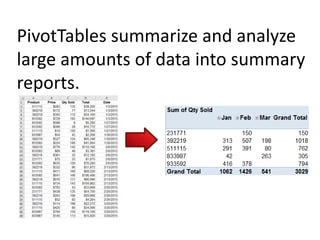
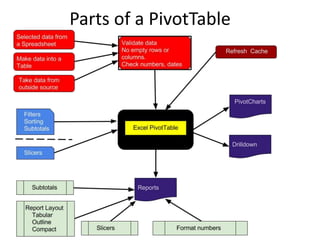
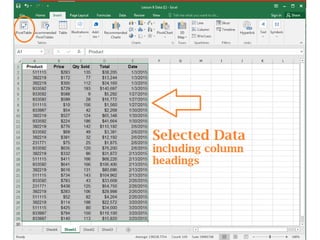
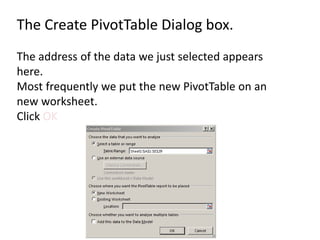
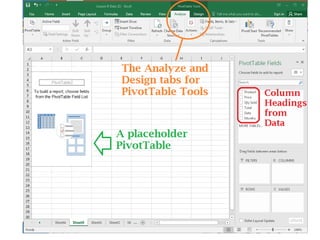
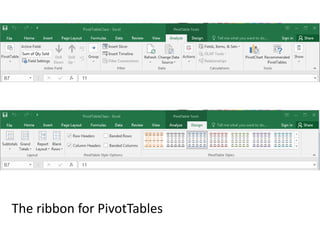
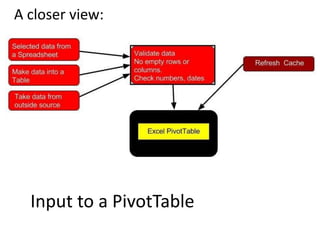
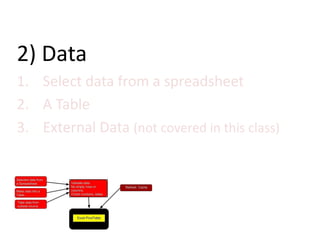
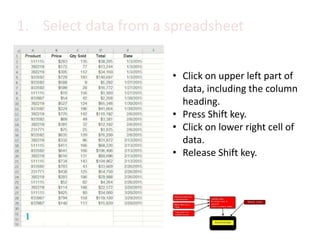
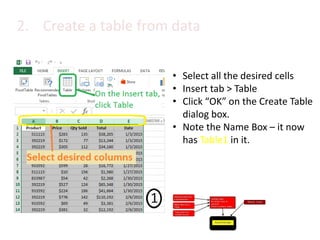
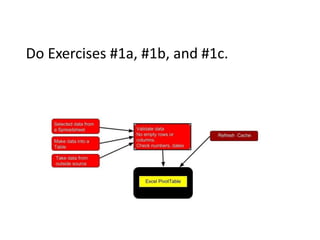
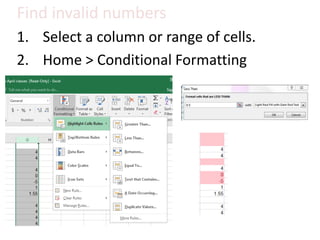
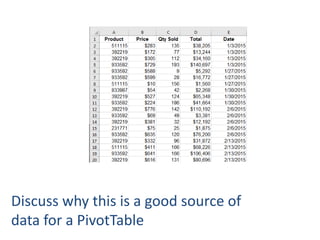
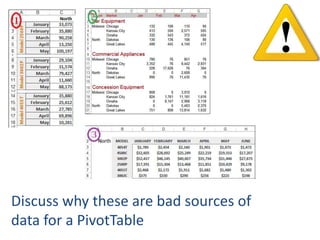
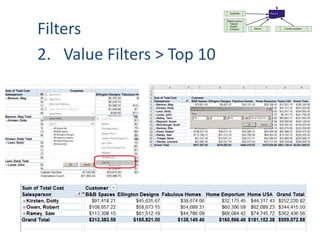
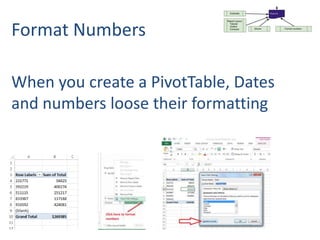
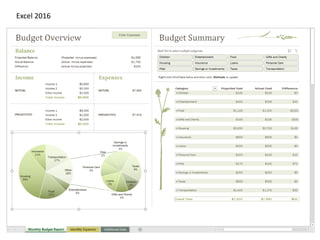
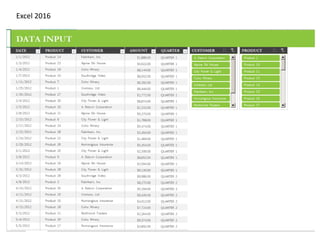
This document provides an overview of the steps for creating and using a PivotTable in Excel. It begins by explaining that PivotTables can summarize and analyze large amounts of data. It then covers the key parts of a PivotTable including the data input, filters, slicers, formatting, and charts. Exercises are included to help learn how to construct a basic PivotTable, add filters and slicers, and turn the data into a chart. The goal is to teach the research and analysis capabilities of PivotTables for summarizing and exploring large datasets.