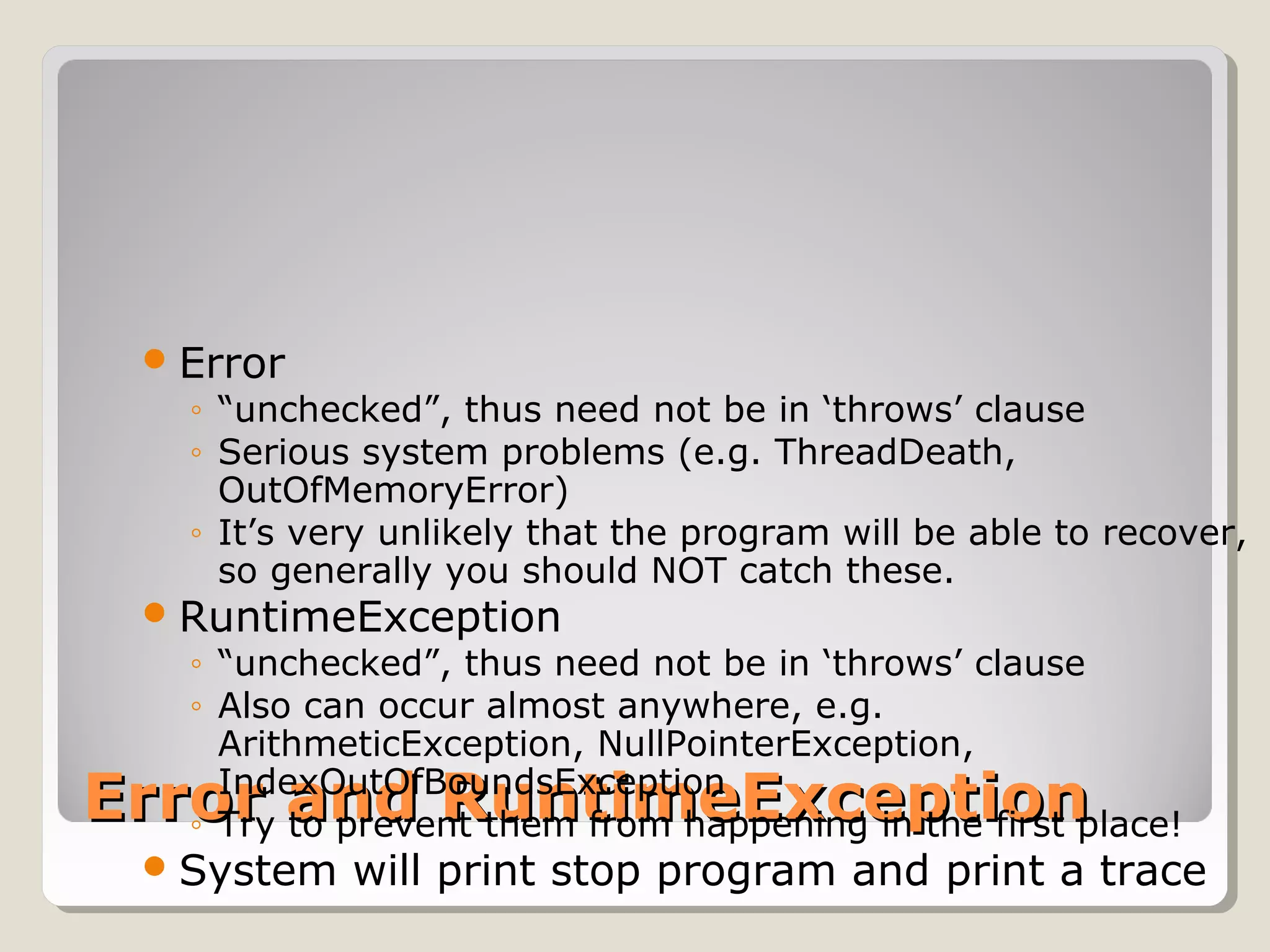
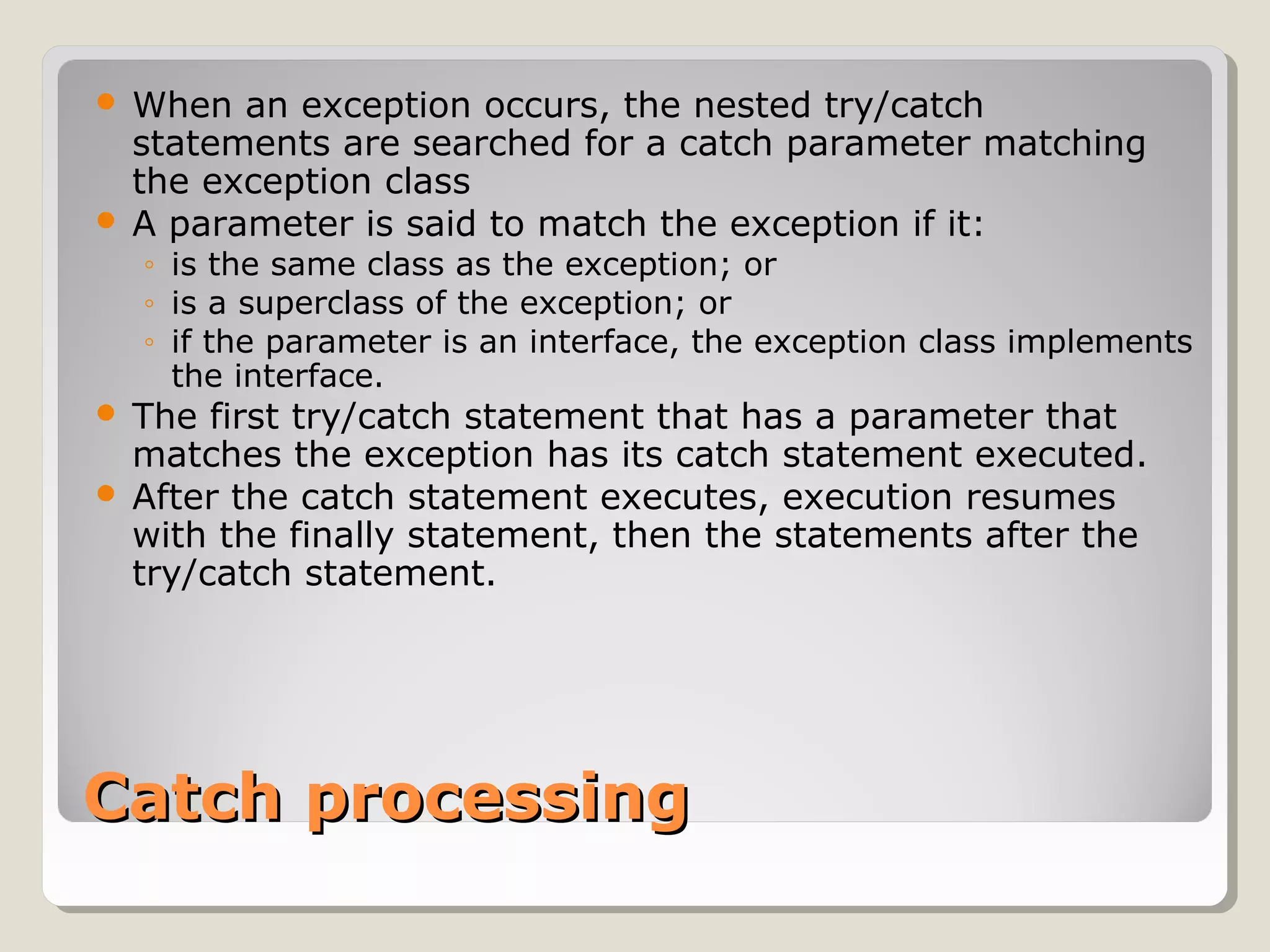
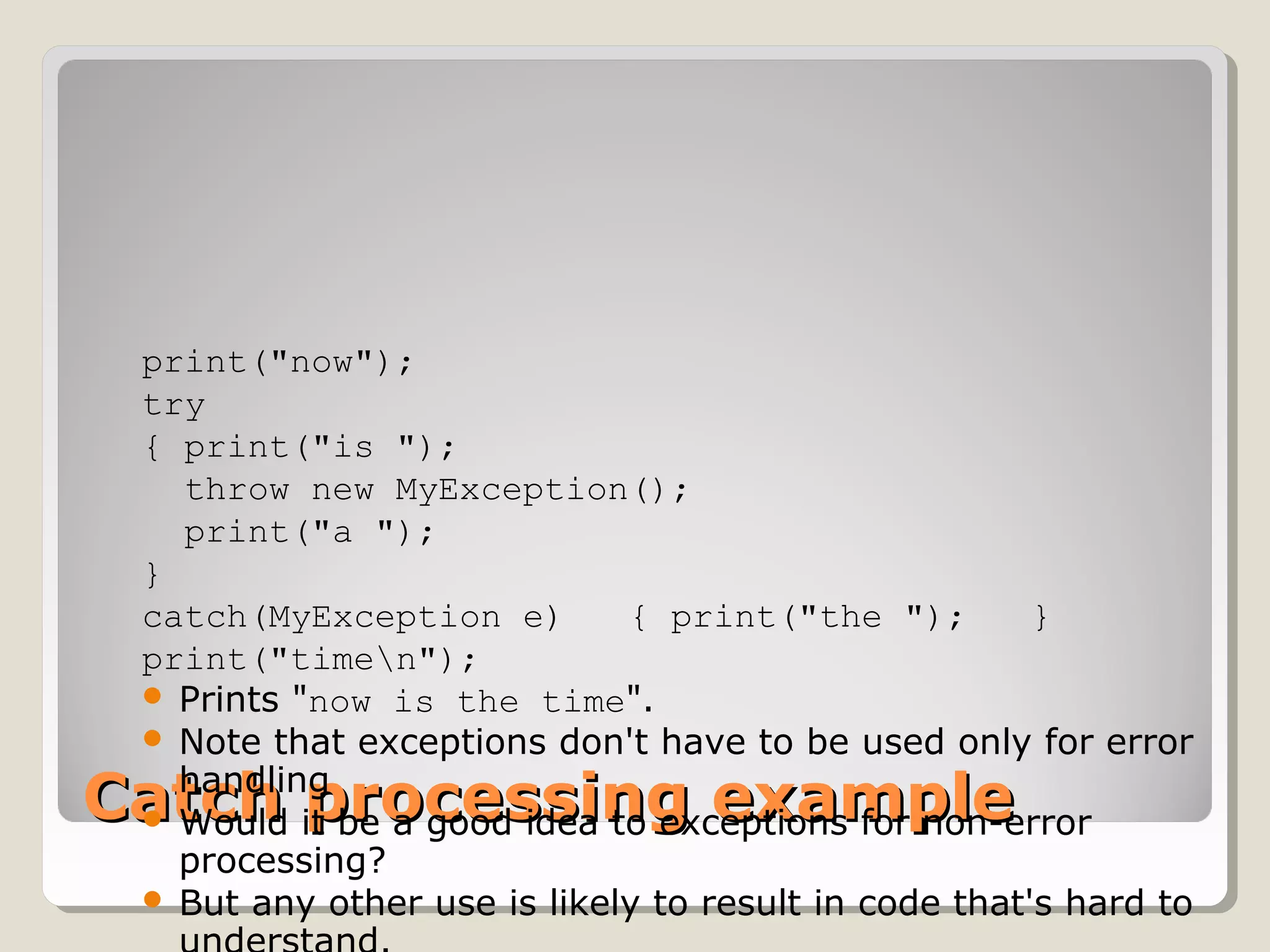
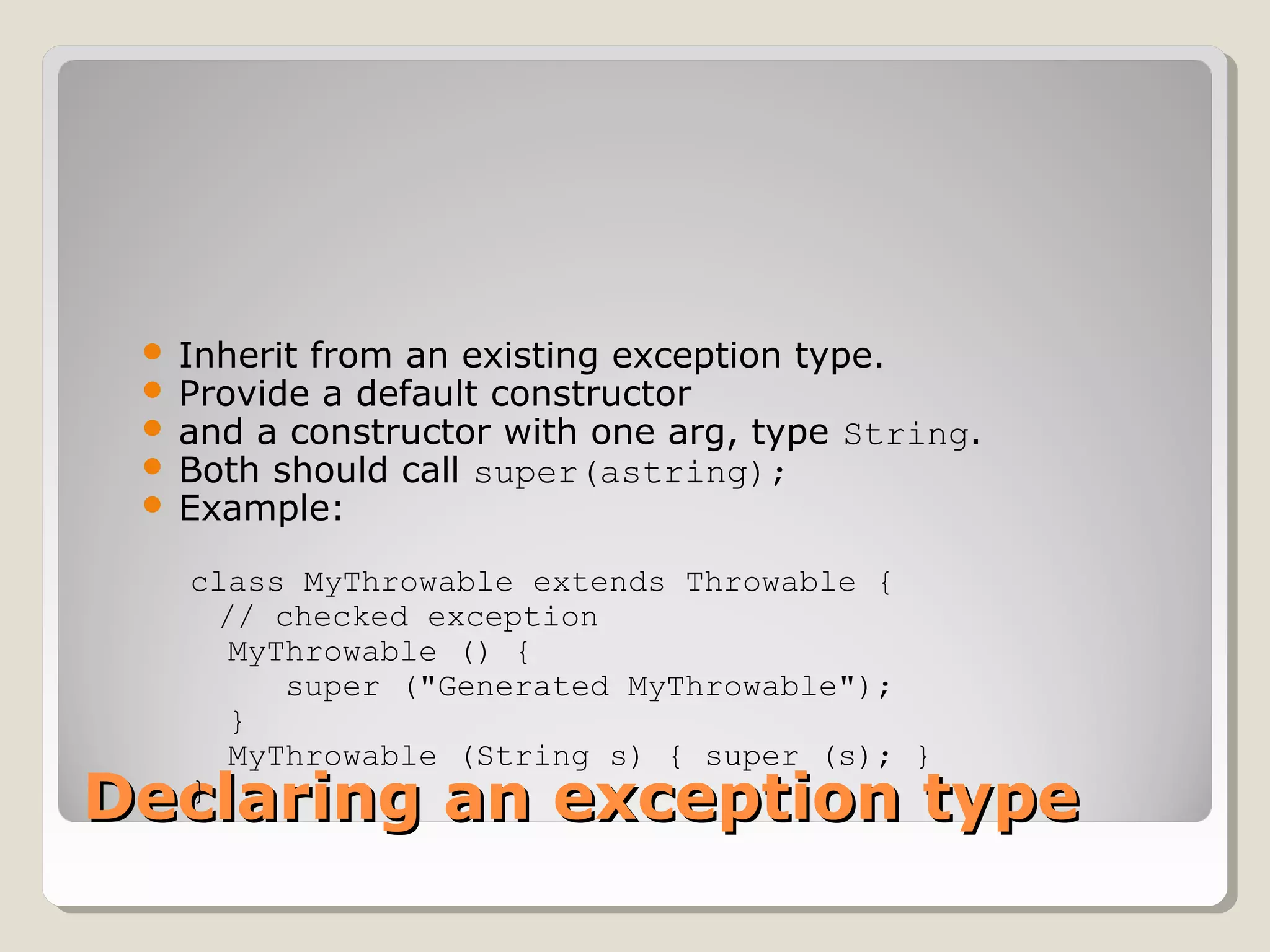
An exception is an error condition that changes the normal flow of control in a program. Exceptions in Java separate error handling from main business logic. Exceptions can be thrown and caught. When an exception occurs, the normal flow is interrupted unless the exception is caught. Exceptions are organized in a hierarchy with Exception at the top. Checked exceptions must be caught or explicitly declared as thrown, while unchecked exceptions like RuntimeException do not need to be declared.