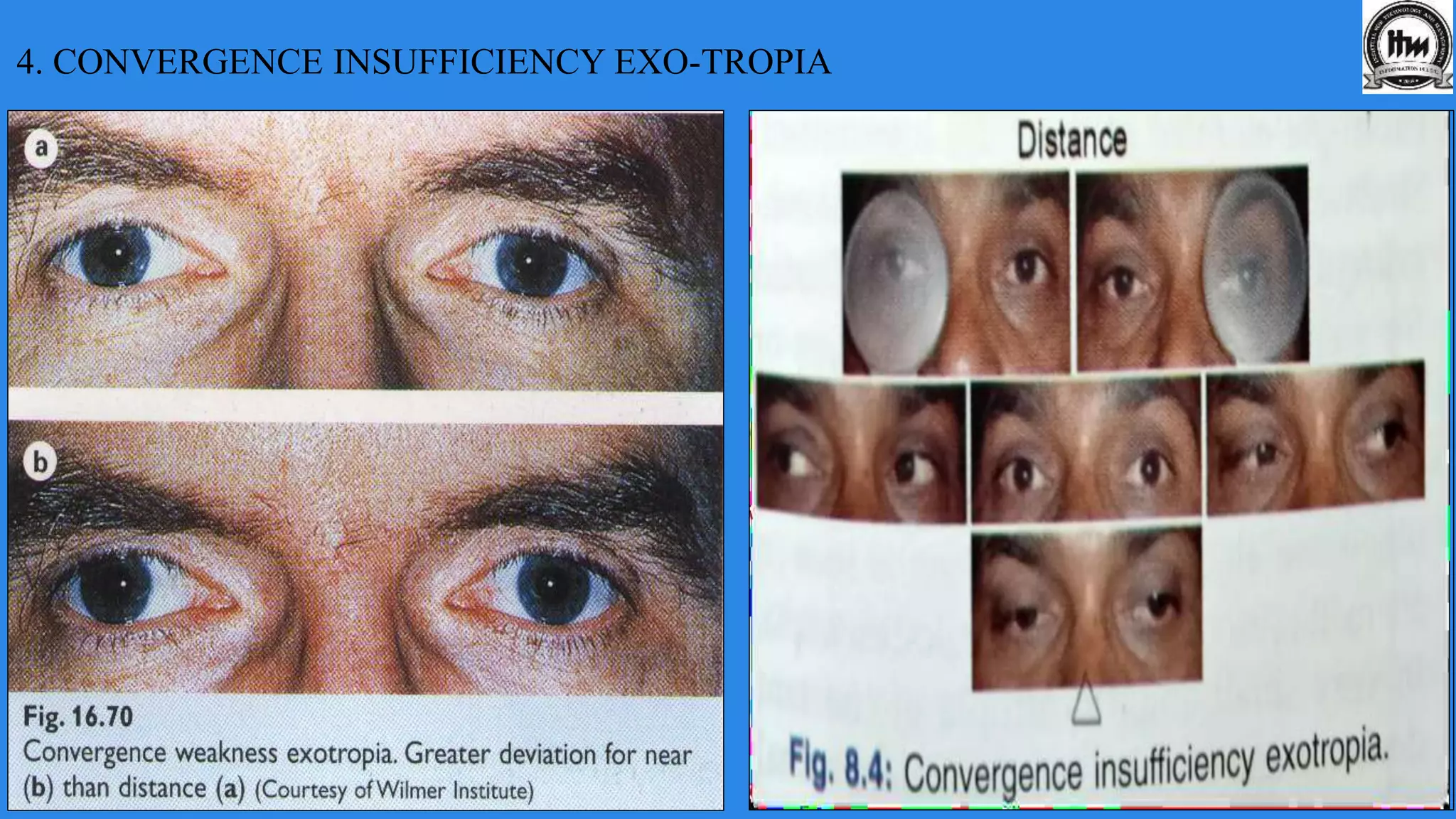
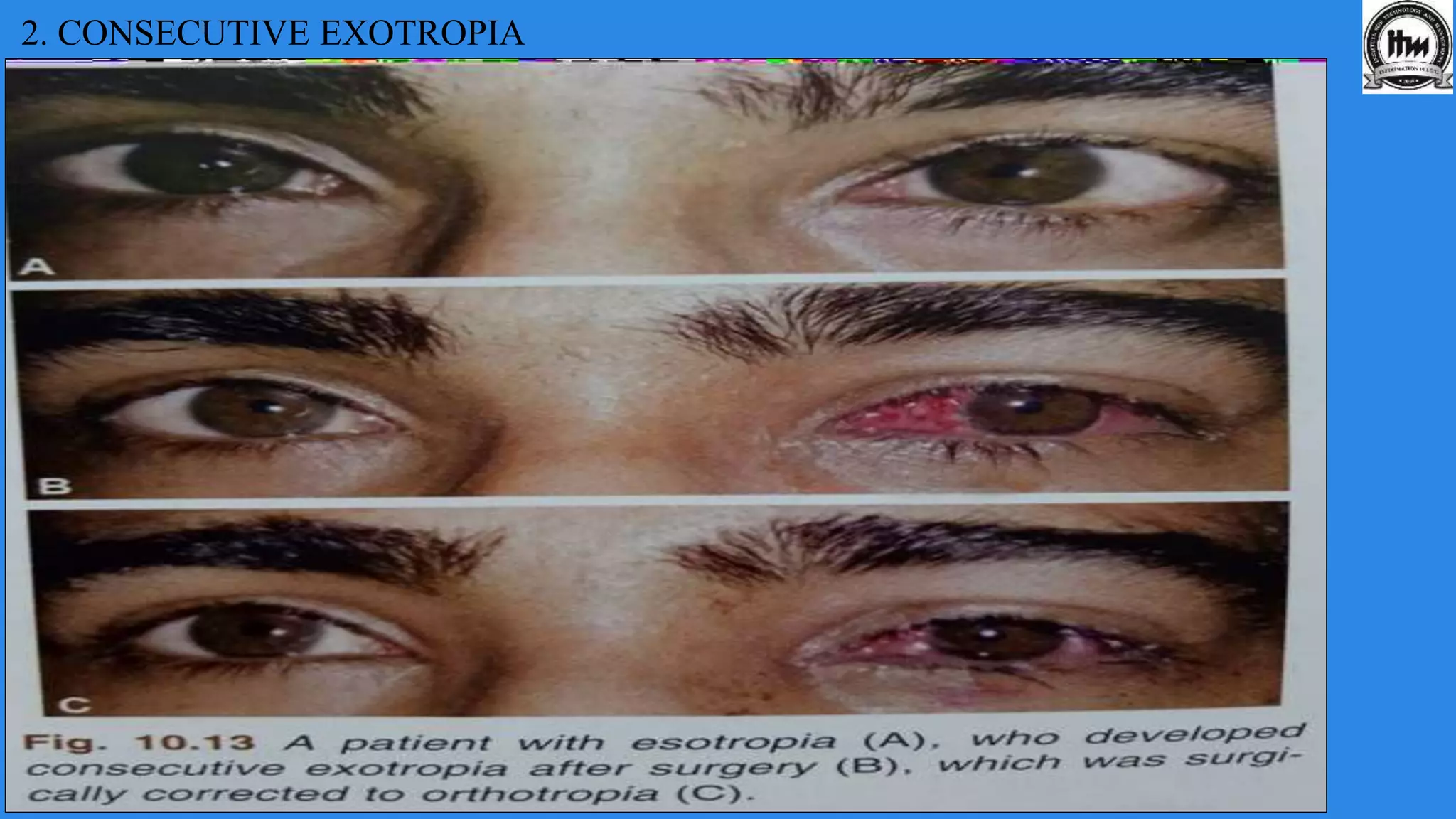
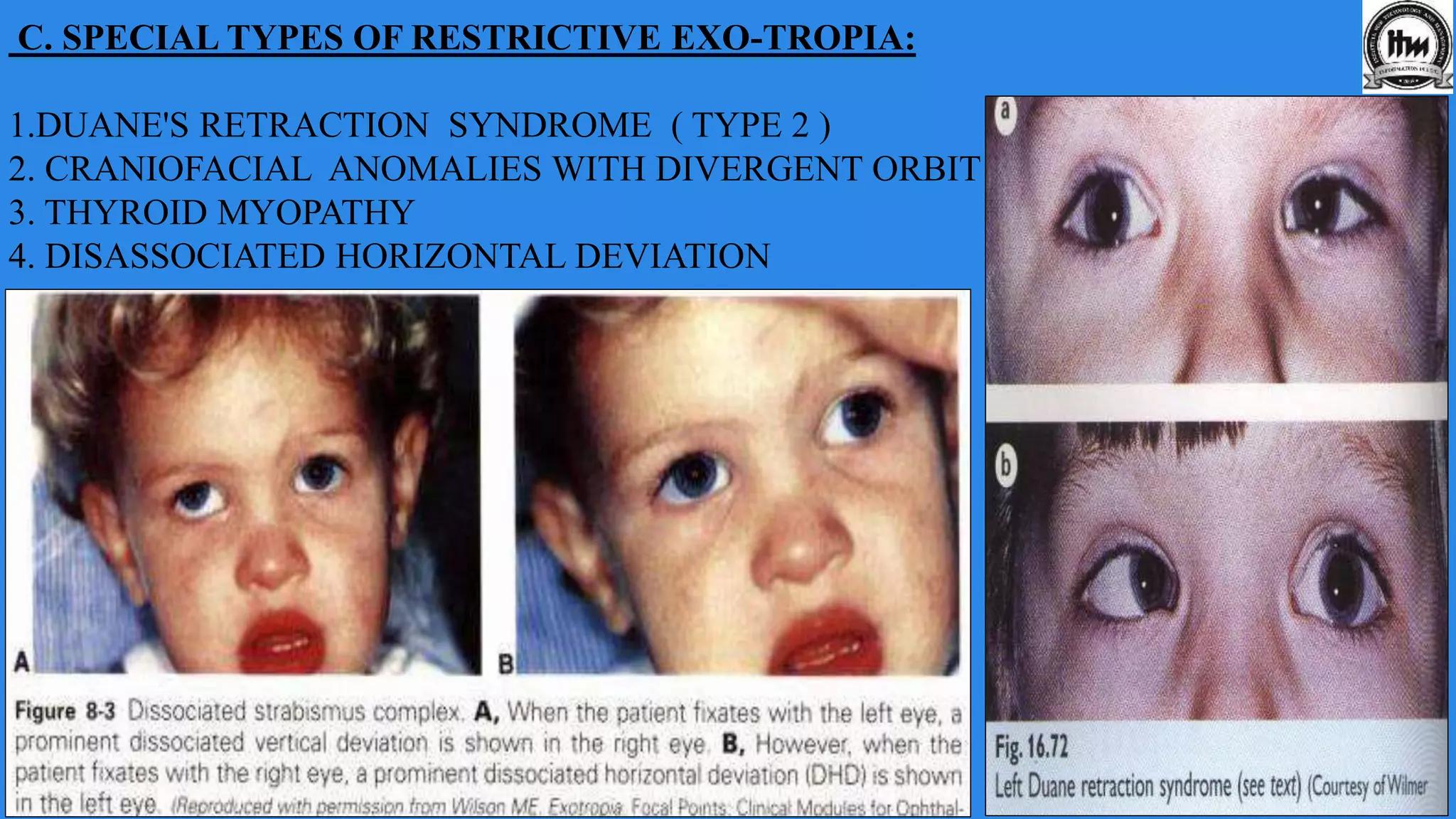
This document discusses exodeviations, which are eye misalignments where one or both eyes turn outward. It classifies exodeviations as comitant or incomitant, and as congenital, primary, or secondary. Primary exodeviations develop from predisposing mechanical or innervational factors and progress through latent, intermittent, and constant stages. Secondary exodeviations are sensory or consecutive types. Specific types discussed include congenital exotropia, divergence excess exotropia, paralytic exotropia, and restrictive exotropia. Treatment options vary depending on the type and stage of exodeviation.