The document discusses various aspects of exception handling in Java including:
- Types of exceptions like checked and unchecked exceptions
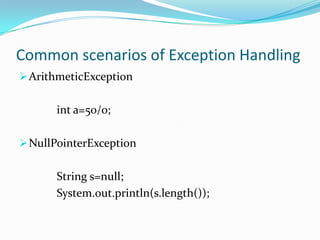
- Common exception scenarios like NullPointerException, ArithmeticException etc.
- Keywords used for exception handling like try, catch, finally, throw, throws
- Examples demonstrating try, catch, multiple catch blocks, nested try, finally block, throw, exception propagation, throws keyword, exception handling with method overriding and custom exceptions.


![Common scenarios of Exception Handling
NumberFormatException
String s=“abc”;
int i=Integer.parseInt(s);
ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
int a[]= new int[5];
a[10]=50;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/exceptionhandling-130321053811-phpapp02/85/Exception-Handling-4-320.jpg)

![try
class sample
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int data=50/0;
System.out.println(“I love india”);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/exceptionhandling-130321053811-phpapp02/85/Exception-Handling-6-320.jpg)
![try
class sample{
public static void main(String args[]){
try{
int data=50/0;
}
catch(ArithmeticException e)
{
System.out.println(e);
}
System.out.println(“I love india”);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/exceptionhandling-130321053811-phpapp02/85/Exception-Handling-7-320.jpg)
![Multiple catch
class sample{
public static void main(String args[]){
try{
int a[]=new int[5];
int a[5]=30/0; }
catch(ArithmeticException e){s.o.p(“task 1”);}
catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsExceptin e){s.o.p(“task 2”);}
catch(Exception e){s.o.p(“task completed”);}
System.out.println(“I love india”);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/exceptionhandling-130321053811-phpapp02/85/Exception-Handling-8-320.jpg)
![Multiple catch
class sample{
public static void main(String args[]){
try{
int a[]=new int[5];
int a[5]=30/0; }
catch(Exception e){s.o.p(“task completed”);}
catch(ArithmeticException e){s.o.p(“task 1”);}
catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsExceptin e){s.o.p(“task 2”);}
System.out.println(“I love india”);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/exceptionhandling-130321053811-phpapp02/85/Exception-Handling-9-320.jpg)
![Nested try
class sample{
public static void main(String args[]){
try{
try{
s.o.p(“divide”);
int a=40/0;
}catch(ArithmeticExceptin e){s.o.p(e);}
try{
int a[]=new int[5];
int a[5]=4;
}catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsExceptin e){
s.o.p(e);}
s.o.p(“other statements”);
}catch(Exception e){s.o.p(“exception handled”);}
s.o.p(“normal flow”);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/exceptionhandling-130321053811-phpapp02/85/Exception-Handling-10-320.jpg)
![finally
Exception doesn’t occur
class sample{
public static void main(String args[]){
try{
int data=25/5;
s.o.p(data);}
catch(NullPointerException e){s.o.p(e);}
finally{s.o.p(“finally block is always excuted”);}
s.o.p(“I love india”);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/exceptionhandling-130321053811-phpapp02/85/Exception-Handling-11-320.jpg)
![finally
Exception occurred but not handled
class sample{
public static void main(String args[]){
try{
int data=25/0;
s.o.p(data);}
catch(NullPointerException e){s.o.p(e);}
finally{s.o.p(“finally block is always excuted”);}
s.o.p(“I love india”);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/exceptionhandling-130321053811-phpapp02/85/Exception-Handling-12-320.jpg)
![finally
Exception occurred but handled
class sample{
public static void main(String args[]){
try{
int data=25/0;
s.o.p(data);}
catch(ArithmeticException e){s.o.p(e);}
finally{s.o.p(“finally block is always excuted”);}
s.o.p(“I love india”);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/exceptionhandling-130321053811-phpapp02/85/Exception-Handling-13-320.jpg)
![throw
class sample{
static void validate(int age){
if(age<18)
throw new ArithmeticException(“not valid”);
else
System.out.println(“welcome to vote”);
}
pulic static void main(String args[]){
validate(13);
System.out.println(“I love india”);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/exceptionhandling-130321053811-phpapp02/85/Exception-Handling-14-320.jpg)
![Exception Propagation
class sample{
void m(){
int data=50/0; }
void n(){
m(); }
void p(){
try{
n();
}catch(Exception e){s.o.p(“Exception handled”);}
}
public static void main(String args[]){
sample obj=new sample();
obj.p();
System.out.println(“I love india”);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/exceptionhandling-130321053811-phpapp02/85/Exception-Handling-15-320.jpg)
![Exception Propagation
class sample{
void m(){
throw new java.io.IOException(“device error”); }
void n(){
m(); }
void p(){
try{
n();
}catch(Exception e){s.o.p(“Exception handled”);}
}
public static void main(String args[]){
sample obj=new sample();
obj.p();
System.out.println(“I love india”);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/exceptionhandling-130321053811-phpapp02/85/Exception-Handling-16-320.jpg)
![throws
Checked exception can be propagated by throws keyword
import java.io.IOException;
class sample{
void m() throws IOException {
throw new IOException(“device error”); }
void n() throws IOException{
m(); }
void p(){
try{
n();
}catch(Exception e){s.o.p(“Exception handled”);}
}
public static void main(String args[]){
sample obj=new sample();
obj.p();
System.out.println(“I love india”);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/exceptionhandling-130321053811-phpapp02/85/Exception-Handling-17-320.jpg)
![Handling the exception if exception occurs in the
method which declares an exception
import java.io.*;
class M{
void method() throws IOException {
throw new IOException(“device error”);}
}
class Test{
publi static void main(String args[]){
try{
M m=new M();
m.method();
}catch(Exceptionn e){s.o.p(“exception handled”);}
System.out.println(“I love india”);}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/exceptionhandling-130321053811-phpapp02/85/Exception-Handling-18-320.jpg)
![Declaring the exception if exception doesn’t
occur in the method which declares an exception
import java.io.*;
class M{
void method() throws IOException {
System.out.println(“device operation perform”);}
}
class Test{
publi static void main(String args[]) throws
IOException{
M m=new M();
m.method();
System.out.println(“I love india”);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/exceptionhandling-130321053811-phpapp02/85/Exception-Handling-19-320.jpg)
![Declaring the exception if exception occurs in the
method which declares an exception
import java.io.*;
class M{
void method() throws IOException {
throw new IOException(“device error”);}
}
class Test{
publi static void main(String args[]) throws
IOException{
M m=new M();
m.method();
System.out.println(“I love india”);}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/exceptionhandling-130321053811-phpapp02/85/Exception-Handling-20-320.jpg)

![ Super class method doesn’t declare an exception
Subclass overridden method can’t declare the checked
exception
import java.io.*;
class Parent{
void msg(){s.o.p(“parent”);}
}
class Child extends Parent{
void msg() throws IOException{
System.out.println(“child”);
}
pulic static void main(String args[]){
Parent p=new Child();
p.msg();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/exceptionhandling-130321053811-phpapp02/85/Exception-Handling-22-320.jpg)
![ Super class method doesn’t declare an exception
Subclass overridden method can declare the unchecked
exception
import java.io.*;
class Parent{
void msg(){s.o.p(“parent”);}
}
class Child extends Parent{
void msg() throws ArithmeticException{
System.out.println(“child”);
}
pulic static void main(String args[]){
Parent p=new Child();
p.msg();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/exceptionhandling-130321053811-phpapp02/85/Exception-Handling-23-320.jpg)
![Super class method declares an exception
Subclass overridden method declares parent exception
import java.io.*;
class Parent{
void msg()throws ArithmeticException{s.o.p(“parent”);}
}
class Child extends Parent{
void msg() throws Exception{System.out.println(“child”); }
pulic static void main(String args[]){
Parent p=new Child();
try{
p.msg();
}catch(Exception e){}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/exceptionhandling-130321053811-phpapp02/85/Exception-Handling-24-320.jpg)
![Super class method declares an exception
Subclass overridden method declares same exception
import java.io.*;
class Parent{
void msg()throws Exception{s.o.p(“parent”);}
}
class Child extends Parent{
void msg() throws Exception{System.out.println(“child”); }
pulic static void main(String args[]){
Parent p=new Child();
try{
p.msg();
}catch(Exception e){}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/exceptionhandling-130321053811-phpapp02/85/Exception-Handling-25-320.jpg)
![Super class method declares an exception
Subclass overridden method declares subclass exception
import java.io.*;
class Parent{
void msg()throws Exception{s.o.p(“parent”);}
}
class Child extends Parent{
void msg() throws ArithmeticException{s.o.p(“child”); }
pulic static void main(String args[]){
Parent p=new Child();
try{
p.msg();
}catch(Exception e){}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/exceptionhandling-130321053811-phpapp02/85/Exception-Handling-26-320.jpg)
![Super class method declares an exception
Subclass overridden method declares no exception
import java.io.*;
class Parent{
void msg()throws Exception{s.o.p(“parent”);}
}
class Child extends Parent{
void msg() {s.o.p(“child”); }
pulic static void main(String args[]){
Parent p=new Child();
try{
p.msg();
}catch(Exception e){}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/exceptionhandling-130321053811-phpapp02/85/Exception-Handling-27-320.jpg)
![Custom Exception
class sample{
static void validate(int age) throws InvalidAgeException{
if(age<18)
throw new InvalidAgeException(“not valid”);
else
System.out.println(“welcome to vote”);
}
pulic static void main(String args[]){
try{
validate(13);
}catch(Exception m){s.o.p(“Exception occured” +m);}
System.out.println(“I love india”);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/exceptionhandling-130321053811-phpapp02/85/Exception-Handling-28-320.jpg)
