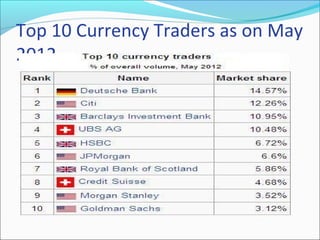
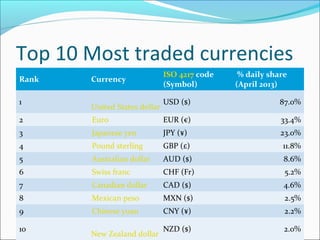
The foreign exchange market allows for the trading of global currencies. It is decentralized and operates 24/7 globally via banks and other financial institutions. The US dollar, euro, Japanese yen and British pound are among the most heavily traded currencies, with over $5 trillion exchanged daily worldwide as of 2013. Factors like interest rates, inflation, economic conditions, and political situations can influence exchange rates. Participants in the forex market include banks, brokers, central banks, corporations and retail investors.