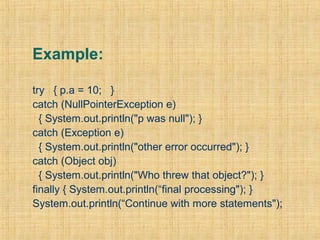
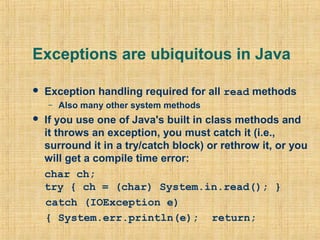
Exceptions in Java allow programs to handle errors and unexpected conditions in a uniform way. Exceptions break normal program flow and can be caught and handled in catch blocks. Common exceptions include runtime exceptions for errors like null pointer exceptions and checked exceptions for errors like IOExceptions. Exceptions are organized in a hierarchy with Throwable at the top. The Java compiler enforces exception handling to improve correctness.