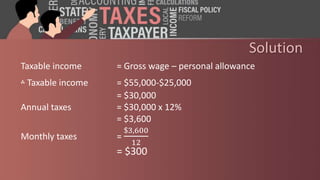
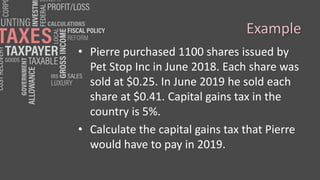
This document distinguishes between direct and indirect taxes. Direct taxes include income tax, corporation tax, capital gains tax, and capital transfer tax, which are paid by individuals and businesses directly. Indirect taxes are levied on the consumption of goods and services, through taxes like customs duty, excise duty, stamp duty, and sales/consumption taxes that are paid by manufacturers and importers and passed on to consumers. Examples are provided of calculating income tax, capital gains tax, customs duties, and excise taxes to illustrate how these different types of direct and indirect taxes are applied.