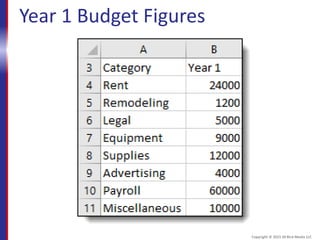
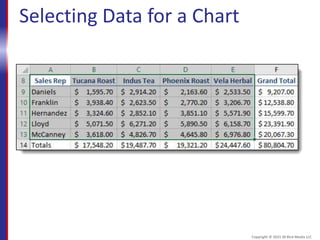
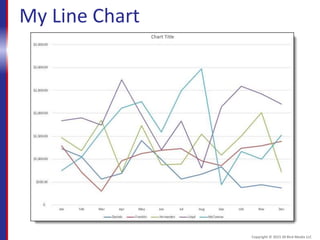
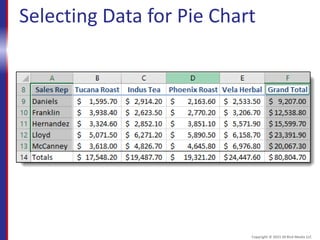
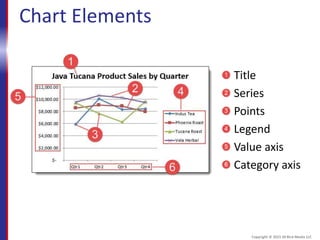
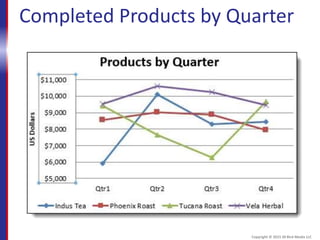
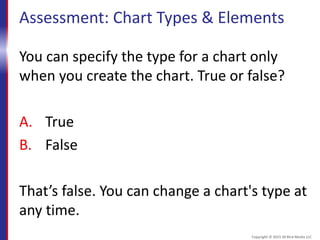
This document provides an overview and objectives for an Excel 2016 Level 1 course. The summary is:
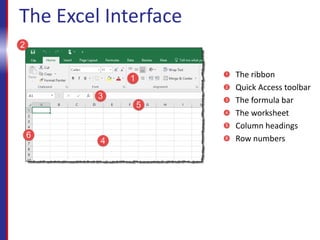
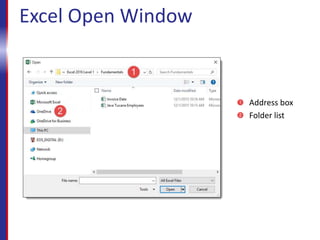
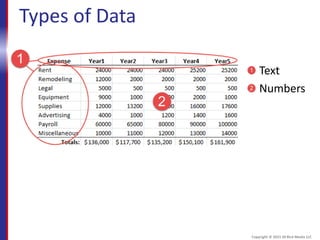
The course will teach students how to interact with and navigate Excel, enter and format data, create formulas and functions, format and print worksheets, and share workbooks. It covers the Excel interface, opening and saving workbooks, entering text and numbers, basic formulas, functions, moving and copying data, and more. Upon completing the course, students will know how to perform essential tasks in Excel like data entry, calculations, formatting, and printing.