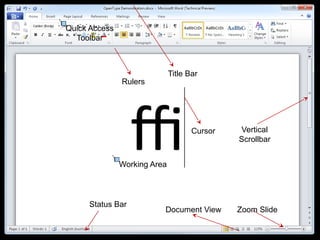
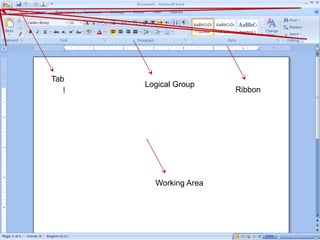
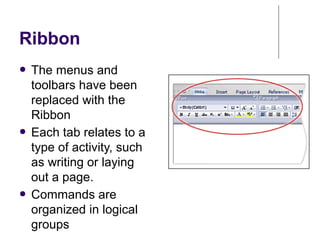
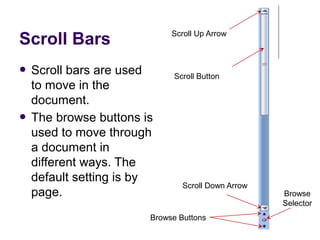
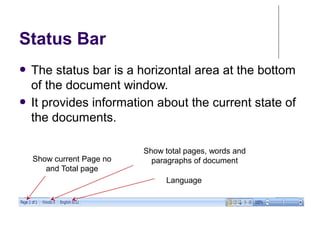
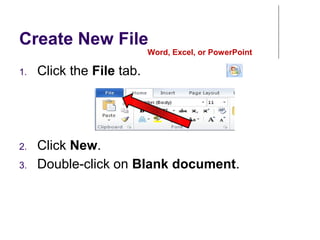
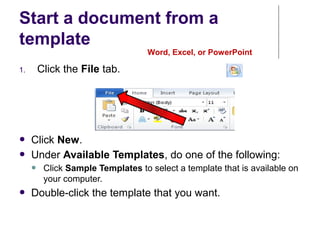
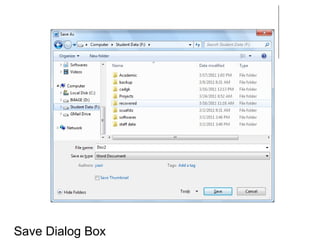
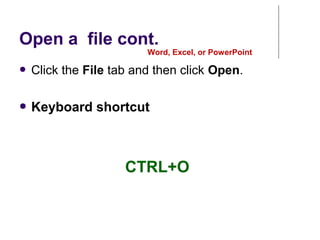
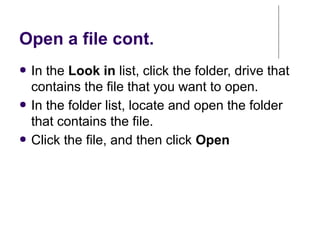
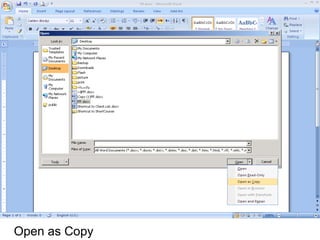
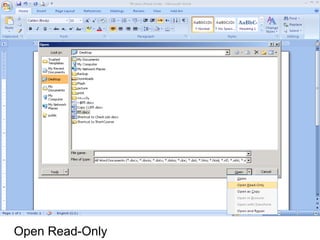
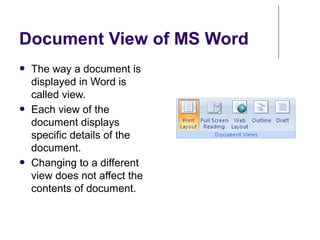
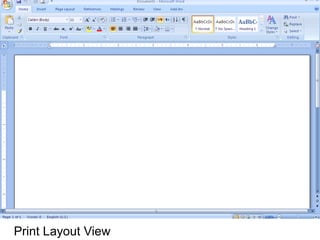
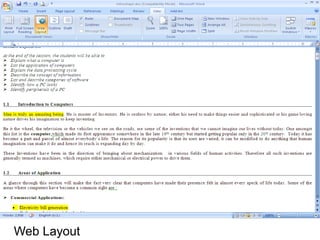
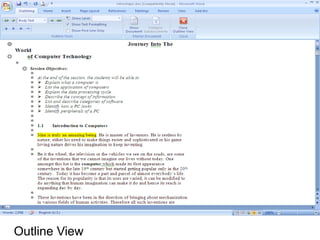
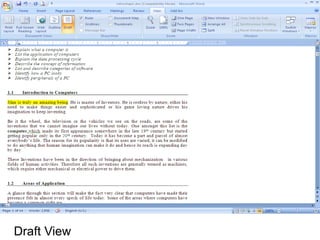
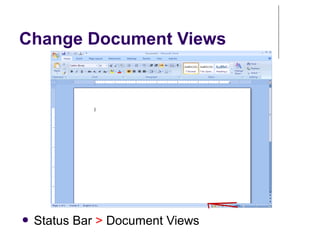
This document provides an overview of Microsoft Word 2010 and its features. It discusses word processors and their advantages over typewriters. It then describes Microsoft Word as a word processing program that can be used to create documents like letters, reports, newsletters and brochures. The document reviews the interface of Word, including the ribbon, title bar, rulers, scroll bars, status bar and zoom controls. It also covers how to perform common tasks in Word like creating and opening files, saving files in different formats, and changing document views.