This document contains sample questions and explanations for the OCP Java SE 8 exam related to lambda expressions and functional interfaces. It includes multiple choice questions testing knowledge of valid lambda expression syntax, lambda behavior and scoping, and proper usage of the @FunctionalInterface annotation. The explanations provide detailed reasoning for the correct answers and why the other options are incorrect.




![Ques8on
Determine the behaviour of the following program:
class BlockLambda {
interface LambdaFunction {
String intKind(int a);
}
public static void main(String []args) {
LambdaFunction lambdaFunction =
(int i) -> { //#1
if((i % 2) == 0) return "even";
else return "odd";
};
System.out.println(lambdaFunction.intKind(10));
}
}
A. Compiler error at #1
B. Prints even
C. Prints odd
D. RunKme error (throws excepKon)
hDps://ocpjava.wordpress.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/quiz-upload-160127104533-160412052525/85/OCP-Java-SE-8-Exam-Sample-Questions-Lambda-Expressions-5-320.jpg)
![Answer
Determine the behaviour of the following program:
class BlockLambda {
interface LambdaFunction {
String intKind(int a);
}
public static void main(String []args) {
LambdaFunction lambdaFunction =
(int i) -> { //#1
if((i % 2) == 0) return "even";
else return "odd";
};
System.out.println(lambdaFunction.intKind(10));
}
}
A. Compiler error at #1
B. Prints even
C. Prints odd
D. RunKme error (throws excepKon)
hDps://ocpjava.wordpress.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/quiz-upload-160127104533-160412052525/85/OCP-Java-SE-8-Exam-Sample-Questions-Lambda-Expressions-6-320.jpg)

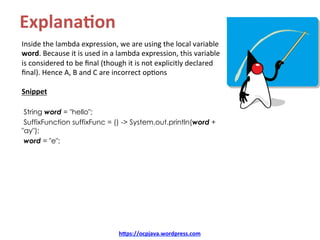
![Ques8on
Predict the output of below program:
interface SuffixFunction {
void call();
}
class Latin {
public static void main(String []args) {
String word = "hello";
SuffixFunction suffixFunc = () -> System.out.println(word + "ay");
word = "e";
suffixFunc.call();
}
}
Choose the correct op8on
A. Prints helloay
B. Prints helloe
C. Prints eay
D. Compiler error
hDps://ocpjava.wordpress.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/quiz-upload-160127104533-160412052525/85/OCP-Java-SE-8-Exam-Sample-Questions-Lambda-Expressions-8-320.jpg)
![Answer
Predict the output of below program:
interface SuffixFunction {
void call();
}
class Latin {
public static void main(String []args) {
String word = "hello";
SuffixFunction suffixFunc = () -> System.out.println(word + "ay");
word = "e";
suffixFunc.call();
}
}
Choose the correct op8on
A. Prints helloay
B. Prints helloe
C. Prints eay
D. Compiler error
LaKn.java:7: error: local variables referenced from a lambda expression must be
final or effecKvely final
hDps://ocpjava.wordpress.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/quiz-upload-160127104533-160412052525/85/OCP-Java-SE-8-Exam-Sample-Questions-Lambda-Expressions-9-320.jpg)


![Ques8on
Predict the output of below program:
class LambdaFunctionTest {
@FunctionalInterface
interface LambdaFunction {
int apply(int j);
boolean equals(java.lang.Object arg0);
}
public static void main(String []args) {
LambdaFunction lambdaFunction = i -> i * i; // #1
System.out.println(lambdaFunction.apply(10));
}
}
A. This program results in a compiler error: interfaces cannot be defined inside
classes
B. This program results in a compiler error: @FuncKonalInterface used for
LambdaFuncKon that defines two abstract methods
C. This program results in a compiler error in code marked with #1: syntax error
D. This program compiles without errors, and when run, it prints 100 in console
hDps://ocpjava.wordpress.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/quiz-upload-160127104533-160412052525/85/OCP-Java-SE-8-Exam-Sample-Questions-Lambda-Expressions-14-320.jpg)
![Answer
Predict the output of below program:
class LambdaFunctionTest {
@FunctionalInterface
interface LambdaFunction {
int apply(int j);
boolean equals(java.lang.Object arg0);
}
public static void main(String []args) {
LambdaFunction lambdaFunction = i -> i * i; // #1
System.out.println(lambdaFunction.apply(10));
}
}
A. This program results in a compiler error: interfaces cannot be defined inside
classes
B. This program results in a compiler error: @FuncKonalInterface used for
LambdaFuncKon that defines two abstract methods
C. This program results in a compiler error in code marked with #1: syntax error
D. This program compiles without errors, and when run, it prints 100 in console
hDps://ocpjava.wordpress.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/quiz-upload-160127104533-160412052525/85/OCP-Java-SE-8-Exam-Sample-Questions-Lambda-Expressions-15-320.jpg)

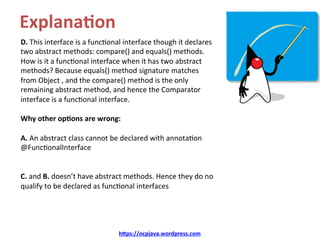
![Ques8on
Predict the output of below program:
interface DoNothing {
default void doNothing() { System.out.println("doNothing"); }
}
@FunctionalInterface
interface DontDoAnything extends DoNothing {
@Override
abstract void doNothing();
}
class LambdaTest {
public static void main(String []args) {
DontDoAnything beIdle = () -> System.out.println("be idle");
beIdle.doNothing();
}
}
A. This program results in a compiler error for DontDoAnything interface: cannot
override default method to be an abstract method
B. This program prints: be idle
C. This program prints: doNothing
D. This program results in a compiler error: DontDoAnything is not a funcKonal
interface
hDps://ocpjava.wordpress.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/quiz-upload-160127104533-160412052525/85/OCP-Java-SE-8-Exam-Sample-Questions-Lambda-Expressions-17-320.jpg)
![Answer
Predict the output of below program:
interface DoNothing {
default void doNothing() { System.out.println("doNothing"); }
}
@FunctionalInterface
interface DontDoAnything extends DoNothing {
@Override
abstract void doNothing();
}
class LambdaTest {
public static void main(String []args) {
DontDoAnything beIdle = () -> System.out.println("be idle");
beIdle.doNothing();
}
}
A. This program results in a compiler error for DontDoAnything interface: cannot
override default method to be an abstract method
B. This program prints: be idle
C. This program prints: doNothing
D. This program results in a compiler error: DontDoAnything is not a funcKonal
interface
hDps://ocpjava.wordpress.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/quiz-upload-160127104533-160412052525/85/OCP-Java-SE-8-Exam-Sample-Questions-Lambda-Expressions-18-320.jpg)

